Phagocytosis
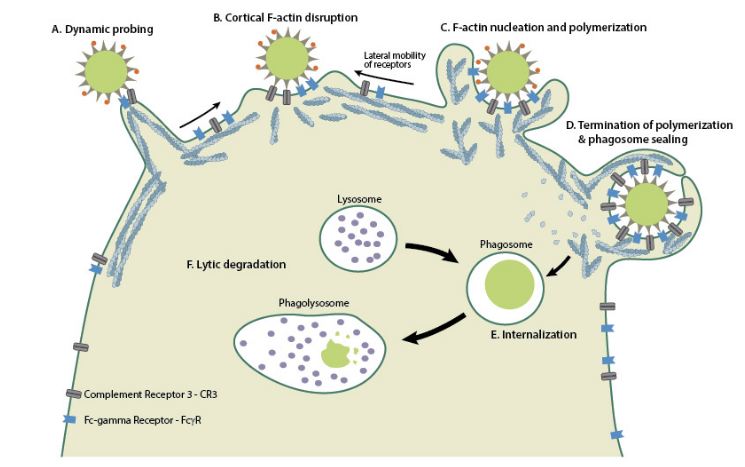
Phagocytosis also referred to as “cell eating“is the process in which particles, microbes or fragments of dead cells are engulfed and internalized usually by specific membrane receptors. The process of phagocytosis begins with binding of specific molecules on the surface of pathogen/particle. The cell membrane then extends around the target, eventually enveloping it and pinching-off to form a descreet phagosome. This vesicle can mature and acidify through fusion with late endosomes and lysosomes to form a phagolysosome in which degradation of the content can occur through the action of lysosomal hydrolases.
What differentiates phagocytosis from pinocytosis is that phagocytes posses special surface proteins that allow them to specifically identify and bind to a given particle before ingesting them. Phagocytosis is dependent on the biding between the cell and the target object or particle.
In a multicellular organism’s immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients.
Other cells that use phagocytosis include:
- Macrophages
- Neutrophils
- Epidermal cells
- Dendritic cells
- Mast cells
- Some vascular endothelial cells
Generally, phagocytes are categorized into two major groups. These include ‘’professional phagocytes’’ such as white blood cells and ‘’non professional phagocytes” such as epithelial cells). Examples of phagocytosis include:
- Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells (efferocytosis)
- Phagocytosis of bacteria
- Phagocytosis of protozoa
- Consumption of food particles by amoeba
What You Need To Know About Phagocytosis
- Phagocytosis also referred to as “cell eating“is the process in which particles are broken down into simpler substances with the help of enzymes for absorption.
- The main function o Phagocytosis is usually for defense of cells.
- Substances are ingested in the form of solid during Phagocytosis.
- Phagocytosis occurs in tissue neutrophills, macrophages and monocytes. It also occurs in the kupffer cells in the liver and Langerhans cells in the skin.
- In the process of Phagocytosis, there is formation of feet-like structures referred to as pseudopodia. The pseudopodia extended around a particle to be swallowed up into the cells. The process is referred to as engulfment.
- The molecules are engulfed to form vesicles; these vesicles are referred to as phagosomes. These vesicles are comparatively large, approximately 75 µm in diameter.
- Engulfment of bacteria by white blood cells and engulfment of food particles by cells are examples for Phagocytosis. Also in the immune system of mammals certain foreign particles like pathogens are engulfed by macrophages (specialized pinocytic cells).
- In Phagocytosis, particles must be broken down into simpler substances for absorption.
- A large amount of energy in the form of ATP is given off during phagocytosis process.
- Lysosomes combine with phagosomes to form food vacuole.
- Exocytosis occurs at the end of phagocytosis to throw out the undigested food particles.
- Phagocytic cells are like macrophage is usually very specific in the particles they engulf.
- Examples of substances engulfed are foreign particles, harmful bacteria and virus dust etc.
- Phagocytosis is a triggered process, involving receptors like IgG.
What Is Pinocytosis?
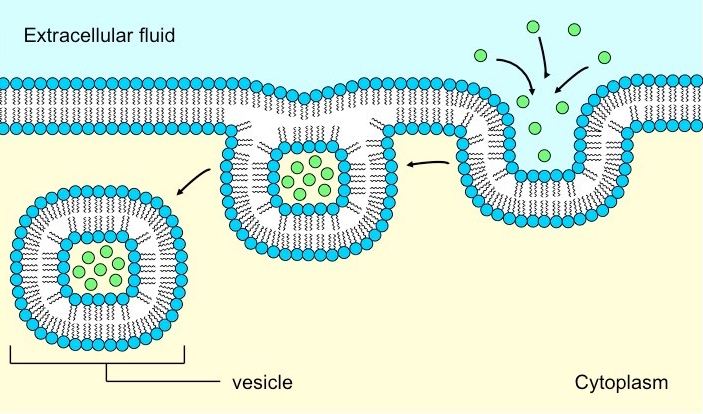
Pinocytosis also referred to as ‘’cell drinking’’ is a cellular process by which fluids and nutrients are ingested by cells. It involves the inward folding of the cell membrane (plasma membrane) and the formation of membrane-bound, fluid-filled vesicles. These vesicles transport extracellular fluid and dissolved molecules across the cell or deposit them in the cytoplasm. This process requires energy carried by adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a chemical compound mostly used as a carrier of energy in the majority of animal cells.
Pinocytosis is initiated by the presence of desired molecules in extracellular fluid near the cell membrane surface. Some of these dissolved molecules include: proteins, sugar molecules and ions. Pinocytosis is a continual process that occurs in most cells and non-specific means of internalizing fluid and dissolved nutrients and therefore it is sometimes referred to as fluid-phase endocytosis or bulk-phase pinoctosis. Examples of pinocytosis include:
- Absorption of nutrients in the gut by microvilli
- Absorption of nutrients by the human egg cells prior fertilization
- Uptake of enzymes and hormones from extracellular fluid
- Root hair cells in plants take water and solute from the soil by pinocytosis.
Pinocytosis can be further divided into five pathways based on the mechanism of vesicle formation as well as the resulting size of the very vesicles. The categories include:
- Macropinocytosis
- Micropinocytosis
- Clathrin-mediated endocytosis
- Caveolin-mediated endocytosis
- Caveolin-independent endocytosis
What You Need To Know About Pinocytosis
- Pinocytosis also referred to as ‘’Cell drinking’’, is a process in which a substance is ingested as it is in dissolved form and ready for cellular absorption.
- The main function of pinocytosis is intake of important materials.
- Substances are ingested in the form of liquid during pinocytosis.
- Pinocytosis usually occurs in secretory cells, cell linings of blood capillaries and in almost all the cells in the body of a multicellular organism.
- In the process of pinocytosis, there is usually unfolding of the cell membrane along with the extracellular fluid and the solute particles dissolved in it. This process is referred to as invagination.
- The vesicles formed during pinocytosis can be referred to as pinocytic vesicles or pinosomes and are small in size, approximately 0.5-5 µm.
- Uptake of enzymes and hormones from extracellular fluid is an example of pinocytosis. Also root hair cells in plants take water and solute from the soil by pinocytosis. Lastly, the epithelial cells of intestines and the human ovum take up nutrients with help of pinocytosis.
- In pinocytosis, the substances being ingested can readily be absorbed.
- During pinocytosis of smaller lipids, small amount of energy in the form of ATP is generated.
- Lysosomes have no functional significance for pinocytosis.
- There is no exocytosis at the end of pinocytosis.
- Pinocytic cells are usually not specific in the molecules they invaginate.
- Examples of substances invaginated include sugars, amino acids, enzymes, hormones etc.
- Pinocytosis is a constitutive process, occurring continuously.
Difference Between Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF DIFFERENCE | PHAGOCYTOSIS | PINOCYTOSIS |
| Description | Phagocytosis is the process in which particles are broken down into simpler substances with the help of enzymes for absorption. | Pinocytosis, is a process in which a substance is ingested as it is in dissolved form and ready for cellular absorption. |
| Alternative Name | Phagocytosis also referred to as “cell eating“ | Pinocytosis also referred to as ‘’Cell drinking’’ |
| Main Function | The main function o Phagocytosis is usually for defense of cells. | The main function of pinocytosis is intake of important materials. |
| Ingestion Of Substances | Substances are ingested in the form of solid during Phagocytosis. | Substances are ingested in the form of liquid during pinocytosis. |
| Occurrence | It occurs in tissue neutrophills, macrophages and monocytes. It also occurs in the kupffer cells in the liver and Langerhans cells in the skin. | It occurs in secretory cells, cell linings of blood capillaries and in almost all the cells in the body of a multicellular organism. |
| Engulfment/Invagination Of Particles | In this process, there is formation of feet-like structures referred to as pseudopodia. The pseudopodia extended around a particle to be swallowed up into the cells. The process is referred to as engulfment. | In this process there is usually unfolding of the cell membrane along with the extracellular fluid and the solute particles dissolved in it. This process is referred to as invagination. |
| Vesicles | The molecules are engulfed to form vesicles; these vesicles are referred to as phagosomes. These vesicles are comparatively large, approximately 75 µm in diameter. | The vesicles formed during pinocytosis can be referred to as pinocyticvesiclesorpinosomes and are small in size, approximately 0.5-5 µm. |
| Examples 0 | Engulfment of bacteria by white blood cells. Engulfment of food particles by cells are examples for Phagocytosis. Also in the immune system of mammals certain foreign particles like pathogens are engulfed by macrophages (specialized pinocytic cells). | Uptake of enzymes and hormones from extracellular fluid is an example of pinocytosis. Root hair cells in plants take water and solute from the soil by pinocytosis. The epithelial cells of intestines and the human ovum take up nutrients with help of pinocytosis. |
| Absorption of Substances | In the process, particles must be broken down into simpler substances for absorption. | In the process, the substances being ingested can readily be absorbed. |
| Energy Production | A large amount of energy in the form of ATP is given off during phagocytosis process. | During the process of smaller lipids, small amount of energy in the form of ATP is generated. |
| Lysosomes | Lysosomes combine with phagosomes to form food vacuole. | Lysosomes have no functional significance for pinocytosis. |
| Exocytosis | Exocytosis occurs at the end of phagocytosis to throw out the undigested food particles. | There is no exocytosis at the end of pinocytosis. |
| Specificity | Phagocytic cells are like macrophage is usually very specific in the particles they engulf. | Pinocytic cells are usually not specific in the molecules they invaginate. |
| Substances To Be Ingested | Foreign particles Harmful bacteria Virus Dust etc. | Sugars, Amino acids, Enzymes, Hormones etc. |
| Nature Of Process | Phagocytosis is a triggered process, involving receptors like IgG. | Pinocytosis is a constitutive process, occurring continuously. |
Similarities Between Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis
- In both process, energy in the form of ATP is generated.
- Both phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of the endocytosis process where the cell takes in material from the extracellular fluid.