The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; most are invisible without the use of a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The cell can be oval, rod-shaped, curved, spherical, concave or rectangular.
Plant cell are eukaryotic cells, which have a true nucleus along with specialized structures known as organelles that carry out different functions. Plant cells are differentiated from the cells of other organisms by their cell walls, chloroplasts and central vacuole. The chloroplasts contain the green-colored pigment chlorophyll that converts the energy of sunlight into chemical energy that the plant uses to make its own food from water and carbon dioxide in the process known as photosynthesis.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. It also comprises of organelles and cellular structures which carry out specific functions necessary for the cell to function properly. The contents of a cell are referred to as protoplasm. The main distinguishing feature between animal and plant cell is that, animal cells do not have cell walls or chloroplasts, the organelle that carries out photosynthesis.
Key Difference
Also Read: Difference Between Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes
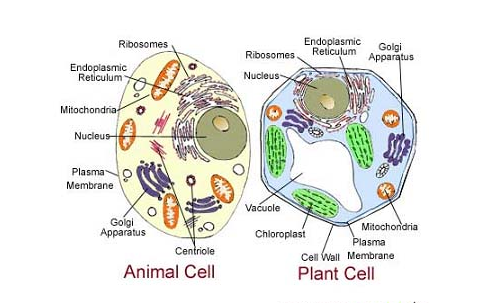
The following points highlight the general differences in the characteristic features between plant and animal cell. The basis of comparison include: size, centrioles, size of the vacuole, cell shape, spindle fiber, food storage, size of the central vacuole, synthesis of amino acids and coenzymes, cytokinesis among others.
- A plant cell is comparatively larger in size (10 to 100 micrometers) whereas an animal cell is comparatively smaller in size (10 to 30 micrometers).
- The plant cell can synthesize amino acids, vitamins and coenzymes while the animal cell cannot synthesize, amino acids, vitamins and coenzymes.
- Centrioles are usually absent in plant cells except in motor cells of lower plants, on the other hand, centrioles are very much present in animal cells.
- In plant cells, food is stored in the form of starch whereas in animal cell, food is stored in the form of glycogen.
- Plant cells contain one large central vacuole that take up to 90% of cell volume whereas animal cell contains numerous small vacuoles embedded in the cytoplasm. In animal cells, vacuoles store water, waste and ions whereas in plant cells, the vacuoles store water and maintain turgidity of the cell.
- The plant cell is usually rectangular and more rigid whereas animal cell is irregular in shape.
- Plant cell does not burst if placed hypotonic solution due to the presence of the cell wall. On the contrary, the animal cell lack contractile vacuoles usually burst, if placed in hypotonic solution.
- In a plant cell, nucleus lies on one side in the peripheral cytoplasm whereas in an animal cell, nucleus usually lies in the center.
- In a plant cell, lysosomes are rare whereas in an animal cell, lysosomes are practically present. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down many kinds of biomolecules. It is involved in cell processes such as secretion, plasma membrane repair, cell signaling and energy metabolism.
- In a plant cell, spindles formed during cell divisions are anastral i.e without asters at opposite poles. On the contrary, spindle formed during cell division is amphiastral i.e has an ester at each pole.
- A plant cell is enclosed by a rigid cellulose cell wall and a plasma membrane while an animal cell is only enclosed by a thin, flexible plasma membrane.
- Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate only in a plant cells whereas in an animal cells, it occurs by furrowing or constrictions.
- Storing of energy is done by chloroplast in plant cells which is absent in animal cells.
- Mitochondria are present in reasonable numbers in animal cells and they play an important role of production of energy. In a plant cell, mitochondria are not often present; however, if present they will be few in number.
- In an animal cell, the tight junctions and desmosomes are absent between cells, though the plasmodesmata is present. On the contrary, in animal cells, tight junctions and desmosomes are present between cells. The plasmodesmata are usually absent.
- Plastids are present in a plant cells whereas plastids are usually absent in animal cells.
- Glyxoxysome is present in plant cells and absent in animal cells.
Also Read: Difference Between Meiosis And Mitosis
Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PLANT CELL | ANIMALS CELL |
| Size | A plant cell is comparatively larger in size (10 to 100 micrometers). | An animal cell is comparatively smaller in size (10 to 30 micrometers). |
| Synthesis of Amino acids & Coenzymes | Can synthesize amino acids, vitamins and coenzymes. | The cell cannot synthesize amino acids, vitamins and coenzymes. |
| Centrioles | Centrioles are usually absent in plant cells, except in motor cells of lower plants. | centrioles are very much present in animal cells. |
| Food Storage | Food is stored in the form of starch. | Food is stored in the form of glycogen. |
| Size of the Vacuole | Contain one large central vacuole that take up to 90% of cell volume. | Contains numerous small vacuoles embedded in the cytoplasm. |
| Cell Shape | Cell is usually rectangular and more rigid. | Cell is irregular in shape. |
| Lysosomes | Lysosomes are rare. | Lysosomes are practically present. |
| What Happens When Placed In Hypotonic Solution | Plant cell does not burst if placed hypotonic solution due to the presence of the cell wall. | The animal cell lack contractile vacuoles usually burst, if placed in hypertonic solution. |
| Spindle Fiber | Spindles formed during cell divisions are anastral i.e without asters at opposite poles. | Spindle formed during cell division is amphiastral i.e has an ester at each pole. |
| Position of Nucleus | Nucleus lies on one side in the peripheral cytoplasm. | Nucleus usually lies in the center. |
| Cell Enclosed In | Cell is enclosed by a rigid cellulose cell wall and a plasma membrane. | Cell is only enclosed by a thin, flexible plasma membrane. |
| Cytokinesis | Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate only in a plant cells. | Cytokinesis it occurs by furrowing or constrictions. |
| Chloroplasts | Storing of energy is done by chloroplast in plant cells. | Chloroplasts are absent. |
| Mitochondria | Mitochondria are not often present; however, if present they will be few in number. | Mitochondria are present in reasonable numbers and are production of energy. |
| Plasmodesmata | The tight junctions and desmosomes are absent between cells, though the plasmodesmata is present. | The tight junctions and desmosomes are present between cells. The plasmodesmata are usually absent. |
| Plastids | Plastids are present in a plant cells. | Plastids are usually absent in animal cells |
| Glyxoxysome | Glyxoxysome is present in plant cells. | Glyxoxysome is absent in animal cells. |
Also Read: Difference Between Sieve Tubes And Companion Cells
What Are Some f The Similarities Between Plant And Animal Cell?
- Double-stranded helical DNA is present in both plant and animal cell.
- All the three types of RNA occur in both plant and cells. The three types of RNA include: rRNA, t-RNA and m-RNA.
- Both types of cells are surrounded by a cell membrane composed of lipids and proteins.
- Membrane bound is present in both cell types. Nucleus has 4 components that is chromatin fibres, nucleoplasm , nuclear envelop and nucleolus.
- Membrane bound organelles are present in both cell types. Membrane bound organelles like mitochondria, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles etc.
- Ribosome occur freely in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum of both cell types.