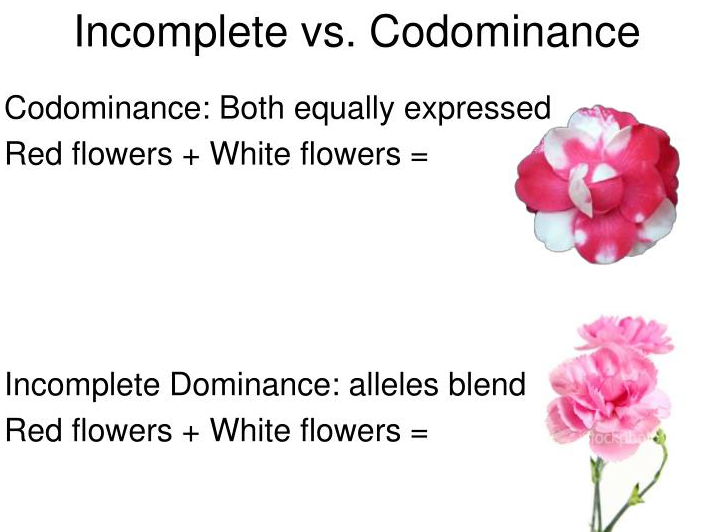
Co–dominance is a form of dominance whereby the alleles of a gene that pair in heterozygote are fully expressed. This results in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. A good example showing co-dominance is the ABO blood group system. On the other hand, Incomplete dominance also referred to as partial dominance is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. This results in a third phenotype in which the expressed physical trait is a combination of the phenotype of both alleles unlike complete dominance inheritance, where one allele does not dominate or mask the other.
As an example, incomplete dominance is seen in cross-pollination experiments between red and white snapdragon plants, whereby the allele that produces the red color (R) is not completely expressed over the allele that produce the white color (r).
1. Definition
Co–dominance is a form of dominance whereby the alleles of a gene that pair in heterozygote are fully expressed. This results in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. Incomplete dominance is a type of gene interaction, which in a heterozygous condition, the dominant allele of a gene at a locus is fully or partially expressed, suppressing the recessive allele, resulting in a dominant phenotype.
2. Dominancy
Dominancy is usually the core difference between co-dominance and incomplete dominance. In co-dominance, one allele is dominant over the other allele in the pair while, in incomplete dominance, neither allele in the pair is recessive or dominant.
3. Examples
Flower color of snapdragon or mirabilis jarapa is a character example of incomplete dominance. On the other hand, the height of a pea plant or A and B blood group in human are examples of Co-dominance.
4. F1 Hybrid when two homozygous parents with different traits are crossed
This is another main difference between complete and incomplete dominance. The F1 hybrid shows an intermediate trait in incomplete dominance while in co-dominance; the F1 hybrid shows the dominant trait.
5. Expression
In incomplete dominance, both alleles in the pair are partially expressed, producing their traits incompletely while in co-dominance, the dominant allele produces its trait, completely masking the effect of the recessive allele.
6. Trait
Trait is also another important distinguishing feature, whereby in incomplete dominance, an intermediate trait occurs with the contribution of both alleles, co-dominance, the dominant trait is expressed in the heterozygous pair.
Difference Between Co-dominance And Incomplete Dominance In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | CO-DOMINANCE | INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE |
| Definition | Co–dominance is a form of dominance whereby the alleles of a gene that pair in heterozygote are fully expressed. This results in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. | Incomplete dominance also referred to as partial dominance is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. |
| Dominancy | One allele is dominant over the other allele in the pair | In incomplete dominance, neither allele in the pair is recessive or dominant. |
| Examples | The height of a pea plant or A and B blood group in human are examples of Complete dominance. | Flower color of snapdragon or mirabilis jarapa is a character example of incomplete dominance. |
| F1 Hybrid when two homozygous parents with different traits are crossed | The F1 hybrid shows the dominant trait. | The F1 hybrid shows an intermediate trait. |
| Expression | The dominant allele produces its trait, completely masking the effect of the recessive allele. | Both alleles in the pair are partially expressed, producing their traits incompletely. |
| Trait | The dominant trait is expressed in the heterozygous pair. | An intermediate trait occurs with the contribution of both alleles. |
Summary
Co–dominance is a form of dominance whereby the alleles of a gene that pair in heterozygote are fully expressed. This results in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. On the other hand, Incomplete dominance is a type of gene interaction, which in a heterozygous condition, the dominant allele of a gene at a locus is fully or partially expressed, suppressing the recessive allele, resulting in a dominant phenotype.
Definition of terms
- Allele- A certain form of a gene.
- Dominant- An allele that masks the phenotype of a recessive allele for the same gene.
- Phenotype- Observable physical characteristics from genes and the environment.