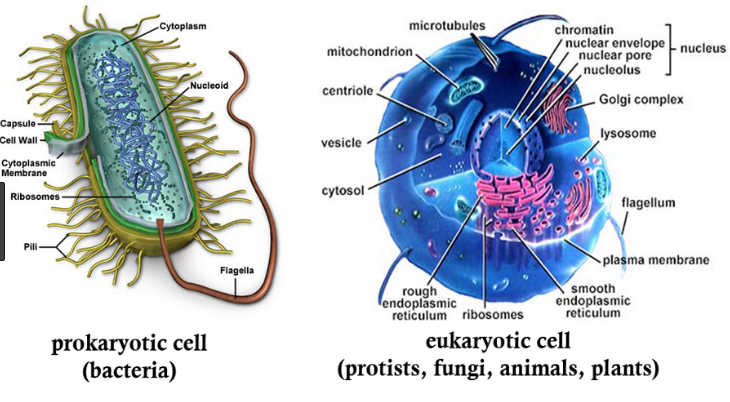
A prokaryote is usually a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane bound organelle. Organisms that have prokaryotic cells are unicellular and they include archaea and bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do; instead they have a nucleoid region, which is an irregular-shaped region that contains the cell’s DNA.
Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus and organelles, and are enclosed by a plasma membrane. Organisms that have eukaryotic cells include protozoa, fungi, plants and animals. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Examples of organelles found in Eukaryotic cells include ribosomes for protein synthesis, mitochondria production of ATP and endoplasmic reticulum which sorts and package the proteins.
In this article, get to understand more details about Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells, Cell Division, organelles and other related details.
Prokaryotes
- Prokaryote cells are mostly found in single cell organisms with their size varies from 0.5-3um.
- Organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, cell wall, chloroplast, are absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Nucleus is not well defined in Prokaryotic cells.
- Genetic material (DNA) is circular and double-stranded.
- Prokaryotes reproduce asexually.
- Cell division takes place through binary fission of budding.
- Genes are expressed in groups called operons.
- Zygote is partially diploid (merozygotic).
- Transcription and translation occur simultaneously.
- Energy yielding mechanism (electron transport chain) occurs in the cytoplasmic membrane.
Eukaryotes
- Eukaryote cells are modified cell structure containing different components in them, their size varies from 2-100um. They are commonly found in multi-cellular organisms.
- Organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, cell wall, chloroplast, are present in eukaryotic cells. Though cell wall and chloroplast are found in the animal cell.
- Nucleus is well structured, arranged and functional in eukaryotes.
- Genetic material (DNA) is linear and double stranded.
- Eukaryotes have a sexual mode of reproduction.
- In eukaryotes cell division happens through the process Mitosis.
- Genes are expressed individually.
- Zygote is fully diploid.
- Transcription occurs in nucleus and then translation occurs in cytoplasm.
- Energy yielding mechanism (electron transport chain) occurs in mitochondria.
Also Read: Difference Between Mitosis And Meiosis
Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells In Tabular Form
| Elements of Comparison | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
| Cell Structure and Size | Prokaryote cells are mostly found in single cell organisms with their size varies from 0.5-3um. | Eukaryote cells are modified cell structure containing different components in them, their size varies from 2-100um. They are commonly found in multi-cellular organisms. |
| Organelles | Organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, cell wall, chloroplast, are absent in prokaryotic cells. | Organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, cell wall, chloroplast, are present in eukaryotic cells. Though cell wall and chloroplast are found in the animal cell. |
| Nucleus | Nucleus is not well defined in Prokaryotic cells. | Nucleus is well structured, arranged and functional in eukaryotes. |
| DNA | Genetic material (DNA) is circular and double-stranded. | Genetic material (DNA) is linear and double stranded. |
| Reproduction | Reproduce asexually. | Reproduce sexually and also asexually. |
| Cell Division | Cell division takes place through binary fission of budding. | Cell division happens through the process Mitosis. |
| Gene Expression | Genes are expressed in groups called operons. | Genes are expressed individually. |
| Zygote | Zygote is partially diploid (merozygotic). | Zygote is fully diploid. |
| Transcription and Translation | Transcription and translation occur simultaneously. | Transcription occurs in nucleus and then translation occurs in cytoplasm. |
| Energy Yielding Mechanism | Energy yielding mechanism (electron transport chain) occurs in the cytoplasmic membrane. | Energy yielding mechanism (electron transport chain) occurs in mitochondria. |
Also Read: Difference Between Animal And Plant Cells
Similarities between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
- Both organisms are composed of cells, the basic unit of life, with each cell surrounded by a cell membrane.
- Both eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells use deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as basis for their genetic information.
- Both Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes have ribosomes that facilitate RNA translation and the creation of protein, which is essential for various functions in these organisms.
- Both have a cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the medium in which the biochemical reactions of the cell take place.
Summary
Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do; instead they have a nucleoid region, which is an irregular-shaped region that contains the cell’s DNA. Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus and organelles, and are enclosed by a plasma membrane. Organisms that have eukaryotic cells include protozoa, fungi, plants and animals.