Covalent Bonding
A covalent bond, also referred to as molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is what is referred to as covalent bonding.
There is a covalent bond between the oxygen and hydrogen in water molecule (H2O). Each of the covalent bonds contains two electrons, one from a hydrogen atom and one from the oxygen atom. Both atoms share the electrons. A hydrogen molecule H2 consists of two hydrogen atoms joined by a covalent bond. Each hydrogen atom needs two electrons to achieve a stable outer electron shell. The pair of electrons is attracted to the positive charge of both atomic nuclei, holding the molecule together.
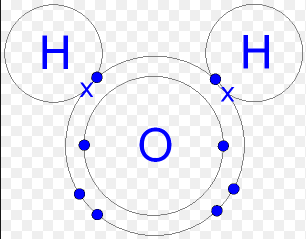
Metallic Bonding
A metallic bond is type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Metallic bonds are seen in pure metals and alloys and some metalloids. For example, graphene (an allotrope of carbon) exhibits two-dimensional metallic bonding. Metals even pure ones can form other types of chemical bonds between their atoms. For example, the ions of mercury can form metal-metal covalent bonds.
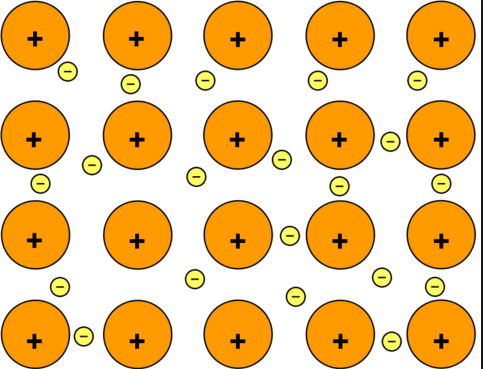
Metallic bonding may be seen as a consequence of a material having many more delocalized energy states than it has delocalized energy states than it has delocalized electrons (electrons deficiency), so localized unpaired electrons may become delocalized and mobile. The electrons can change energy states and move throughout a lattice in any direction. Metallic bonding can also take the form of metallic cluster formation, in which delocalized electrons flow around localized cores.
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. An ionic bond is demonstrated by sodium chloride in table salt. The sodium donates an electron to the chloride forming a pair of charged ions, where sodium is positively charged and chloride is negatively charged. The two opposite charges attract forming what is referred to as an ionic bond.
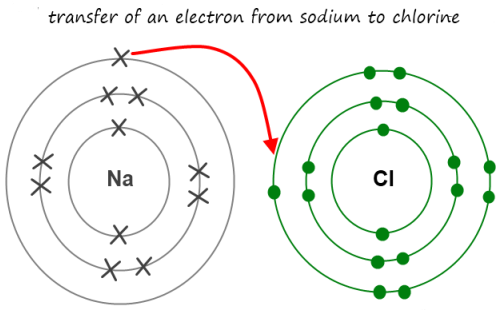
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in aqueous state. They also have a high melting point depending on the charge of the ions they constitute of. The higher the charge the stronger the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point. They also tend to be soluble in water, the stronger the cohesive forces, the lower the solubility.
The Key Differences
Description
- Covalent: a covalent bond is a bond formed when a strong electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged nuclei and shared pair of electron.
- Metallic: A metallic bond is a bond formed when there is presence of strong electrostatic force of attraction between cation or atoms and the delocalized electrons in the geometrical arrangement of the two metals.
- Ionic: An Ionic bond is a bond formed when there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between a cation and an anion (two oppositely charged ions) of elements.
Formation
- Covalent: A covalent bond is formed between two non-metals that have similar electro-negativities (Neither of the atoms is strong enough to attract electrons from the other. For stabilization, they share their outer molecular valence electrons with others.
- Metallic: Metallic bonds form when a given number of atoms share a variable number of electrons in a metal lattice.
- Ionic: Ionic bonds form when one atom provides electrons to another atom.
Conductivity
- Covalent Bonds: Covalently bonded atoms are poor conductors of electricity.
- Metallic Bonds: Atoms with metallic bonds have a excellent conductors of both heat and electricity.
- Ionic Bonds: Atoms with Ionic bonds have a very low electrical and thermal conductivity.
Occurrence
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metals.
- Metallic Bonding: Metallic bonding occurs between two metals.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal.
Bond Energy
- Covalent bonds: Bond Energy is higher than that of metallic bonds.
- Metallic bonds: Bond Energy is lower than that of covalent and ionic bonds.
- Ionic bonds: Bond Energy is higher than that of metallic bonds.
Ductility
- Covalent Bonds: Materials with covalent bonds are non-ductile in nature.
- Metallic Bonds: Materials with Metallic bonds are ductile in nature.
- Ionic Bonds: Materials with Ionic bonds are non-ductile in nature.
Examples
- Covalent Bonds: Examples of atoms and compounds with covalent bonds include: hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, water molecule, diamond, silica, carbon etc.
- Metallic Bonds: Examples of elements with metallic bonds include: silver, lead, copper, iron, potassium, sodium, aluminum, nickel, copper, silver etc.
- Ionic Bonds: Examples of compounds with ionic bonds include: Magnesium chloride, Sodium Chloride, potassium chloride, Lithium Iodide, sodium floride, sodium bromide, Lithium floride etc.
Strength
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent Bonds are not very strong bonds with exception of silicon, diamond and carbon.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds are very strong bonds.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are very strong due to crystalline nature.
Malleability
- Covalent Bonds: Materials with covalent bonds are not malleable.
- Metallic Bonds: Materials with metallic bonds are malleable.
- Ionic Bonds: Materials with ionic bonds are not malleable.
Entails
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons in the valence shell.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds entail attraction between the delocalized electrons present in the lattice of the metals.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds entail the transfer and acceptance of electrons from the valence shell.
Physical State At Room Temperature
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds exist in compounds that are either in liquid, gasses and solid states.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds exist in elements that are only in solid state.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds exist in compounds that are only in solid state.
Melting And Boiling Points
- Covalent Bonds: Compounds with covalent bonds have lower melting and boiling points.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds have high melting and boiling points.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds have higher melting and boiling points.
Shape
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds are definite in shape.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds are not definite in shape.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are not definite in shape.
Nature
- Covalent Bonds: Compounds with covalent bonds are relatively soft and waxy.
- Metallic Bonds: Compounds with metallic compounds are relatively hard.
- Ionic Bonds: Compounds with ionic bonds are relatively hard.
Solubility In Non-polar Solvents
- Covalent Bonds: Compounds with covalent bonds are readily soluble in non-polar solvents.
- Metallic Bonds: Compounds with metallic bonds are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
- Ionic Bonds: Compounds with metallic bonds are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
Read Further: Differences & Similarities Between Covalent Bonds And Hydrogen Bonds
Covalent Bonds Vs. Metallic Bonds Vs. Ionic Bonds In Tabular
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | COVALENT BONDS | METALLIC BONDS | IONIC BONDS |
| Description | A covalent bond is a bond formed when a strong electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged nuclei and shared pair of electron. | A metallic bond is a bond formed when there is presence of strong electrostatic force of attraction between cation or atoms and the delocalized electrons in the geometrical arrangement of the two metals. | Ionic bond is a bond formed when there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between a cation and an anion (two oppositely charged ions) of elements. |
| Formation | A covalent bond is formed between two non-metals that have similar electro-negativities (Neither of the atoms is strong enough to attract electrons from the other. | Metallic bonds form when a given number of atoms share a variable number of electrons in a metal lattice. | Ionic bonds form when one atom provides electrons to another atom. |
| Conductivity | Covalently bonded atoms are poor conductors of electricity. | Atoms with metallic bonds have a excellent conductors of both heat and electricity. | Atoms with Ionic bonds have a very low electrical and thermal conductivity. |
| Occurrence | Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metals. | Metallic bonding occurs between two metals. | Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal. |
| Bond Energy | Bond Energy is higher than that of metallic bonds. | Bond Energy is lower than that of covalent and ionic bonds. | Bond Energy is higher than that of metallic bonds. |
| Ductility | Materials with covalent bonds are non-ductile in nature. | Materials with Metallic bonds are ductile in nature. | Materials with Ionic bonds are non-ductile in nature. |
| Examples | Examples of atoms and compounds with covalent bonds include: hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, water molecule, diamond, silica, carbon etc. | Examples of elements with metallic bonds include: silver, lead, copper, iron, potassium, sodium, aluminum, nickel, copper, silver etc. | Examples of compounds with ionic bonds include: Magnesium chloride, Sodium Chloride, potassium chloride, Lithium Iodide, sodium floride, sodium bromide, Lithium floride etc. |
| Strength | Covalent Bonds are not very strong bonds with exception of silicon, diamond and carbon. | Metallic bonds are very strong bonds. | Ionic bonds are very strong due to crystalline nature. |
| Malleability | Materials with covalent bonds are not malleable. | Materials with metallic bonds are malleable. | Materials with ionic bonds are not malleable. |
| Entails | Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons in the valence shell. | Metallic bonds entail attraction between the delocalized electrons present in the lattice of the metals. | Ionic bonds entail the transfer and acceptance of electrons from the valence shell. |
| Physical State At Room Temperature | Covalent bonds exist in compounds that are either in liquid, gasses and solid states. | Metallic bonds exist in elements that are only in solid state. | Ionic bonds exist in compounds that are only in solid state. |
| Melting & Boiling Point | Compounds with covalent bonds have lower melting and boiling points. | Metallic bonds have high melting and boiling points. | Ionic bonds have higher melting and boiling points. |
| Shape | Covalent bonds are definite in shape. | Metallic bonds are not definite in shape. | Ionic bonds are not definite in shape. |
| Nature | Compounds with covalent bonds are relatively soft and waxy. | Compounds with metallic compounds are relatively hard. | Compounds with ionic bonds are relatively hard. |
| Solubility | Compounds with covalent bonds are readily soluble in non-polar solvents. | Compounds with metallic bonds are insoluble in non-polar solvents. | Compounds with metallic bonds are insoluble in non-polar solvents. |