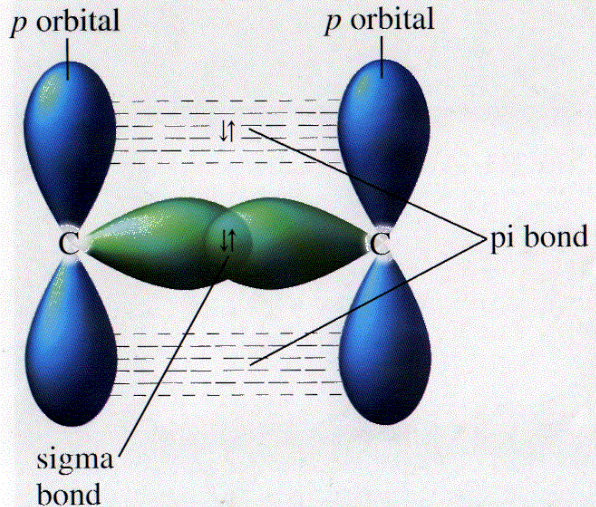
Pi Bond & Sigma Bond
A Pi bond is a covalent bond which is formed by the side-to-side overlap of two atomic orbitals. Each of these atomic orbitals has zero electron density at a shared nodal plane, passing through the two bonded nuclei. The same plane is also a nodal plane for the molecular orbital of the pi bond.
A sigma bond is a covalent bond which is formed by the head on overlap of two atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding can be an antibonding interaction or a bonding interaction (bonding interaction results by overlapping of two atomic orbitals in the same phase whereas antibonding interaction occurs by the overlapping in opposite phase).
Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bonds due to the direct overlap of orbitals and the electrons in these bonds are sometimes referred to as sigma electrons. Typically, a single bond is a sigma bond whereas a multiple bond is composed of one sigma bond together with pi or other bonds for example, in a molecule of nitrogen (N2), the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms comprises a sigma bond and two pi bonds.
Pi bonds are often weaker than sigma bonds. The C-C double bond composed of one sigma and one pi bond has a bond energy less than twice that of a C-C single bond, indicating that the stability added by the pi bond is less than the stability of a sigma bond. Below is a detailed comparison between a Pi bond and a sigma bond.
The Key Differences
- Sigma bonds are bonds between atoms within molecules formed along the axis connecting the bound nuclei of the atoms. On the other hand, Pi Bonds are bonds between atoms within molecules where the electrons are above and below the axis connecting the nuclei of the joined atoms but not along the axis. They are second type of bond which will form within a molecule after the sigma bond.
- Pi bonds are formed from the combination of p and similar orbitals in different atoms whereas sigma bonds are often formed by the combination of s orbitals in different atoms.
- Pi bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas sigma bond is formed when the head of atomic orbitals overlaps with each other along the internuclear axis of the atoms.
- Pi bond is a weaker type of covalent bond as compared to sigma bond, which is the strongest type of covalent bond between two atoms. This is because in Pi bond overlapping happens to a lesser extent and therefore, the bond is weak. In the case of sigma bond, the overlapping takes place to a larger extent and therefore, the bond formed is a strong bond.
- A single pi bond contains only one Pi bond whereas multiple bonds like double bond have two Pi bonds and triple bond has three Pi bonds. On the other hand, a single bond of sigma bond contains only one sigma bond while multiple bonds like double bond contain only one sigma bond.
- Pi bond cannot rotate symmetrically around an internuclear whereas a sigma bond can rotate symmetrically around the internuclear axis.
- Pi bonds decide the length of the molecule whereas sigma bond decides the shape of the molecule.
- In Pi bond, the relativity of the compound formed is directly proportional to some Pi bonds whereas the stability of the compound is inversely proportional to the number of pi bonds. On the contrast, in sigma bond, the relativity of the compound formed is inversely proportional to some sigma bonds whereas the stability of the compound is directly proportional to the number of sigma bonds.
- In the formation of Pi bond, s-orbitals cannot participate whereas in the formation of sigma bond, S-orbitals can participate.
- In Pi bonds, the molecular orbitals is discontinuous and consist of two charged clouds above and below the plane of atoms. On the other hand, in sigma bond, the molecular orbital is symmetrical about the intermolecular axis.
- Pi bonds are less reactive whereas sigma bonds are more reactive.
- Formation of pi bond is preceded by the formation of sigma bonds. On the other hand, when atoms get closer sigma bonds are formed first.
Also Read: Difference Between Covalent, Metallic and Ionic Bond
Pi Bond Vs. Sigma Bond In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | Pi BOND | SIGMA BOND |
| Description | Pi Bonds are bonds between atoms within molecules where the electrons are above and below the axis connecting the nuclei of the joined atoms but not along the axis. | Sigma bonds are bonds between atoms within molecules formed along the axis connecting the bound nuclei of the atoms. |
| Formation | Formed from the combination of p and similar orbitals in different atoms. | Often formed by the combination of s orbitals in different atoms. |
| Formation | Formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. | Formed when the head of atomic orbitals overlaps with each other along the internuclear axis of the atoms. |
| Strength | Pi bond is a weaker type of covalent bond as compared to sigma bond. | Sigma bond is a stronger type of covalent bond as compared to pi bond. |
| Number Of Bonds | A single pi bond contains only one Pi bond whereas multiple bonds like double bond have two Pi bonds and triple bond has three Pi bonds. | A single bond of sigma bond contains only one sigma bond while multiple bonds like double bond contain only one sigma bond. |
| Symmetrical Rotation | Pi bond cannot rotate symmetrically around an internuclear. | A sigma bond can rotate symmetrically around the internuclear axis. |
| Effect of on Length of Molecule | Pi bonds decide the length of the molecule. | Sigma bond decides the shape of the molecule. |
| Relativity Of Compound Formed | In Pi bond, the relativity of the compound formed is directly proportional to some Pi bonds whereas the stability of the compound is inversely proportional to the number of pi bonds. | In sigma bond, the relativity of the compound formed is inversely proportional to some sigma bonds whereas the stability of the compound is directly proportional to the number of sigma bonds. |
| s-orbitals | In the formation of Pi bond, s-orbitals cannot participate. | In the formation of sigma bond, S-orbitals can participate. |
| Molecular Orbital | In Pi bonds, the molecular orbitals is discontinuous and consist of two charged clouds above and below the plane of atoms. | In sigma bond, the molecular orbital is symmetrical about the intermolecular axis. |
| Reactivity | Pi bonds are less reactive. | Sigma bonds are more reactive. |
| Which One Is Formed First | Formation of pi bond is preceded by the formation of sigma bonds. | When atoms get closer sigma bonds are formed first. |