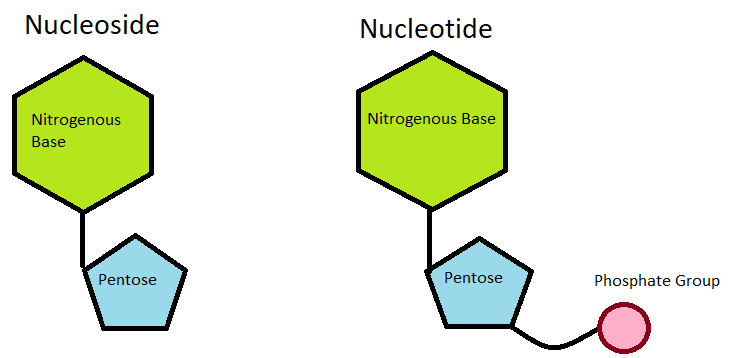
Nucleoside is a structural sub-unit of nucleic acids, the heredity-controlling component of all living cells, consisting of a molecule of sugar linked to a nitrogen-containing organic ring compound. Nucleosides are usually obtained by chemical or enzymatic decomposition of nucleic acids. In nucleosides, the sugar is either ribose or deoxyribose and the nitrogen-containing compound is either a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine or uracil) or a purine (adenine or guanine).
A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Other than storage of genetic material, nucleotides serve as messengers and energy moving molecules. Both nucleotide and nucleoside form the key structural elements of a genetic material. However, they may be having almost similar components but structurally, they are different.
In this article, get to understand the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide. The basis of comparison include: medical relevance, chemical composition, structure and role in nucleic acids.
The Difference
- A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) but without the phosphate group. On the other hand, a nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups.
- Several nucleoside analogues are used in medicine as antiviral or anticancer agents whereas dysfunctional nucleotides lead to accumulation of DNA damage, eventually leading to the onset of cancer.
- Nucleoside undergoes phosphorylation to form nucleotides whereas nucleotide forms covalent bonds with other nucleotides to form the nucleic acid strand.
- Nucleoside=Pentose sugar + nitrogenous base (nucleobase) whereas Nucleotide=Nucleoside + one or more phosphate groups.
- Examples of nucleosides include: Cytidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine and Thymidine whereas examples of nucleotides include: 5’-Cytidine monophosphate, 5’-Uridine monophosphate, 5’-Adenosine monophophate, 5’-Guanosine monophosphate and 5’- Thymidine monosphoshate.
Also Read: Difference Between RNA And DNA
Nucleotide Vs. Nucleoside In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | NUCLEOSIDE | NUCLEOTIDE |
| Structure | A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) but without the phosphate group. | A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups. |
| Medical Relevance | Several nucleoside analogues are used in medicine as antiviral or anticancer agents. | Dysfunctional nucleotides lead to accumulation of DNA damage, eventually leading to the onset of cancer. |
| Role In Nucleic Acids | Nucleoside undergoes phosphorylation to form nucleotides. | Nucleotide forms covalent bonds with other nucleotides to form the nucleic acid strand. |
| Chemical Composition | Nucleoside=Pentose sugar + nitrogenous base (nucleobase). | Nucleotide=Nucleoside + one or more phosphate groups. |
| Examples | Examples of nucleosides include: Cytidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine Thymidine | Examples of nucleotides include: 5’-Cytidine monophosphate, 5’-Uridine monophosphate, 5’-Adenosine monophophate, 5’-Guanosine monophosphate 5’- Thymidine monosphoshate. |
Also Read:
- Difference Between Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Difference Between Introns And Exons
- Difference Between Template And Conding Strand
Comments are closed.