What Are ZooPlankton?
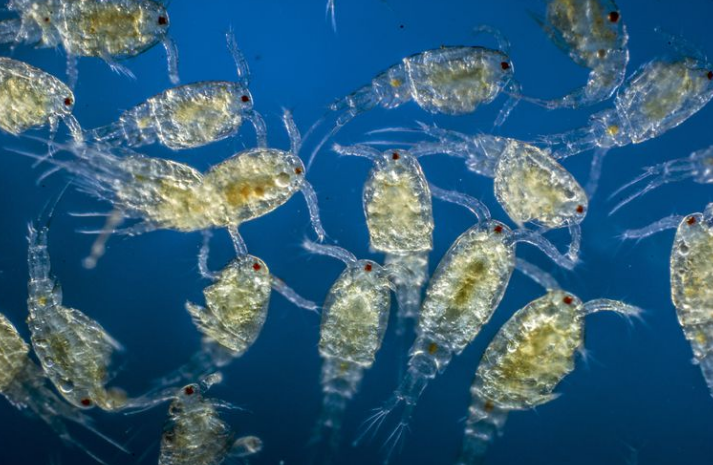

Zooplankton are a type of heterotrophic plankton that range from microscopic to large species. They are found within large bodies of water, including oceans and freshwater systems. Zooplankton community is composed of both primary consumers which eat free-floating algae and secondary consumers which feed on other zooplankton.
Zooplankton can also be described as small free-floating aquatic microorganism including crustaceans, rotifers, open water insect larvae and aquatic mites. The zooplankton community are ecologically important organisms that are an integral component of the food chain. These organisms serve as an intermediary species in the food chain, transferring energy from plankton algae (primary producers) to the large invertebrate predators and fish that eventually feed on them.
Usually, the abundance of certain species relative to another can serve as a measure of biological condition. Zooplankton can also be an indicator of environmental disturbance as through changes in their composition, abundance and body size distribution.
Examples of Zooplankton Include: cnidarians such as jellyfish, crustaceans such as copepods, ostracods, isopods, amphipods, mysids and krill; molluscs such aspteropods and chordates such as salps and juvenile fish.
What Are Phytoplankton?
Phytoplankton also referred to as microalgae are microscopic biotic organisms that are mostly found in water bodies including the oceans, lakes, rivers and ponds. These organisms, in the same way that plants do, they obtain their energy from the sun in order to produce nutrients in a process referred to as photosynthesis. For the process to occur, they must live close to the surface of body water or the euphotic zone where they use sunlight to produce carbohydrates.
Phytoplankton are microscopic in nature and can only be observed when they grow in huge quantities in a process referred to as bloom. When they do, satellite photos show them as patches of bluish or green colors in the oceans, lakes or rivers even in ponds.
Phytoplankton are some of the Earth’s most critical organisms in the sense that they generate half of the atmosphere oxygen. More importantly, they are primary producers in the aquatic food web whereby organisms such as zooplankton feed on phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are also critical to other ocean biogeochemical cycles. They take up, transform and recycle elements needed by other organisms and help cycle elements between species in the ocean.
The Difference
- Phytoplankton are plant plant-like aquatic microorganism whereas zooplanktons are animal-like organisms and the larval stages of other life forms.
- Phytoplankton are primary producers, they absorb sunlight, carbon dioxide and nutrients and convert them into oxygen and carbohydrates (photosynthesis). On the contrary, zooplanktons obtain their energy by eating phytoplankton, bacterioplankton, zooplankton and nektonic organisms.
- Examples of phytoplankton are blue-green algae, cynobacteria, diatoms and dinoflagellates. On the other hand, examples of zooplankton are krill, protozoans, holoplankton, arrow worms, jellyfish and even the eggs and larvae of larger organisms.
- Phytoplankton are autotrophic whereas zooplankton are heterotrophic.
- Majority of phytoplankton are autotrophic, they require sunlight to live hence they are found on the euphotic layer of the water bodies or near water surfaces. On the other hand, zooplankton are mostly found in cold, shaded regions or in the deep sections of water body. There are some zooplankton that drift towards the surface during the day.
- In the aquatic food chain, phytoplanktons are primary producers whereas zooplanktons are the primary or secondary consumers.
- All phytoplankton do not have the ability to swim against ocean currents whereas zooplankton such as the comb jelly and jellyfish do have the ability to swim in order to avoid predators.
- Zooplankton are usually the larval stage of fish, sea worms and crustaceans. Some of them eventually metamorphosize into free-swimming creatures like sea stars while others metamorphosize to become sessile like sea squirts and sea urchins. Phytoplankton do not undergo metamorphosis.
- Phytoplankton generally release lots of oxygen gas whereas zooplankton consume oxygen to release lots of carbon dioxide.
- Majority of phytoplankton have a brown color. When they grow as a group, cloudy patches do actually form. On the other hand, zooplanktons generally exist in different colors and shapes, however majority are translucent.
- Phytoplankton act as the basic food source for many marine animals. They also act as indicators of health of marine water. On the other hand, Zooplankton are indicators of toxicity levels in marine water. In case there is a sudden change in level of pollution, acidity or temperature, the zooplanktons will eventually act as sign of reference.
Also Read: Difference Between Short Day Plants and Long Day Plants
Difference Between Phytoplankton And Zooplankton In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PHYTOPLANKTON | ZOOPLANKTON |
| Description | Phytoplankton are plant plant-like aquatic microorganism. | Zooplanktons are animal-like organisms and the larval stages of other life forms. |
| Source of Food | They are primary producers; they absorb sunlight, carbon dioxide and nutrients and convert them into oxygen and carbohydrates (photosynthesis). | They obtain their energy by eating phytoplankton, bacterioplankton, zooplankton and nektonic organisms. |
| Examples | Examples of phytoplankton include: Blue-green algae Cynobacteria, Diatoms Dinoflagellates. | Examples of zooplankton include: Krill Protozoans Holoplankton Arrow worms Jellyfish and even the eggs and larvae of larger organisms. |
| Mode Of Nutrition | They are autotrophic. | They are heterotrophic. |
| Habitat | Majority of phytoplankton are autotrophic, they require sunlight to live hence they are found on the euphotic layer of the water bodies or near water surfaces. | They are mostly found in cold, shaded regions or in the deep sections of water body. There are some zooplankton that drift towards the surface during the day. |
| Trophic Level | In the aquatic food chain, phytoplanktons are primary producers. | In the aquatic food chain, zooplankton are the primary or secondary consumers. |
| Ability To Swim | All phytoplankton do not have the ability to swim against ocean currents. | Zooplankton such as the comb jelly and jellyfish do have the ability to swim in order to avoid predators. |
| Metamorphosis | They do not undergo metamorphosis. | They undergo metamorphosis. |
| Release Of Oxygen Gas | They generally release lots of oxygen gas. | They consume oxygen to release lots of carbon dioxide. |
| Morphology | Majority of phytoplankton have a brown color. When they grow as a group, cloudy patches do actually form. | Zooplanktons generally exist in different colors and shapes, however majority are translucent. |
| Ecological Significance | They act as the basic food source for many marine animals. They also act as indicators of health of marine water. | They are indicators of toxicity levels in marine water. In case there is a sudden change in level of pollution, acidity or temperature, the zooplanktons will eventually act as sign of reference. |