Learn the difference between Tendon and Ligament. The basis of comparison include: description, color of the connective tissue, categories, injuries, arrangement of fibers, collagen content, flexibility, structure, fibroblast among others.
Key Differences
Description
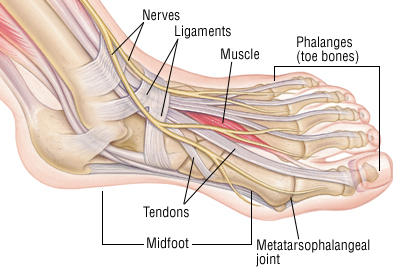
A tendon also known as sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Ligament on the other hand, is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also referred to as articular ligament, fibrous ligament, true ligament or articular larua.
Color of the Connective Tissue
Tendon is composed of white fibrous connective tissues whereas ligament is composed of yellow fibrous connective tissues.
Categories
Tendon is not categorized into any type, whereas, ligaments can be further categorized into three types: fetal remnant ligaments, periotoneal ligaments and articular ligaments.
Injuries
An injury in the tendon due to excessive pressure can be referred to as tendinitis, tenosynovitis or avulsion. Conversely, an injury in the ligament due to excessive pressure can be referred to as torn ligament or sprains.
Arrangement of Fibers
In tendon, fibers are arranged in dense, parallel bundles; however, ligaments have compactly arranged bundles of fibers, but not in parallel manner.
Significance
Tendons are a mechanism by which muscles connect to bone. Also due to their arrangement or connection, tendons are able to passively modulate forces during locomotion, providing additional stability with no active work.
Ligaments prevent the elbow joint from extending backward, it also provide similar range of motion control for other joints and more importantly, ligaments stabilize joints, so that bones stay properly aligned during movement.
Collagen content
Collagen content in tendons is more than in ligaments.
Presence
Tendons are found at the ends of the skeletal muscles, they are found throughout the body from the head and neck all the way down to the feet while ligaments are found in joints such the neck, shoulder, wrist, knee and spine.
Structure
Structurally, tendons are inelastic and tough, but ligaments are elastic and strong.
Flexibility
Tendons are less flexible in nature while ligaments are more flexible in nature.
Fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a cell in all connective tissues which produces collagen and other fibers. The fibroblasts of tendons lie in continuous raw whereas the fibroblasts of ligaments are scattered.
Proteoglycan
Proteoglycan are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. Proteoglycan content in tendons is way less than in ligaments.
Number
Tendon is usually one per muscles whereas ligaments are many per joint.
Blood supply
Tendons are characterized by heavy blood supply while ligaments’ blood supply is comparatively poor.
Differences Between Tendon And Ligament In Tabular Form
| Points Of Difference | Tendon | Ligament |
| Definition | A tendon also known as sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. | Ligament on the other hand, is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also referred to as articular ligament, fibrous ligament, true ligament or articular larua. |
| Significance | Tendons are a mechanism by which muscles connect to bone. Also due to their arrangement or connection, tendons are able to passively modulate forces during locomotion, providing additional stability with no active work. | Ligaments prevent the elbow joint from extending backward, it also provide similar range of motion control for other joints and more importantly, ligaments stabilize joints, so that bones stay properly aligned during movement. |
| Color Of Connective Tissue | Tendon is composed of white fibrous connective tissues. | Ligament is composed of yellow fibrous connective tissues. |
| Categories | Not categorized into any type. | Can be further categorized into three types: fetal remnant ligaments, periotoneal ligaments and articular ligaments. |
| Injury | An injury in the tendon due to excessive pressure can be referred to as tendinitis, tenosynovitis or avulsion. | An injury in the ligament due to excessive pressure can be referred to as torn ligament or sprains. |
| Arrangement of Fibers | Fibers are arranged in dense, parallel bundles. | Have compactly arranged bundles of fibers, but not in parallel manner. |
| Collagen Content | Collagen content is more than in ligaments. | Collagen Content is less than in tendons. |
| Presence | Found at the ends of the skeletal muscles, they are found throughout the body from the head and neck all the way down to the feet. | Found in joints such the neck, shoulder, wrist, knee and spine. |
| Structure | Are inelastic and tough. | Are elastic and strong. |
| Flexibility | Are less flexible in nature. | Are more flexible in nature. |
| Fibroblast | The fibroblasts of tendons lie in continuous raw. | The fibroblasts of ligaments are scattered. |
| Proteoglycan | Proteoglycan content in tendons is way less than in ligaments. | Proteoglycan content is more than in tendons. |
| Number | Tendon is usually one per muscles. | Ligaments are many per joint. |
| Blood Supply | Tendons are characterized by heavy blood supply. | Ligaments’ blood supply is comparatively poor. |
What are the similarities between Tendons and Ligaments?
- Both ligaments and tendons are made up of collagen and fibers.
- Both ligaments and tendons are connective tissues.
- Both tendons and ligaments are made up of living cells.
- Both tendon and ligament are part of the musculoskeletal system.
- Both ligament and tendon are greatly affected by injuries.
- All are important in the structural support and flexibility of muscles in the body.
Summary
A tendon also known as sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Ligament on the other hand, is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also referred to as articular ligament, fibrous ligament, true ligament or articular larua.