Step-up and Step-down transformers are two categories of transformers, categorized based on their function. A transformer is a static apparatus with no moving components. It transforms electrical power from one circuit to another with changes in voltage and current and no change in frequency. In its basic form, a transformer consists of two coils with high mutual inductance that are electrically separated but have common magnetic circuit.
In a transformer, the first set of the coil referred to as primary coil (primary winding) is connected to an alternating voltage source referred to as Primary voltage. The second set of the coil referred as secondary coil or Secondary winding is connected to the load and the load draws the resulting alternating voltage (Secondary Voltage).
Step-Up Transformer
A Step-up transformer is an electrical device in which the output (secondary) voltage is greater than its input (primary) voltage. The Step-up transformer decreases the output current for keeping the input and output power of the system equal. The amount by which it decreases the input voltage depends on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil.
Power companies use Step-up transformers to help transmit electricity over long distances. They are also useful in devices such as air bags and power supplies.
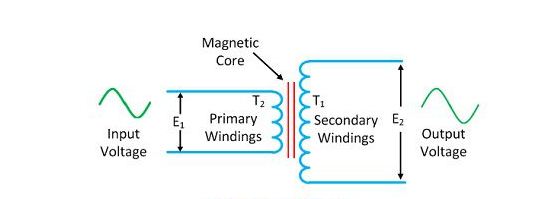
What You Need To Know About Step-Up Transformer
- A transformer that increases the voltage from primary to secondary voltage is referred to as a Step-up transformer. Step-up transformer increases voltage from 220v to 11kv or more.
- The output voltage of Step-Up transformer is more than the source voltage.
- In a Step-up transformer, the primary winding is made up of thick insulated copper wire and the secondary is made up of thin insulated copper wire.
- In a Step-up transformer, the high voltage winding is the secondary winding whereas the low voltage winding is the primary winding.
- In a step-up transformer, the current and magnetic field is less developed in the secondary winding and highly developed in the primary winding.
- In a Step-up transformer, there are more secondary winding turns than primary winding turns.
- Step-up transformer is generally used in transmission lines for transforming the high voltage produced by the alternator.
Step-Down Transformer
A Step-down transformer is a device which is designed to convert high-voltage, low-current power to a low-voltage, high-current power. In a Step-down transformer, the primary winding of a coil has more turns than the secondary winding.
Applications Of A Step Down Transformer
- It is used in televisions, inverters, voltage stabilizers etc.
- In welding machines, it is used in reducing voltage and increasing current.
- Used to step down the voltage level in transmission line.
- Used in the main adapters and chargers for cell phones, CD players and stereos.

What You Need To Know About Step-Down Transformer
- A transformer that reduces the voltage from secondary to primary voltage is referred to as Step-down transformer. A Step-down transformer reduces the voltage from 440v to 220v, 220v to 110v or 110v to 20v or even 10v.
- The output voltage of Step-down transformer is less than the source voltage.
- In a Step-down transformer, the output current is high so, the thick insulated copper wire is used for making secondary winding.
- In a Step-down transformer, low voltage winding is the secondary winding.
- In a Step-down transformer, voltage is low on secondary ends and therefore, the current and magnetic field is high.
- The number of turns in primary winding is more than the secondary winding.
- Step-down transformer is used in power distribution. It is used for electrical isolation, in a power distribution network, for controlling the home appliances, in a doorbell etc.
Also Read: Difference Between Half Wave And Full Wave Rectifier
7 Difference Between Step-Up Transformer And Step-down Transformer In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | STEP-UP TRANSFORMER | STEP-DOWN TRANSFORMER |
| Description | A transformer that increases the voltage from primary to secondary voltage is referred to as a Step-up transformer. Step-up transformer increases voltage from 220v to 11kv or more. | A transformer that reduces the voltage from secondary to primary voltage is referred to as Step-down transformer. A Step-down transformer reduces the voltage from 440v to 220v, 220v to 110v or 110v to 20v or even 10v. |
| Output Voltage | The output voltage of Step-Up transformer is more than the source voltage. | The output voltage of Step-down transformer is less than the source voltage. |
| Secondary & Primary Winding | In a Step-up transformer, the primary winding is made up of thick insulated copper wire and the secondary is made up of thin insulated copper wire. | In a Step-down transformer, the output current is high so, the thick insulated copper wire is used for making secondary winding. |
| Voltage Winding | In a Step-up transformer, the high voltage winding is the secondary winding whereas the low voltage winding is the primary winding. | In a Step-down transformer, low voltage winding is the secondary winding. |
| Magnetic Field | In a step-up transformer, the current and magnetic field is less developed in the secondary winding and highly developed in the primary winding. | In a Step-down transformer, voltage is low on secondary ends and therefore, the current and magnetic field is high. |
| Winding Turns | In a Step-up transformer, there are more secondary winding turns than primary winding turns. | The number of turns in primary winding is more than the secondary winding. |
| Application | Step-up transformer is generally used for power transmission. A good example of a Step-up transformer is the generator transformer in power plants. | Step-down transformer is used in power distribution. A good example of a Step-down transformer is, transformer in residential areas. |
Comments are closed.