Sensory Neuron
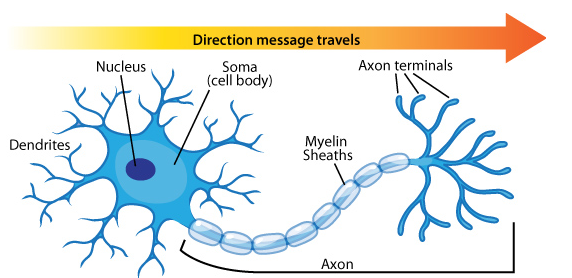
Sensory neurons also referred to as afferent neurons, are nerve cells within the nervous system responsible for converting external stimuli from an organism’s environment into internal electrical impulses. The sensory information travels along afferent nerve fibers in an afferent or sensory nerve to the brain through the spinal cord. The stimuli can come from outside the body example light and sound or from inside the body for example bloods pressure or the sense of body position.
Motor Neuron
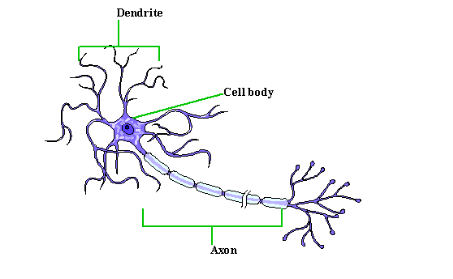
A motor neuron also referred to as motoneuron, is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands.
The Difference
- Motor neuron facilitates muscle contraction and modifies proprioceptive sensitivity. On the other hand, sensory neurons convert external stimuli from the organism’s environment into internal electrical impulse.
- Motor neurons carry motor impulses from the central nervous system to specific effectors whereas Sensory neurons bring impulse from sensory organs to the central nervous system.
- The cell body of the motor neuron is located in the ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord and consists of dendrites. On the other hand, cell body of the sensory neuron is situated in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord and no dendrites are found in it.
- Motor neurons follow efferent pathways whereas sensory neurons follow afferent pathways.
- An adult averagely half million of motor neurons whereas an adult has an average of 10 million sensory neurons.
- Motor neurons are multipolar whereas sensory neurons are unipolar.
- Motor neurons are mainly found in muscles and glands whereas sensory neurons are found in the skin, eyes, ears, tongue and nose.
- Motor neuron has efferent fiber whereas sensory neuron has afferent fiber.
- Motor neuron consists of many short dendrons whereas sensory neuron consists of one long dendron.
- Motor neurons do not have a receptor whereas sensory neurons have a receptor.
- Motor neurons consist of a long axon whereas sensory neuron consists of a short axon.
- Motor neurons do not generate commands to communicate with muscles but receive from sensory neurons.
Also Read: Difference Between Myelinated And Unmyelinated Neurons
Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neuron In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | MOTOR NEURON | SENSORY NEURON |
| Function | Motor neuron facilitates muscle contraction and modifies proprioceptive sensitivity. | Sensory neurons convert external stimuli from the organism’s environment into internal electrical impulse. |
| Role | Carry motor impulses from the central nervous system to specific effectors. | Bring impulse from sensory organs to the central nervous system. |
| Cell Body Location | The cell body is located in the ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord and consists of dendrites. | Cell body is situated in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord and no dendrites are found in it. |
| Pathways | Follow efferent pathways. | Follow afferent pathways. |
| Number | An adult averagely half million of motor neurons. | An adult has an average of 10 million sensory neurons. |
| Polarity | Motor neurons are multipolar. | Sensory neurons are unipolar. |
| Presence | Found in muscles and glands. | Found in the skin, eyes, ears, tongue and nose. |
| Fiber | Has efferent fiber. | Has afferent fiber. |
| Length Of Dendron | Consists of many short dendrons. | Consists of one long dendron. |
| Receptor | Do not have a receptor. | Have a receptor. |
| Axon Length | Consist of a long axon. | Consists of a short axon. |
| Command Generation | Motor neurons do not generate commands to communicate with muscles but receive from sensory neurons. | Sensory neurons do generate commands. |
Also Read: Difference Between Axon And Dendrite