Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cables
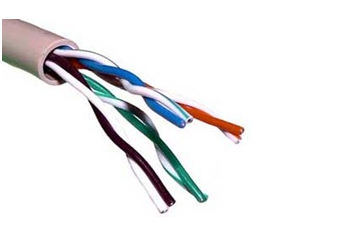
In UTP cable, conductors which form a single circuit are twisted around each other in order to cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources. Unshielded means no additional shielding like meshes or aluminum foil which add bulk is used. UTP cables are often groups of twisted pairs grouped with color coded insulators, the number of which depends on the purpose. Alternatives to UTP cable include coaxial cable and fiber optic cable.
Inside a UTP cable, there are up to four twisted pairs of copper wires of copper wires, enclosed in a protective plastic cover, with the greater number of pairs corresponding to more bandwidth. The two individual wires in a single pair are twisted around each other and then the pairs are twisted around each other, as well. This is usually done to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference, each of which can degrade network performance. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires. UTP is commonly used in telephone wiring and local area networks (LANs).
Categories Of UTP Cables
- CAT3: Not commonly used today but it can be deployed in phone lines. It supports 10 Mbps for up to 100 meters.
- CAT 4: It supports 16 Mbps for up to 100 meters. Commonly used in token ring networks.
- CAT5: It supports 100 Mbps for up to 100 meters. It typically made up of two twisted pairs and commonly used in Ethernet-based LANs.
- CAT5e: It supports 1 Gbps for up to 100 meters. It typically made up of two twisted pairs and commonly used in Ethernet-based LANs.
- CAT6: It supports 1 Gbps for up to 100 meters and 10 Gbps for up to 50 meters. This cable is typically used in data center networks and in Ethernet-based LANs.
What You Need To Know About UTP Cables
- Electromagnetic interference and noise is more in UTP.
- It offers speed or throughput of about 10 to 1000Mbps.
- It offers maximum cable length of about 100 meters.
- Each of the 8 individual copper wires in UTP cable is covered by insulating material. In addition, wires in each pair are twisted around each other.
- In UTP, attenuation is high when compared to STP.
- UTP is widely used for data transmission within short distance and is very popular for home network connecting.
- In UTP the generation of crosstalk is high when compared to STP.
- The cost of UTP is less when compared to that of STP.
- In UTP grounding cable is not required.
- UTP cables are available from category-1 to category-6.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cables
In a shielded twisted pair (STP), the wires are enclosed in a shield that functions as a grounding mechanism. Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable was originally designed by IBM for token ring networks that include two individual wires covered with a foil shielding. The shielding is done to provide greater protection from electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference leaking into or out of the cable; thereby transporting data faster. However, STP cable is more expensive and difficult to install, compared with UTP.
Shielded twisted pair cable is available in three different configurations:
- Each pair of wire is individually shielded with foil
- There is a foil or braid shield inside the jacket covering all wires (as a group).
- There is a shield around each individual pair, as well as around the entire group of wires (referred to as double shield twisted pair).
STP cable has an impedance of 150 ohms, has a maximum length of 90 meters and is used primarily in networking environments with a high amount of EMI due to motors, air conditioners, power lines or other noisy electrical components. SPT is the default type of cabling for IBM token ring network.
Categories Of STP Cable
- IBM Type 1
- IBM Type 1A
- IBM Type 2A
- IBM Type 6A

What You Need To Know About STP Cables
- STP cable reduce electrical noise within the cable and from outside of the cable (e.g EMI, RFI).
- It offers speed or throughput of about 10 to 100 Mbps.
- It supports maximum segment of length about 100 meters.
- Each pair of wires in STP cable is wrapped in an overall metallic foil usually 150 Ohm cable.
- In STP, attenuation is low when compared to UTP.
- STP is mainly used for connection of enterprises over a long distance.
- In STP, generation of crosstalk is quite less when compared to UTP.
- STP is costlier than UTP.
- In STP, grounding cable is required.
- It combines techniques of shielding, cancellation and wire twisting.
Also Read: Difference Between Twisted Pair Cable, Coaxial Cable And Fibre Optic Cable
Difference Between Unshielded Twisted Pair UTP And Shielded Twisted Pair STP In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | UTP | STP |
| Electromagnetic Interference | Electromagnetic interference and noise is more in UTP. | STP cable reduce electrical noise within the cable and from outside of the cable (e.g EMI, RFI). |
| Speed | It offers speed or throughput of about 10 to 1000Mbps. | It offers speed or throughput of about 10 to 100 Mbps. |
| Distance | It offers maximum cable length of about 100 meters. | It supports maximum segment of length about 100 meters. |
| Characteristic | Each of the 8 individual copper wires in UTP cable is covered by insulating material. In addition, wires in each pair are twisted around each other. | Each pair of wires in STP cable is wrapped in an overall metallic foil usually 150 Ohm cable. |
| Attenuation | In UTP, attenuation is high when compared to STP. | In STP, attenuation is low when compared to UTP. |
| Application | UTP is widely used for data transmission within short distance and is very popular for home network connecting. | STP is mainly used for connection of enterprises over a long distance. |
| Crosstalk Generation | In UTP the generation of crosstalk is high when compared to STP. | In STP, generation of crosstalk is quite less when compared to UTP. |
| Cost | The cost of UTP is less when compared to that of STP. | STP is costlier than UTP. |
| Grounding | In UTP grounding cable is not required. | In STP, grounding cable is required. |