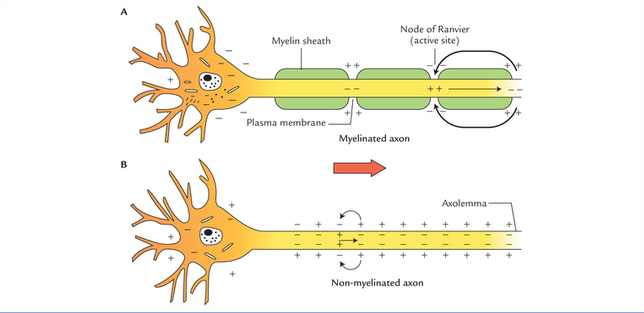
Get to understand a clear distinction between myelinated and unmyelinated neurons. The basis of comparison include: Speed of transmission, description, node of ranvier, axon, diameter, impulse conduction and location.
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | MEDULLATED NERVE FIBRE | Non-MEDULLATED |
| Description | Medullated nerve fibre is a nerve fibre with a medullary sheath. | Non-medullated nerve fibre is a nerve fibre without medullary sheath. |
| Alternative Name | Medullated nerve fibre is also referred to as myelinated nerve fibre. | Non-medullated nerve fibre is also referred to non-myelinated nerve fibre. |
| Location | Medullated nerve fibre is found in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. | Non-medullated nerve fibre is found in the gray matter of the brain and in autonomous nervous system. |
| Color | Medullated nerve fibre is white in color. | Non-medullated nerve fibre is grey in color. |
| Diameter | The diameter of medullated nerve fibre is relatively more than that of non-medullated nerve fibre. | The diameter of non-medullated nerve fibre is relatively less when compared to that of medullated nerve fibre. |
| Nature of Nerve Impulse Conduction | Nerve impulse conduction is salutatory. | Nerve impulse conduction is smooth. |
| Nodes of Ranvier | Nodes of Renvier are present in medullated nerve fibre at intervals. | Nodes of Ranvier are absent in non-medulated nerve fibre. |
| Action Potential | The action potential does not propagate over the internodes and jumps from node to node. | Action potential propagates all along the axon. |
| Conduction of Nerve Impulse | The conduction of nerve impulse in medullated nerve fibre is much faster than in non-medullated nerve fibres. | The conduction of impulse in non-medullated nerve fibres is much slower than in the medullated nerve fibre. |
| Collateral Nerve Fibres | Collateral nerve fibres are present in medullated fibre. | Collateral nerve fibres are absent in non-medullated fibres. |
| Common Presence | Medullated nerve fibres are very much common in vertebrates. | Non-medullated nerve fibres are common in invertebrates, though some vertebrates have non-myelinated nerve fibre. |
| Voltage-gated ion Channels | Voltage-gated ion channels are concentrated at the nodes. | The voltage-gated ions are spread all over the axon. |
| Extracellular Fluid | Extracellular fluid is in contact with the axon only at the nodes. | Extracellular fluid is in contact with the axon along its entire length. |
Also Read: Difference Between Axon And Dendrite
