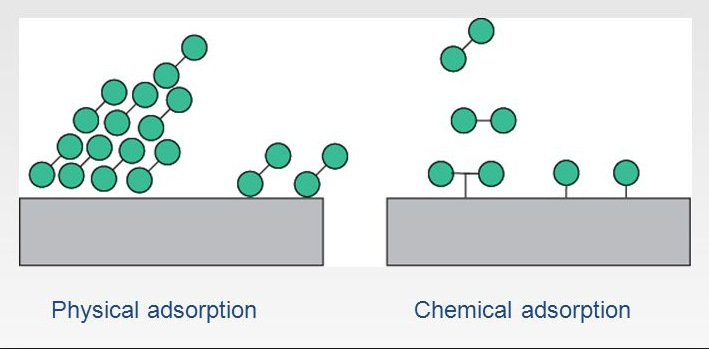
Chemical Adsorption also known as chemisorptions is a kind of adsorption which involves a chemical reaction between the surface and the adsorbate whereas Physical adsorption is a kind of adsorption which attaches the target substance on a chip as a result of hydrogen bonding, van der waals forces, electrostatic forces and hydrophobic interactions. Physical adsorption can also be referred to as physioadsorption.
In this article, get more insights on the general differences between chemical adsorption and physical adsorption. The basis of difference include: specificity, bonding, description, surface area, molecular layer and effect of different factors on the entire process.
Chemical Adsorption
The general features include:
- Chemical adsorption is a kind of adsorption which involves a chemical reaction between the surface and the adsorbate. Chemical adsorption can also be referred to as chemisorption.
- An example of chemical adsorption include, rubbing pain balm on forehead, removing color of water by activated charcoal.
- The process is specific in nature; it occurs only if there is a chemical bond formation between the adsorbent and adsorbate.
- The process is irreversible in nature.
- Chemical adsorption involves chemical bonds between the gas molecules and the adsorbent surface.
- Chemical adsorption is slow at low temperature and it occurs at a higher rate with increase in pressure.
- Chemical adsorption requires a certain level of energy for activation.
- The rate of chemical adsorption is directly proportional to surface area. An increase in surface area increases with increase in surface area.
- Forms unimolecular layer.
Physical Adsorption
- Physical adsorption is a kind of adsorption which attaches the target substance on a chip as a result of hydrogen bonding, van der waals forces, electrostatic forces and hydrophobic interactions. Physical adsorption can also be referred to as physioadsorption.
- Common examples of physical adsorbents are clay, silica gel, colloids and metals.
- There is no specificity as any gas can be adsorbed onto the surface.
- Physical adsorption is reversible in nature and dependent on pressure and temperature.
- Physical adsorption involves the use of weak van der waal forces
- Increase in temperature increases physical adsorption and in the same regard, a decrease in temperature will decrease the rate of physical adsorption.
- Physical adsorption does not require energy for activation.
- The porous substances are usually perfect adsorbents. The porous nature is synonymous to increasing surface area. The rate of physical adsorption increases with increase in surface area.
- Forms multimolecular layers on adsorbent surface.
Also Read: Difference Between Adsorption And Absorption
Difference Between Physical And Chemical Adsorption
| BASIS OF COMPARISON Description | CHEMICAL ADSORPTION Chemical adsorption is a kind of adsorption which involves a chemical reaction between the surface and the adsorbate. | PHYSICAL ADSORPTION Physical adsorption is a kind of adsorption which attaches the target substance on a chip as a result of hydrogen bonding, van der waals forces, electrostatic forces and hydrophobic interactions. |
| Also known as | Chemiadsorption. | Physioadsorption. |
| Common Example | An example of chemical adsorption include, rubbing pain balm on forehead, removing color of water by activated charcoal. | Common examples of physical adsorbents are clay, silica gel, colloids and metals. |
| Specificity | The process is specific in nature; it occurs only if there is a chemical bond formation between the adsorbent and adsorbate. | There is no specificity as any gas can be adsorbed onto the surface. |
| Nature of the Process | The process is irreversible in nature. | Physical adsorption is reversible in nature and dependent on pressure and temperature. |
| Bonding | The process is specific in nature; it occurs only if there is a chemical bond formation between the adsorbent and adsorbate. | Physical adsorption involves the use of weak van der waal forces. |
| Factors Affecting the Process | Chemical adsorption is slow at low temperature and it occurs at a higher rate with increase in pressure. | Increase in temperature increases physical adsorption and in the same regard, a decrease in temperature will decrease the rate of physical adsorption. |
| Activation | Chemical adsorption requires a certain level of energy for activation. | Physical adsorption does not require energy for activation. |
| Surface Area | The rate of chemical adsorption is directly proportional to surface area. An increase in surface area increases with increase in surface area. | The porous substances are usually perfect adsorbents. The porous nature is synonymous to increasing surface area. The rate of physical adsorption increases with increase in surface area. |
| Molecular Layers | Forms unimolecular layer. | Forms multimolecular layers on adsorbent surface. |
General Applications of Adsorption
- Analysis such as chromatography is based on principle of adsorption.
- Adsorption is used in the formulation of stable emulsions in cosmetics and syrups.
- The cleaning action of soap and detergents in general is based on the principle of adsorption.
- Adsorption is used in paint manufacturing to remove dissolved gases from paint that would otherwise make the paint to have a poor covering power.
- Gas masks used in chemical factories or in coal plants are based on the principle of adsorption.
- Separation of noble gases is usually done using activated charcoal as an adsorbent.
- Adsorption of drugs is used to kill germs and bacteria.
- Aluminum and silica are used to absorb moisture from the air to reduce humidity.
What are the Similarities between Chemical and Physical Adsorption?
- Both chemical and physical adsorption is a surface phenomenon.
- Both chemical and physical adsorption increase with increase in surface area.