What Is BOOTP?
BOOTP stands for Bootstrap Protocol. BOOTP was originally defined as specification RFC 951 and was configured to replace the Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP), also referred to as RFC 903. BOOTP can be defined as a networking protocol used by a client for obtaining an IP address from a server.
When a computer that is connected to a network is powered up and boots its operating system, the system software broadcasts BOOTP messages onto the network to request an IP address assignment. A BOOTP configuration server assigns an IP address based on the request from a pool of addresses configured by an administrator.
BOOTP was intended for diskless systems because they require such a protocol in order to contact a server to obtain a network address and some information on which operating system to use. BOOTP operates only on IPv4 networks and is implemented using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as a transport protocol.
What You Need To know About BOOTP
- BOOTP stands for Bootstrap Protocol.
- BOOTP can only provide an IP to a computer while it is booting.
- BOOTP supports a limited number of client configuration parameters referred to as vendor extensions.
- BOOTP client do not rebind or renew configuration with the BOOTP server except when the system restarts.
- BOOTP uses a two-phase bootstrap configuration process in which clients contact BOOTP servers to perform address determination and boot file name selection and clients contact Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) servers to perform file transfer of their boot image.
- BOOTP has a 30 day lease on the IP address as a default.
- BOOTP does not support mobile machines.
- In BOOTP, manual-configuration takes place.
- Due to manual-configuration BOOTP is faced with errors.
- BOOTP does not provide temporary IP addressing.
- BOOTP provides the information to the diskless computer or workstation.
- BOOTP is not compatible with DHCP clients.
What Is DHCP?
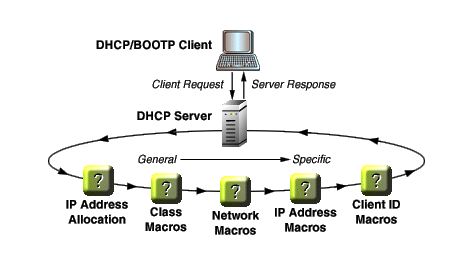
DCHP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. DHCP is a protocol that automatically assigns a unique IP address and other information to each host on the network so they can communicate efficiently with other endpoints. Therefore, no user configuration is required to connect to a DHCP-based network. In addition to the IP address, DCHP also assigns the subnet mask, default gateway address, domain name server (DNS) address and other pertinent configuration parameters.
The time it takes to connect via DCHP depends on the type of router and size of the network, but it usually takes around three to ten seconds. It also works perfectly for both wired and wireless connections. Due to its ease of use and widespread support, DCHP is the default protocol used by most routers and networking equipments.
What You Need To Know About DHCP
- DHCP stands for Dynamic host configuration protocol.
- DCHP can provide an IP when the OS is already loaded.
- DHCP supports a larger and extensible set of client configuration parameters referred to as options.
- DHCP clients do not require a system restart to rebind or renew configuration with the DHCP server.
- DHCP uses a single-phase boot configuration process whereby a DHCP client negotiates with a DHCP server to determine its IP address and obtain any other initial configuration details it needs for network operation.
- DHCP has eight-day lease duration for Microsoft and one day for Cisco routers.
- DHCP supports mobile machines.
- In DCHP, auto-configuration takes place.
- Due to auto-configuration in DHCP, it is immune to errors.
- DCHP provides temporary IP addressing for only limited amount of time.
- DCHP requires disks to store and forward the information.
- DHCP support BOOTP clients.
Also Read: Difference Between MAC Address And IP Address
BOOTP Vs DHCP In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | BOOTP | DHCP |
| Acronym For | BOOTP stands for Bootstrap Protocol. | DHCP stands for Dynamic host configuration protocol. |
| IP | BOOTP can only provide an IP to a computer while it is booting. | DCHP can provide an IP when the OS is already loaded. |
| Client Configuration | BOOTP supports a limited number of client configuration parameters referred to as vendor extensions. | DHCP supports a larger and extensible set of client configuration parameters referred to as options. |
| System Restart | BOOTP client do not rebind or renew configuration with the BOOTP server except when the system restarts. | DHCP clients do not require a system restart to rebind or renew configuration with the DHCP server. |
| Configuration Process | BOOTP uses a two-phase bootstrap configuration process in which clients contact BOOTP servers to perform address determination and boot file name selection and clients contact Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) servers to perform file transfer of their boot image. | DHCP uses a single-phase boot configuration process whereby a DHCP client negotiates with a DHCP server to determine its IP address and obtain any other initial configuration details it needs for network operation. |
| Lease | BOOTP has a 30 day lease on the IP address as a default. | DHCP has eight-day lease duration for Microsoft and one day for Cisco routers. |
| Mobile Machine Support | BOOTP does not support mobile machines. | DHCP supports mobile machines. |
| Configuration Type | In BOOTP, manual-configuration takes place. | In DCHP, auto-configuration takes place. |
| IP Addressing | BOOTP does not provide temporary IP addressing. | DCHP provides temporary IP addressing for only limited amount of time. |
| Possibility Of Errors | Due to manual-configuration BOOTP is faced with errors. | Due to auto-configuration in DHCP, it is immune to errors. |
| Storage Disk | BOOTP provides the information to the diskless computer or workstation. | DCHP requires disks to store and forward the information. |
| Compatibility With Clients | BOOTP is not compatible with DHCP clients. | DHCP support BOOTP clients. |