What Is A Conductor?
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electricity) through them. Conductors have free electrons on its surface which allows current to pass through. This is the reason why they are able to conduct electricity. Conductors also have can allow transfer of heat from one source to another.
Usually, the resistance of a given conductor depends on the material it is made of, and on its dimensions. For a given material, the resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area. For example, a thick copper wire has lower resistance than an otherwise-identical thin copper wire. Also, for a given material, the resistance is proportional to the length, for example, a long copper wire has higher resistance than an otherwise-identical short copper wire.
Conduction materials include metals (copper, aluminum, iron etc), electrolytes, superconductors, semiconductors, plasmas and some nonmetallic conductors such as graphite and conductive polymers.
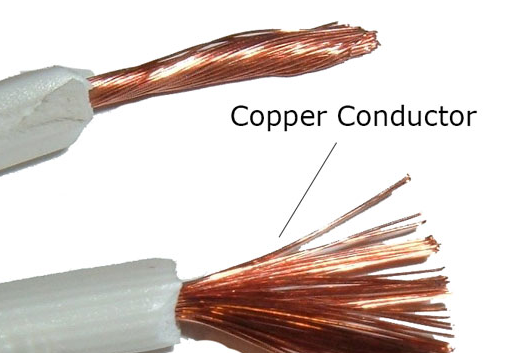
Application Of Conductors In Daily Life
- Mercury is a common ingredient in thermometer to check temperature of the body.
- Aluminum finds use in making foils to store food and also in the production of fry pans to store heat quickly.
- Conductors are used in car radiators to eradicate heat away from the engine.
- Iron is used in vehicle engine manufacturing to conduct heat.
What You Need To Know About Conductor
- Conductor is a material which permits the electric current or heat to pass through it.
- The conductors have very high conductivity, (10-7 Ʊ/m) thus they can conduct electrical current easily.
- The conduction in conductors is due to the free electrons in metal bonding.
- The resistance of a conductor increases with an increase in temperature.
- In conductors, electrons are charge carriers.
- In conductors, there is only one valence electron in the outermost shell.
- In conductors, there is low energy gap between the conduction and valence band of a conductor. It does not need extra energy for the conduction state.
- Conductors have a positive coefficient of resistivity. Its resistance increases with increase in temperature.
- Some special conductors turn into superconductors when supercooled down while other have finite resistance.
- Valence band and conduction band of conductors is completely filled.
- On increasing temperature, the number of carriers decreases.
- Examples include gold, copper, silver, aluminum etc.
- The metals like iron, copper, aluminum etc that conduct electricity are made into wires and capable for carrying electric current.
- Conductors have ionic type of bonding in their structure.
- In conductors, current flow under the influence of electric field takes place easily.
What Is Semiconductor?
Semiconductors are materials which have an intermediate conductivity between that of conductors (generally metals) and insulator (such as most ceramics); either due to the addition of an impurity or because of temperature effects. Semiconductors can be pure elements, such as silicon or germanium or compounds such as gallium arsenide or cadmium selenide. Semiconductors are employed in manufacture of various kinds of electronic devices, including diodes, transistors and integrated circuits.
Semiconductor devices can display a range of useful properties such as passing current more easily in one direction than the other, showing variable resistance and sensitivity to light or heat. Because the electrical properties of a semiconductor material can be modified by doping, or by the application of electrical fields or light, devices made from semiconductors can be used for amplification, switching and energy conversion.
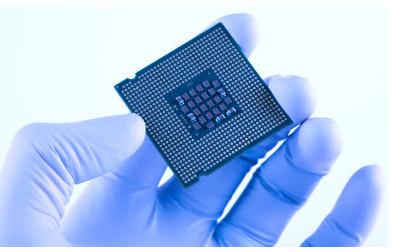
Application Of Semiconductors In Daily Life
- Semiconductors are used in solar technology.
- Used in making temperature sensors used in air conditioners.
- Semiconductor devices are used in computer, calculator, solar plates and other electronic devices.
- Used in self-driving cars
- Semiconductors play a role in the operation of bank ATMs.
- Used in microchips which are used in electronic devices.
What You Need To Know About Semi-conductor
- Semi-conductor is a material or substance that may act as a conductor as well as insulators under different conditions.
- Semiconductors have intermediate conductivity (between 10-7 Ʊ/m to 10-13 Ʊ/m), thus they can act as insulator and conductor at different conditions.
- The conduction in semiconductors is due to the movement of electrons and holes.
- The resistance of a semiconductor decreases with increase in temperature. Thus it acts as an insulator at absolute zero.
- In semiconductors, intrinsic charge carriers are holes and electrons.
- In semiconductors, there are four valence electrons in the outermost shell.
- The band gap of semiconductor is greater than that of conductor but smaller than that of an insulator.
- Semiconductors have a negative coefficient of resistivity.
- The semiconductors turn into insulators at absolute zero.
- Valence band is partially empty and conduction band is partially filled.
- On increasing temperature, the number of carriers increases.
- Examples include: silicon, Germanium, Selenium, Antimony, Boron etc.
- Semiconductors are used every day electronic devices such as cellphone, computer, solar panel etc as switches, energy converters, amplifiers etc.
- Semiconductors have ionic bond and covalent type of bonding in their structure.
- In semiconductors, current flow does not take place under the influence of electric field.
Also Read: Difference Between P-type And N-type Semiconductors
What Is An Insulator (Non-Conductors)?
An insulator also referred to as nonconductor is an object or type of material that does not allows the flow of charge (electricity) through them. According to electronic band theory (a branch of physics), a charge flows if states are available into which electrons can be excited. This allows electrons to gain energy and thereby move through a conductor such as metal. If no such states are available, the material is an insulator.
Insulators support and keep electrical conductor from making unintended contact with each other. Insulating materials include paper, wood, plastic, porcelain, rubber, glass, Teflon and air. Porcelain and glass insulators are frequently used in cases of high voltage transmission. Plastic does not have the same level of resistance as glass and porcelain though it is still fairly resistant and therefore used more frequently for mass applications. Plastics are commonly used to insulate wires and cables.
The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity. Insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. A material is said to have high resistance when it can effectively reduce the amount of current passing through it. Insulators are generally rated at hundred of volts, but some that are used in power transmission and distribution are rated as high as hundreds of thousands of volts.
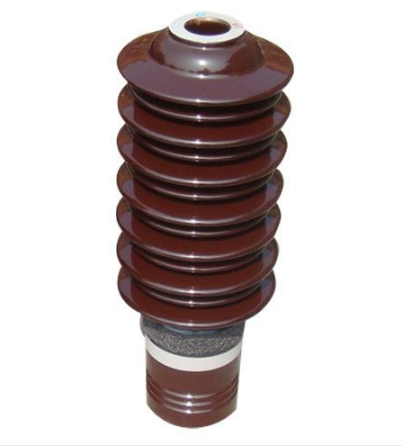

Application of Insulators In Daily Life
- Sound insulators are used for soundproofing rooms or for noise control.
- Electrical insulators are used for circuit boards, high voltage systems and coating on electric wire and cable.
- Thermal insulators are used to prevent transfer of heat from one section to another. Others are used in keeping houses warm.
What You Need To Know About Insulator
- Insulators are materials or substances which do not allow heat or electricity to pass through it.
- They have very low conductivity (10-13 Ʊ/m), thus they do not allow current flow.
- Non conduction is due to absence free electrons or holes.
- Insulators have very high resistance but it decreases with temperature.
- Insulators do not have any charge carriers.
- Insulators have eight valence electrons in the outermost shell.
- The band gap in insulators is huge, which needs an enormous amount of energy like lightning to push electrons into the conduction band.
- The coefficient of resistivity of an insulator is also negative but it has very huge resistance.
- The insulator resistance increases when cooled down to absolute zero.
- Valence band of insulators is completely filled and conduction band is completely empty.
- On increasing temperature, number of carries increase.
- Examples include rubber, glass, wood, Mica, Plastic, Paper etc.
- The insulators are used for protection against high voltages and prevention of electrical short between cables in circuits.
- Insulators have covalent type of bonding in their structure.
- In insulators, current flows slowly under the influence of electric field.
Also Read: Difference Between Electric Field And Magnetic Field
Difference Between Conductor, Insulator And Semi-Conductor In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | CONDUCTOR | SEMICONDUCTOR | INSULATOR |
| Description | Conductor is a material which permits the electric current or heat to pass through it. | Semi-conductor is a material or substance that may act as a conductor as well as insulators under different conditions. | Insulators are materials or substances which do not allow heat or electricity to pass through it. |
| Conductivity | Have very high conductivity, (10-7 Ʊ/m) thus they can conduct electrical current easily. | Have intermediate conductivity (between 10-7 Ʊ/m to 10-13 Ʊ/m), thus they can act as insulator and conductor at different conditions. | They have very low conductivity (10-13 Ʊ/m), thus they do not allow current flow. |
| Reason For Conductivity Or Otherwise | The conduction in conductors is due to the free electrons in metal bonding. | The conduction in semiconductors is due to the movement of electrons and holes. | Non conduction is due to absence free electrons or holes. |
| Resistance Vs Temperature | The resistance of a conductor increases with an increase in temperature. | The resistance of a semiconductor decreases with increase in temperature. | Insulators have very high resistance but it decreases with temperature. |
| Charge Carrier | In conductors, electrons are charge carriers. | In semiconductors, intrinsic charge carriers are holes and electrons. | Insulators do not have any charge carriers. |
| Valence Electrons | They have only one valence electron in the outermost shell. | They have four valence electrons in the outermost shell. | They have eight valence electrons in the outermost shell. |
| Band Gap | In conductors, there is low energy gap between the conduction and valence band of a conductor. It does not need extra energy for the conduction state. | The band gap of semiconductor is greater than that of conductor but smaller than that of an insulator. | The band gap in insulators is huge, which needs an enormous amount of energy like lightning to push electrons into the conduction band. |
| Coefficient Of Resistivity | Conductors have a positive coefficient of resistivity. Its resistance increases with increase in temperature. | Semiconductors have a negative coefficient of resistivity. | The coefficient of resistivity of an insulator is also negative but it has very huge resistance. |
| Absolute Zero | Some special conductors turn into superconductors when supercooled down while other have finite resistance. | The semiconductors turn into insulators at absolute zero. | The insulator resistance increases when cooled down to absolute zero. |
| Valence Band & Conduction Band | Valence band and conduction band of conductors is completely filled. | Valence band is partially empty and conduction band is partially filled. | Valence band of insulators is completely filled and conduction band is completely empty. |
| Temperature Increase Vs Number Of Carriers | On increasing temperature, the number of carriers decreases. | On increasing temperature, the number of carriers increases. | On increasing temperature, number of carries increase. |
| Overlapping Of Bands | The valence and conduction bands are overlapped. | Valence band and conduction band are separated energy gap of 1.1eV. | Both the bands get divided by an energy gap of 6eV -10eV. |
| Examples | Gold, Copper, Silver, Aluminum etc. | Silicon, Germanium, Selenium, Antimony, Boron etc. | Rubber, Glass, Wood, Mica, Plastic, Paper etc. |
| Application | The metals like iron, copper, aluminum etc that conduct electricity are made into wires and capable for carrying electric current. | Semiconductors are used every day electronic devices such as cellphone, computer, solar panel etc as switches, energy converters, amplifiers etc. | The insulators are used for protection against high voltages and prevention of electrical short between cables in circuits. |
| Type Of Ionic Bonding | Conductors have metallic type of bonding in their structure. | Semiconductors have ionic bond and covalent type of bonding in their structure. | Insulators have covalent type of bonding in their structure. |
| Effect Of Electric Field On Current Flow | In conductors, current flow under the influence of electric field takes place easily. | In semiconductors, current flow does not take place under the influence of electric field. | In insulators, current flows slowly under the influence of electric field. |
Also Read: Difference Between Intrinsic And Extrinsic Semi-Conductor