In terrestrial plants, Xylem is the vascular tissue that plays a role in conduction of water and nutrients from the roots to the shoots and leaves. A xylem can be classified as either primary or secondary based on the stage and origin of growth.
Primary xylem is a type of xylem that forms during primary growth (growth in length) of plants whereas secondary xylem forms during secondary growth (growth in girth) of plants. Secondary xylem is usually absent in non-woody plants but present in trees and shrubs. More importantly, primary xylem comes from the procambium whereas secondary xylem originates from the vascular cambium.
Also, secondary xylem may show growth rings (or annual rings). In large woody plants, the secondary xylem is differentiated into sapwood and heartwood. Secondary xylem has cells that are thickened with lignin, therefore giving mechanical support to plants.
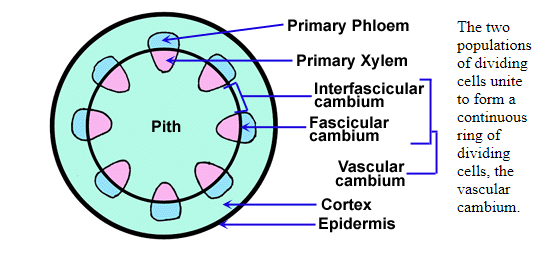
Below get to understand detailed difference and similarities between primary xylem and secondary xylem. The basis of comparison includes: Types of differentiation, radial xylem system, tyloses, thickenings, tracheids and vessels among others.
What You Need To Know About Primary Xylem (Characteristics)
- Primary xylem is the xylem formed during primary growth from the procambium of the apical meristem.
- Primary xylem is differentiated into two parts: Metaxylem and Protoxylem.
- Primary xylem is not differentiated into sap wood and heart wood.
- Primary xylem is found in all type of organs.
- Type of primary xylem differentiation include: Endarch, Exarch, centrarch and mesarch.
- The tracheids and vessels are longer and with comparatively narrow walls.
- The medullary rays are derived from the apical meristem.
- It occurs towards the center of the xylem.
- The vessels of primary xylem do not contain tyloses.
- The xylem fibres are either absent or few in numbers.
- All types of thickenings can occur in tracheid elements.
- A radial system and annual rings are absent.
What You Need To Know About Secondary Xylem (Characteristics)
- The secondary xylem is the xylem formed as a result of secondary growth from the vascular cambium of the lateral meristem.
- Secondary xylem is not differentiated into Metaxylem and Protoxylem.
- Secondary xylem is clearly differentiated into sap wood and heart wood in woody trees.
- Secondary xylem is restricted to stems and roots of only perennial dicots and gymnosperms.
- There are no special types of differentiation in secondary xylem.
- The tracheids and vessels are short and with comparatively thick/wide walls.
- The secondary medullar rays are derived from ray initials of the cambium.
- It occurs towards the outer side of primary xylem.
- The vessels and tracheids of secondary xylem get blocked by development of tyloses.
- The xylem fibres are abundant in number.
- Pitted thickenings occur in the tracheary elements.
- A radial system of xylem rays and annual rings are present.
Primary Xylem Vs Secondary Xylem In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PRIMARY XYLEM | SECONDARY XYLEM |
| Description | Primary xylem is the xylem formed during primary growth from the procambium of the apical meristem. | The secondary xylem is the xylem formed as a result of secondary growth from the vascular cambium of the lateral meristem. |
| Differentiation | It is differentiated into two parts: Metaxylem and Protoxylem. | It is not differentiated into Metaxylem and Protoxylem. |
| It is not differentiated into sap wood and heart wood. | It is clearly differentiated into sap wood and heart wood in woody trees. | |
| Presence | It is found in all type of organs. | It is restricted to stems and roots of only perennial dicots and gymnosperms. |
| Types Of Differentiation | Endarch Exarch Centrarch Mesarch. | There are no special types of differentiation in secondary xylem. |
| Tracheids And Vessels | The tracheids and vessels are longer and with comparatively narrow walls. | The tracheids and vessels are short and with comparatively thick/wide walls. |
| Medullary Rays | The medullary rays are derived from the apical meristem. | The secondary medullar rays are derived from ray initials of the cambium. |
| Occurrence | It occurs towards the center of the xylem. | It occurs towards the outer side of primary xylem. |
| Tyloses | The vessels of primary xylem do not contain tyloses. | The vessels and tracheids of secondary xylem get blocked by development of tyloses. |
| Xylem Fibres | The xylem fibres are either absent or few in numbers. | The xylem fibres are abundant in number. |
| Thickenings | All types of thickenings can occur in tracheary elements. | Pitted thickenings occur in the tracheary elements. |
| Radial Xylem System And Annual Rings | A radial xylem system and annual rings are absent. | A radial system of xylem rays and annual rings are present. |
What Are Some Of The Similarities Between Primary Xylem And Secondary Xylem?
- Both primary and secondary xylem contains vessels, xylem fibers and xylem parenchyma.
- Both primary and secondary xylem conducts water from the root to the upper part of the plant.
- Both types of xylem differentiate from the cambium.
- They both occur in gymnosperms and some angiosperms.
- They both provide mechanical strength to the plant.
You May Also read:
- Difference Between Gymnosperms And Angiosperms
- Difference between meristematic tissues and permanent tissues in plants
- Difference Between simple permanent and complex permanent tissues
- Difference Between Protoxylem and Metaxylem
Comments are closed.