The heart is a pump that supplies all tissues and organs with oxygen rich blood. The heartbeat is caused by the heart muscles relaxing and contracting. The heart contains atria and the left ventricles that determine the phases of blood pressure; that is, diastolic and systolic blood pressures. Diastolic and systolic blood pressure can simply be defined as effects of blood being pumped throughout the body by the heart.
When the ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart, the blood pressure reaches its maximum value in the cycle and that can be referred to as systolic pressure. On other hand, when the ventricles relax and relax and get filled again with blood, the blood pressure reaches its minimum value in the cycle and this can be described as diastolic pressure.
Key Difference
Definition
Systolic pressure is the pressure exerted by your blood flowing through your arteries while diastolic pressure is the pressure the blood exerts within the arteries in between heartbeats, that is when the heart is not actively ejecting blood into the arteries.
Normal Range
In children normal systolic measurement is about 95 mmHg and in adults it ranges between 90-120 mmHg. Normal diastolic measurement is about 65 mmHg in children and ranges between 60-80 mmHg in adults.
Blood Pressure reading
When it comes to blood pressure readings, they are usually provided as a pair of numbers, the lower number is usually the diastolic blood pressure and it represents the minimum pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest. The higher number is the systolic blood pressure reading and it represents the maximum pressure exerted when the heart contracts.
Clinical Significance
Systolic blood pressure is particularly important in monitoring blood pressure in adults because the pressure tends to rise with age as a result of hardening of the arteries. On the hand, diastolic readings are important in monitoring the blood pressure in younger individual.
Cardiovascular Risk
Systolic blood pressure measurements can be used to accurately predict the cardiovascular risk in both middle-aged and old-aged individuals. On the other hand, diastolic blood pressure can be used to understand better, the cardiovascular risk identified by systolic blood pressure.
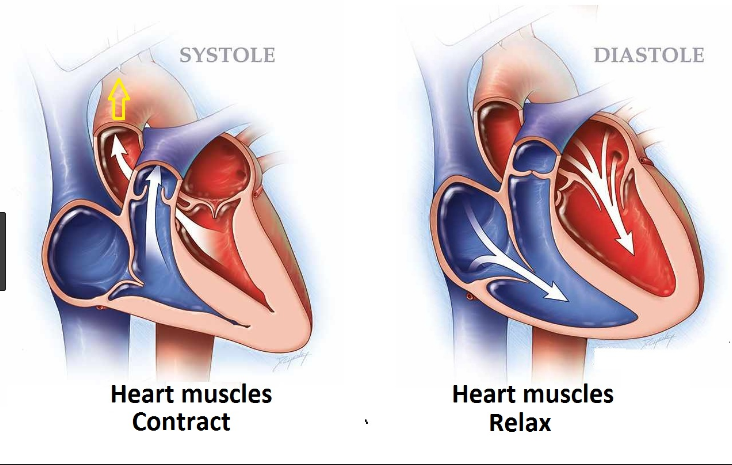
Ventricles of the heart
During the systolic phase, the left ventricle and blood vessel get contracted while in the diastolic phase, the left ventricle and blood vessel get relaxed.
Blood Vessels
During the systolic blood pressure, blood vessels contract while during the diastolic blood pressure blood vessels relax.
Indication
Systolic blood pressure indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls when the heart beats while diastolic blood pressure indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
Difference Between Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressures
| Basis of Comparison | Systolic | Diastolic |
| Definition | Is the pressure exerted by your blood flowing through your arteries and vessels while the heart beats. | Is the pressure the blood exerts on the walls of the arteries while the heat is resting (relaxed) between beats. |
| Blood Pressure | Systolic indicates the maximum pressure exerted on the arteries and vessels. | Diastolic represents the minimum pressure in the arteries. |
| Normal Range | Adults (90-120 mmHg) Infants (95-100 mmHg) | Adults 60-80 mmHg Infants 65 mmHg |
| Changes With Age | Increases | Decreases |
| Blood Vessel | Contracts | Relaxes |
| Behavior of Ventricles | At systolic phase, the left ventricle gets contracted | At diastolic phase, the left ventricle gets relaxed. |
| Blood pressure Reading | The higher number is systolic pressure. | The lower number is diastolic pressure. |
| Cardiovascular risk | Systolic blood pressure measurements can be used to accurately predict the cardiovascular risk in both middle-aged and old-aged individuals | Diastolic blood pressure can be used to understand better, the cardiovascular risk identified by systolic blood pressure |
| Clinical Significance | Systolic blood pressure is particularly important in monitoring blood pressure in adults because the pressure tends to rise with age as a result of hardening of the arteries. | Diastolic readings are important in monitoring the blood pressure in younger individual. |
Summary
The level of blood pressure depends on the activity of the heart and the elasticity of the arteries and for this reason, the measurements of a person’s blood pressure is recorded as two different numbers, the systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure.

The comparison table really made this page zing! Lots of information into a very tight space. Interesting…!!