What is Pollination?
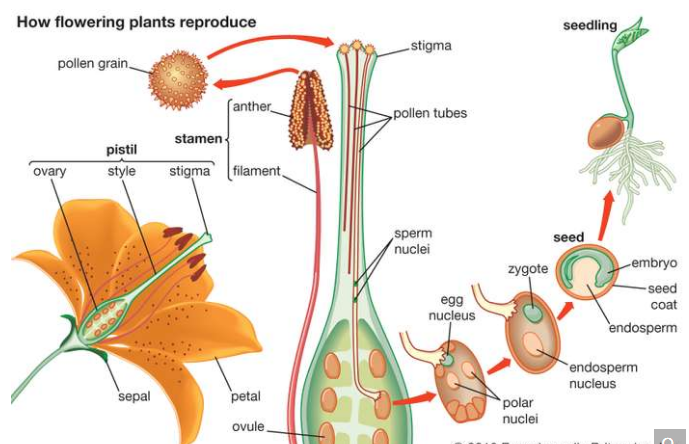
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male (anther) of a flower to the female part (stigma) of the same or different flower. Pollen grains contain the male gametes and are present in the anthers of the flower. Pollination is usually the first process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants. There are two types of pollination, self pollination and cross-pollination.
- Self-pollination is when the anthers of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same plant. Self pollination is usually common in hermophradite or diocius plants. These plants contain both male and female sexual parts on the same flower. Self pollination depends on external factors such a wind and other insects that come to the flower regularly.
- Cross-pollination is when the pollen is transferred from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. In the case of cross-pollination, the two flowers are genetically different from each other. Cross-pollination depends on external factors to cause transfer of pollen grains. The agents of pollination include birds, animals, water, wind and insects. Gymnosperm pollen is predominantly dispersed by air current (i.e anemophilous) whereas angiosperm pollen may be dispersed by animals (zoophilous), air currents (anemophilous) and water (hydrophilous).
Generally, abiotic environment and geographical factors such as temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation play a crucial role in pollination, influencing anther opening, pollen vectors, pollen exposure, pollen transport by air currents and pollinator flight. Usually, honeybees are the best pollinators because they visit a single plant species for as long as there flowers are available. Usually, the type of pollen vector and sexual expression of a species (dioecy, monoecy, hermaphroditism) determines the success of pollination, that is, whether pollen lands on stigma of the same or another species.
What You Need To Know About Pollination/Characteristics
- Pollination is a biological process whereby pollen grains are transferred from the male reproductive organ (anthers) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) of the same or different flower.
- Pollination can be categorized into two different types based on the distribution of pollen grains. They include self-pollination and cross-pollination.
- Formation of pollen tube is not necessary for pollination.
- Pollination is an external process/mechanism and takes place on the outer part of a flower.
- Pollination occurs in the early stages of reproduction in all flowering plants. In other words, it occurs before fertilization.
- Pollination only happens in flowering plants.
- Pollination is achieved by external pollinating agents like water, wind, insects and animals.
- Pollination is a physical process.
What is Fertilization?

Fertilization in flowering plants also referred to as syngamy, fecundation or generative fertilization was discovered by Ralph B. Strassburger in 1884. Fertilization is a process of sexual reproduction in plants. It is usually a physiochemical process which occurs after pollination of the carpels. It can be defined as the fusion of the male gamates (pollen) in haploid condition with the female gamete (ovum) in haploid condition to form a diploid zygote. The male gamates of the flower are transferred on to the female reproductive organs through pollinators. The final product of this process is the formation of embryo in a seed.
In flowers, the pollen grain germinates after the pollination of the carpel and grows into the style by creating the pathway for pollen grain to move down to the ovary. The pollen tube breaks into the ovule through the micropyle and bursts into embryo sac. Inside the embryo sac, the male nucleus fuses with the nucleus of an egg inside the ovule forming a diploid zygote, which eventually swells up and develop into a fruit.
The three main types of plant fertilization are porogamy, chalazogamy and misogamy. They are distinguished by how the pollen tube enters the ovule. Of these three, porogamy is the most common.
- Porogamy- is the fertilization of a seed plant involving passage of the pollen tube into the ovule by the micropyle. It is the most common type of fertilization.
- Chalazogamy- is the process of fertilization in which the pollen tube penetrates to the embryo sac through the tissue of the chalaza. This type of fertilization is common in casaurina species of plants.
- Misogamy – in this type of fertilization, the pollen tube enters the ovule through its middle part or through the integuments of the ovule. This type of fertilization is common in all cucurbit plants, such as pumpkin, ridge gourds, bitter gourd and other gourd plants.
What You Need To Know About Fertilization
Fertilization is necessary for the continuing life cycle of not only plants but almost every living organism on Earth.
- Fertilization is a physiochemical process during which the diploid zygote is developed by the fusion of both male and female gametes.
- The process of fertilization in flowering plants can be categorized into three types based on the entry of pollen tube into the ovule. They include porogamy, chalazogamy and misogamy.
- For fertilization to occur in flowering plants, formation of pollen tube is necessary in the transferring of male gametes up to an egg cell.
- Fertilization in flowering plants is an internal process/mechanism and takes place inside the flowers.
- Fertilization takes place after pollination.
- Fertilization occurs in both flowering and non-flowering plants. Also, in humans and animals, fertilization is part of the reproduction process.
- Fertilization does not require external agents.
- Fertilization is a cellular, genetic and biochemical process.
Also Read: Difference Between Cross-Pollination And Self-pollination
Pollination Vs Fertilization In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF POLLINATION | POLLINATION | FERTILIZATION |
| Description | Pollination is a biological process whereby pollen grains are transferred from the male reproductive organ (anthers) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) of the same or different flower. | Fertilization is a physiochemical process during which the diploid zygote is developed by the fusion of both male and female gametes. |
| Types | It can be categorized into two different types based on the distribution of pollen grains. They include self-pollination and cross-pollination. | The process of fertilization in flowering plants can be categorized into three types based on the entry of pollen tube into the ovule. They include porogamy, chalazogamy and misogamy. |
| Pollen Tube | Formation of pollen tube is not necessary for pollination. | For fertilization to occur in flowering plants, formation of pollen tube is necessary in the transferring of male gametes up to an egg cell. |
| Nature Of The Process | It is an external process/mechanism and takes place on the outer part of a flower. | In flowering plants it is an internal process/mechanism and takes place inside the flowers. |
| Occurrence | It occurs in the early stages of reproduction in all flowering plants. In other words, it occurs before fertilization. | It takes place after pollination. |
| It only happens in flowering plants. | It occurs in both flowering and non-flowering plants. Also, in humans and animals, fertilization is part of the reproduction process. | |
| Agents | Pollination is achieved by external pollinating agents like water, wind, insects and animals. | Fertilization does not require external agents. |
| Type Of Process | It a physical process. | It is a cellular, genetic and biochemical process. |
Comments are closed.