Permanent tissues are tissues formed when meristematic tissues lose their ability to divide and re-divide after some extent. They can be thin walled or thick walled and have permanent shape. Permanent tissues can either be simple or permanent complex tissues. The permanent tissue in plants mainly helps in providing support, protection as well as in photosynthesis, conduction of water, minerals and nutrients.
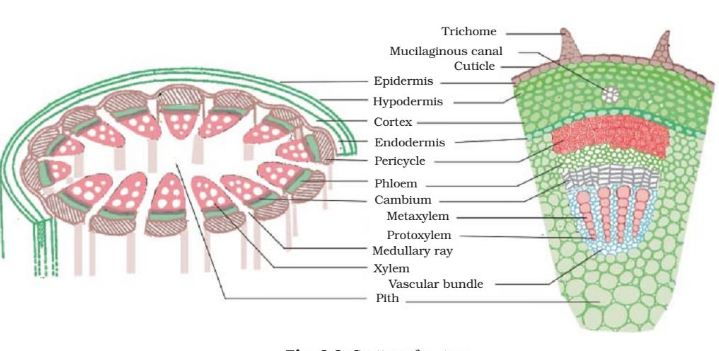
Complex permanent tissue is made up of a group of same type of cells which have common origin and but perform different functions. Xylem and phloem are complex tissues and form vascular tissue of the plant. Xylem helps in the transport of water molecules and dissolved substances from the root hairs to the aerial parts of the plant. Phloem on the other hand, transports food molecules to the place of necessity in plants.
Simple permanent tissue is made up of only one type of cell. All cells that make up the tissue are similar and have same structure. Simple permanent tissues can be classified into three main types, parenchyma, collenchymas and schlerenchyma.
Parenchyma mainly acts as a packing tissue provides mechanical and storage of food. Collenchyma tissue provides flexibility as well as mechanical support to plants and lastly schlerenchyma also provides rigidity and mechanical support to the plant body.
The Key Difference
- The simple permanent tissue is a type of tissue which has a single type of cells. All the cells of this tissue are functionally and structurally similar. On the other hand, the complex permanent tissue is the plant tissue having different type of cells. These cells perform different functions within the tissue.
- Simple permanent tissue is composed of a single type of cells whereas complex permanent tissue is composed of multiple types of cells.
- Simple permanent tissues are located virtually in every part of the plant whereas permanent tissues are mostly located in the vascular regions of the plant.
- Major functions of the simple permanent tissue include: tissue repair, secretion, food storage and photosynthesis. In contrast, the major functions of complex permanent tissue are protection of plant from hydration, structural support and conduction of water and nutrients.
- In simple permanent tissue, all cells perform the same function whereas in complex permanent tissue, different type of cells performs different functions.
- Examples of simple complex tissue include: Sclerenchyma, parenchyma and collenchymas. On the other hand, examples of complex permanent tissue include: Xylem and Phloem.
Also Read: Difference Between Hardwood And Softwood
Simple Permanent Tissue Vs. Complex Permanent Tissue In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE | COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUE |
| Description | The simple permanent tissue is a type of tissue which has a single type of cells. All the cells of this tissue are functionally and structurally similar. | The complex permanent tissue is the plant tissue having different type of cells. These cells perform different functions within the tissue. |
| Composition | Simple permanent tissue is composed of a single type of cells. | Complex permanent tissue is composed of multiple types of cells. |
| Location | Simple permanent tissues are located virtually in every part of the plant. | Permanent tissues are mostly located in the vascular regions of the plant. |
| Major Functions | Major functions of the simple permanent tissue include: tissue repair, secretion, food storage and photosynthesis. | The major functions of complex permanent tissue are protection of plant from hydration, structural support and conduction of water and nutrients. |
| Cell Differentiation | In simple permanent tissue, all cells perform the same function. | In complex permanent tissue, different type of cells performs different functions. |
| Examples | Examples of simple complex tissue include: Sclerenchyma parenchyma Collenchymas | Examples of complex permanent tissue include: Xylem Phloem |