What Are Gymnosperms?
The gymnosperms also referred to as Acrogymnospermae are a group of plants that share one common characteristic in that they bear seeds, but their seeds do not develop from within an ovary. Gymnosperms are abundant in temperate forest and boreal forest biomes with species that can tolerate moist or dry conditions. The gymnosperms do not produce flowers or fruits. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones. At maturity, a gymnosperm embryo has two or more seed leaves, known as cotyledons.
Gymnosperms, like all vascular plants, have a sporophyte-dominant life cycle, which means they spend most of their life cycle with diploid cells, while gametophyte (gamete-bearing phase) is relatively short-lived. Two spore types, microspores and megaspores are typically produced in pollen cones or ovulate cones, respectively.
Gymnosperms produce multiple archegonia, which produce the female gamete. During pollination, pollen grains are physically transferred between plants from the pollen cone to the ovule. Pollen is usually moved by wind or insects.
Examples of gymnosperms include:
- Pine
- Conifers
- Cycads
- Gnetophytes
- Ginkgo
- Spruce
- Cactus
- Fir.
Facts About Gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms are seed producing, non-flowering plants whose seeds are exposed and not enclosed in an ovule.
- They are perennial or woody, forming trees or bushes.
- They are not differentiated into ovary, style and stigma.
- Gymnosperms mainly rely on the wind for the process of pollination.
- Many of gymnosperms possess taproot system only.
- Gymnosperms possess two types of branches i.e long shoots and dwarf shoots collectively referred to as spur.
- In gymnosperms, endosperm is derived from female gamytophyte and therefore, a haploid is formed.
- They form cones with reproductive structures.
- Angiosperms possess true stomata.
- The male gametophyte produce two gametes, but only one of them is functional.
- Majority of gymnosperms lack vessels for conducting water except for the phylum gnetophyta which has vessels.
- Gymnosperms lack companion cells in phloem tissue.
- In gymnosperms one fertilization occurs in the ovules and result in formation of a zygote (2n).
- The leaves of gymnosperms are cone bearing or needle like.
- The male and female gametophyte structures are present on separate male and female cones in gymnosperms.
- The life cycle of gymnosperms is characterized by alternation of generations.
- The seeds contain endosperm that stores food for the growth and development of the plant.
- Gymnosperms have vascular tissues which help in transportation of nutrients and water.
- Since stigma is absent, they are pollinated directly by the wind.
- The gymnosperms are known as softwood as they have the ability to last during the winter.
- In gymnosperms, mature pollen grains consist of three cells, that is, one tube cell and two sperm cells.
- In gymnosperm, a mature gametophyte contains 2-3 archegonia which contain large egg nucleus.
- In gymnosperms, archegonia are present in the mature gametophyte.
- Xylem does not have vessels and the phloem has no companion cells and sieve tubes.
Also Read: Difference Between Hemosporous And Heterosporous Pteridophytes
What Are Angiosperms?
Angiosperms are seed-bearing vascular plants. Their reproductive structures are flowers in which ovules are enclosed in an ovary. Angiosperms have triploid vascular tissue, flat leaves in numerous shapes and hardwood stems. Because of the innumerable varieties of the fruit and flower-bearing plants, they have variagated colors and shapes of leaves, flowers and fruits.
Angiosperms are found in almost every habitat from forests and grasslands to sea margins and deserts. Angiosperms make up the majority of all plants on earth, they are the most advanced and beneficial group of plants. They can grow in various habitats as trees, herbs, shrubs and bushes.
Examples of angiosperms include:
- Roses
- Peas
- Grains
- Lettuce
- Lilies
- Daffodils
- Sunflowers
- Maples
- Orchids.
Facts About Angiosperms
- Angiosperms are seed-producing, flowering plants whose seeds are enclosed within an ovary.
- Angiosperms mainly rely on the insects for the process of pollination.
- The vascular system has true vessels in the xylem and companion cells in the phloem.
- Angiosperm plants possess not only taproot but also various roots and stem modification. These are meant for the accumulation of food and capable of vegetative propagation.
- Angiosperms can survive in a variety of habitats including marine habitats.
- The sporophyte is differentiated into stems, roots and leaves.
- Angiosperm possesses only one type of branches.
- In angiosperms, endosperm is derived from fertilization of sperm nucleus with two polar nuclei and therefore a triploid is formed.
- Gymnosperms possess sunken stomata.
- The process of fertilization is quicker in angiosperms. The seeds are also produced quickly due to the smaller female reproductive Parts.
- Angiosperms on the other hand, have vessels for conducting water.
- Angiosperms have companion cells in phloem tissue.
- In angiosperms, double fertilization occurs and result in formation of zygote (2n) and endosperm (3n).
- The leaves of angiosperms are flat.
- The male and female gametophyte structures in angiosperms are part of the flower.
- Angiosperms life cycle is dominated by the sporophyte generation.
- The angiosperms are known as hardwood and usually change color during summer a die.
- Angiosperm has a mature pollen grain consisting of two sperm nuclei.
- In angiosperm, embryo sac of a mature megagametophyte consists of 7 cells, with a total of 8 nuclei.
- In angiosperm, there are no archegonia in mature megagametophyte.
- The root system is very complex and consist of cortex, xylem, phloem and epidermis.
- The flowers undergo double and triple fusion which leads to the formation of diploid zygote and triploid endosperm.
- Angiosperms are heterosporous i.e produce two kinds of spores, megaspore (pollen grains) and megaspores.
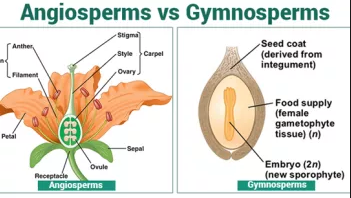
Similarities Between Gymnosperms And Angiosperms
- There is presence of seeds in both
- Close similarity in the general life history of species (members) of both groups.
- Presence of pollen tubes for carrying the male gametes to the female gamete.
- Presence of flowers in both groups
- Presence of cambium in both gymnosperms and angiosperms
- Presence of well-organized plant body, differentiated into roots, stems and leaves.
Also Read: Difference Between Bryophytes And Pteridophytes
Difference Between Gymnosperms And Angiosperms In Tabular Form
| Basis of Comparison | Gymnosperms | Angiosperms |
| Meaning | Gymnosperms are seed producing, non-flowering plants whose seeds are exposed and not enclosed in an ovule. | Angiosperms are seed-producing, flowering plants whose seeds are enclosed within an ovary. |
| Examples | Examples of gymnosperms include pine, conifers, cycads, Gnetophytes, Ginko, spruce, cactus, fir. | Examples of angiosperms include roses, peas, grains, lettuce, lilies, daffodils, sunflowers, maples, orchids. |
| Process of pollination | Mainly rely on the wind for the process of pollination. | Mainly rely on the insects for the process of pollination. |
| Root system | Many of gymnosperms possess taproot system. | Angiosperm plants possess not only taproot but also various roots and stem modification. |
| Type of Branches | Possess two types of branches i.e long shoots and dwarf shoots collectively referred to as spur. | Possesses only one type of branches. |
| Endosperm | E`ndosperm is derived from female gamytophyte and therefore, a haploid is formed. | Endosperm is derived from fertilization of sperm nucleus with two polar nuclei and therefore a triploid is formed. |
| Stomata | Possess true stomata. | Possess sunken stomata |
| Flowers | Do not possess flowers instead they possess cones. | Possess flowers. |
| Vessels | Majority of gymnosperms lack vessels for conducting water except for the phylum gnetophyta which has vessels. | Angiosperms on the other hand, have vessels for conducting water. |
| Companion Cell | Lack companion cells in phloem tissue. | Have companion cells in phloem tissue. |
| Fertilization | One fertilization occurs in the ovules and result in formation of a zygote (2n). | Double fertilization occurs and results in formation of zygote (2n) and endosperm (3n). |
| Leaves | The leaves of gymnosperms are cone bearing or needle like. | The leaves of angiosperms are flat. |
| Gametophyte structures | The male and female gametophyte structures are present on separate male and female cones in gymnosperms. | The male and female gametophyte structures in angiosperms are part of the flower. |
| Life cycle | The life cycle of gymnosperms is characterized by alternation of generations. | Angiosperms life cycle is dominated by the sporophyte generation. |
| Alternative Name | The gymnosperms are known as softwood as they have the ability to last during the winter. | The angiosperms are known as hardwood and usually change color during summer a die. |
| Mature Pollen | Mature pollen grains consist of three cells, that is, one tube cell and two sperm cells. | Has a mature pollen grain consisting of two sperm nuclei. |
| Nuclei | Mature gametophyte contains 2-3 archegonia which contain large egg nucleus. | Embryo sac of a mature megagametophyte consists of 7 cells, with a total of 8 nuclei. |
| Archegonia | Archegonia are present in the mature gametophyte. | There are no archegonia in mature megagametophyte. |
Also Read: Difference Between Monocot And Dicot Seeds
Summary
What is the main difference between Angiosperm and Gymnosperms?
Gymnosperms are seed producing, non-flowering plants whose seeds are exposed and not enclosed in an ovule whereas; angiosperms are seed-producing, flowering plants whose seeds are enclosed within an ovary.
Simple and concise article. Really helped with getting overview.
I love the way you explain everything to my understanding thanks. Now I know and have a very clear and precise difference Gymnosperms and Angiosperms. Thank you.
The article was very helpful. I even lack words to thank you. This Quality work.
The article very helpful indeed. I even lack words to thank you.This quality work.
What is Archegonia ??