What is Xylem?
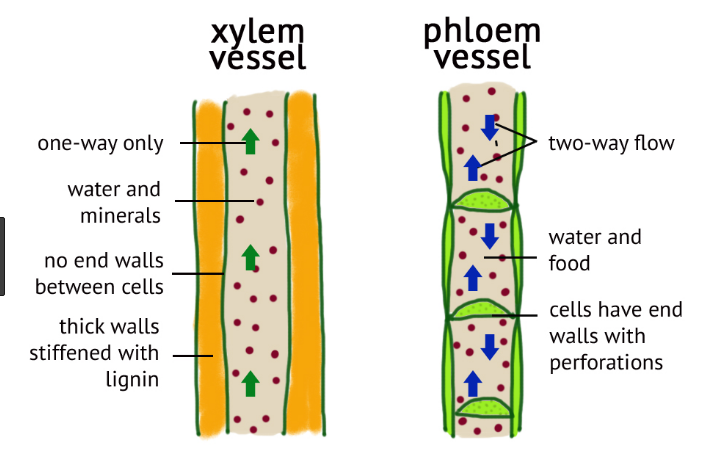
Xylem vessels are hollow cells arranged end to end and joined by perforation plates to form continuous tubes. In these cells both nucleus and cytoplasm are absent. The end walls of these cells are often completely broken to form a long distance channel for transport of water.
The main function of xylem is to transport nutrients and water from the soil interface to stems and leaves; and provides mechanical support and storage. The water conducting cells of mature xylem are dead, and therefore the transport of water is mostly a passive process with a very small active root pressure component.
In most woody plants, xylem grows by the division and differentiation of cells of a bifacial lateral meristem, the vascular cambium, which produces secondary xylem and phloem. Xylem is found in all vascular plants including the seedless club mosses, fern, horsetails, as well as angiosperms and gymnosperms.
What You Need To Know About Xylem
- Xylem is a complex tissue in vascular plants responsible for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves. It also transports nutrients.
- Xylem tissue is located in the center of the vascular bundle.
- Xylem tissues have unidirectional movement; the water and mineral are only moved up from the roots.
- Mainly contains Dead cells with parenchyma being the only living cell present in the xylem.
- The cells provide mechanical support to plants.
- At maturity, xylem is a dead tissue, with no cell content.
- Xylem cell comprises of xylem vessels, fiber and tracheids.
- In xylem, the conducting cells or tracheary cells are dead with lignin thickening in the wall.
- Xylem often constitutes the bulk of the plant body/wood.
- Conducting channels (vessels) do not have septa.
- Tracheary elements have different types of wall thickenings.
- In mature plants, the xylem is differentiated into heart wood and sap wood.
- Tyloses formation occurs in the xylem.
- Xylem fibers are usually smaller.
- Xylem tissues are found in leaves, roots and stems.
- The quantity of xylem tissue in the vascular bundles is more than the phloem tissue.
- The primary function of xylem is to transport water and dissolved minerals from the root to different parts of the plant.
Also Read: Difference Between Simple Permanent And Complex Permanent Tissue
What is Phloem?
Phloem is composed of various specialized cells known as sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma cells. Sieve elements are type of cell t with group of pores at their ends; they are responsible for transport of sugars throughout the plant.
The main function of phloem is to transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis to various parts of plant where they are needed. This transport process is known as translocation.
At maturity, phloem does not have a nucleus; it only has a few organelles, so they rely on companion cells for most of their metabolic needs.
What You Need To Know About Phloem
- Phloem is a complex living tissue in vascular plants that transports soluble organic compounds (foods) made during photosynthesis from the leaves.
- Phloem is present on the outer area of the vascular bundle.
- Phloem tissues have bidirectional movement; the food can travel both up and down the plant.
- Mainly contains living cells with fibers being the only dead cells in phloem.
- Phloem cells do not provide mechanical support to plants.
- At maturity, phloem is a living tissue but not with nucleus.
- Phloem comprises of phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells, parenchyma and companion cells.
- In phloem the conducting cells or sieve tubes are living and do not possess lignin.
- Phloem forms a small part of the plant.
- Sieve tubes have bulging and porous septa.
- Wall thickenings are absent in conducting channels.
- No such differentiation of phloem occurs.
- Tyloses formation does not occur in the phloem.
- Phloem fibers are usually larger (commonly referred to as bast fibers).
- Phloem tissues are found in stems.
- The quantity of phloem tissue is comparatively less to that of xylem in the vascular bundles.
- The primary function of the phloem is to transport the prepared sugars from leaves to different parts of the plant.
Also Read: Difference Between Companion Cells And Sieve Tubes

phloem vs xylem
Also Read: Difference Between Tracheids And Vessels In Xylem
Difference Between Xylem and Phloem In Tabular Form
| Elements of Comparison | Xylem | Phloem |
| Definition | Xylem is a complex tissue in vascular plants responsible for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves. It also transports nutrients. | Phloem is a complex living tissue in vascular plants that transports soluble organic compounds (foods) made during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts. |
| Location | Xylem tissue is located in the center of the vascular bundle. | Phloem is present on the outer area of the vascular bundle. |
| Movement | Xylem tissues have unidirectional movement. | Phloem tissues have bidirectional movement. |
| Cells | Mainly contains Dead cells with parenchyma being the only living cell present in the xylem. | Mainly contains living cells with fibers being the only dead cells in phloem. |
| Support | The cells provide mechanical support to plants. | Phloem cells do not provide mechanical support to plants. |
| Structure | At maturity, xylem is a dead tissue, with no cell content. | At maturity, phloem is a living tissue but not with nucleus. |
| Components | Xylem cell comprises of xylem vessels, fiber and tracheids. | Phloem comprises of phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells, parenchyma and companion cells. |
| Conducting Cells | In xylem, the conducting cells or tracheary cells are dead with lignin thickening in the wall. | In phloem the conducting cells or sieve tubes are living and do not possess lignin. |
| Proportion on plant | Xylem often constitutes the bulk of the plant body. | Phloem forms a small part of the plant. |
| Septa | Conducting channels (vessels) do not have septa. | Sieve tubes have bulging and porous septa. |
| Wall thickening | Tracheary elements have different types of wall thickenings. | Wall thickenings are absent in conducting channels. |
| Differentiation | In mature plants, the xylem is differentiated into heart wood and sap wood. | No such differentiation of phloem occurs. |
| Tyloses | Tyloses formation occurs in the xylem. | Tyloses formation does not occur in the phloem. |
| Fibres | Xylem fibres are usually smaller. | Phloem fibres are usually larger (commonly referred to as bast fibres). |
Similarities between xylem and Phloem
- Both phloem and Xylem are complex tissue composed of more than one type of cells.
- Both Phloem and Xylem exhibit primary and secondary growth.
- Both develop from the cambium
- Both contain parenchymatous cells.
- Both contain living and dead cells.
- Both are the components of vascular system of plants.
- Both phloem and xylem contain fibres.
- Both terms “phloem’’ and “Xylem” were proposed for the first time by Carl wilhelm
Also Read: Difference Between Metaphloem And Protophloem
Summary
What is the main difference between Xylem and Phloem?
Xylem is a complex tissue in vascular plants responsible for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves. It also transports nutrients. On the other hand, Phloem is a complex living tissue in vascular plants that transports soluble organic compounds (foods) made during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts.