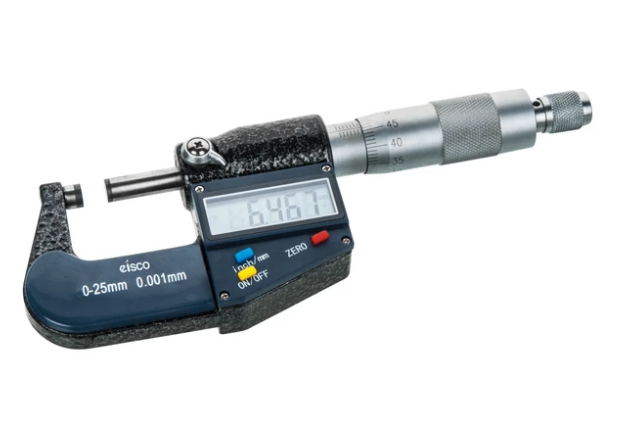
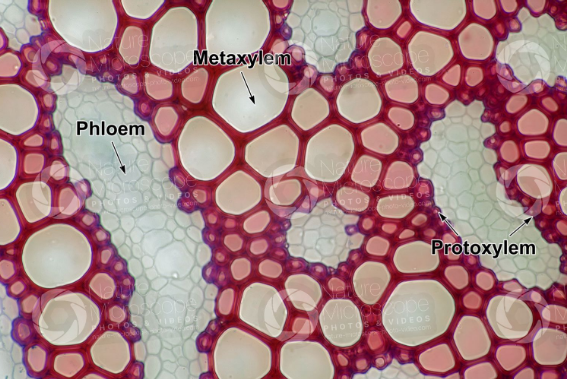
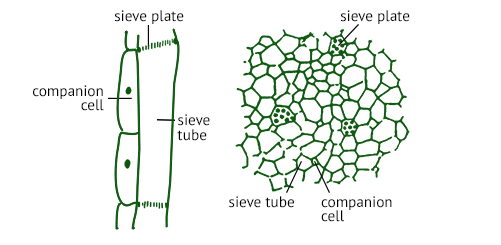
15 Difference Between Protoxylem And Metaxylem (With Pictures)
Xylem and phloem are the major conducting tissues in vascular plants. The main function of xylem is conduction of water and minerals towards the apical shoot. Xylem tissues can be classified as primary and secondary xylem depending on where they originate. The primary xylem is the type of xylem that is produced from the primary … Read more