Transpiration is the process in which plants lose water in the form of moisture or water vapor. Parts of plant like stem, small pores on leaves and flowers evaporate the water to the atmosphere. 90% of the transpiration occurs through foliar surface or surface of leaves. Types of transpiration include: stomatal, lenticular and cuticular transpiration. Below are is a detailed explanation of how they differ from one another.
Lenticular Transpiration
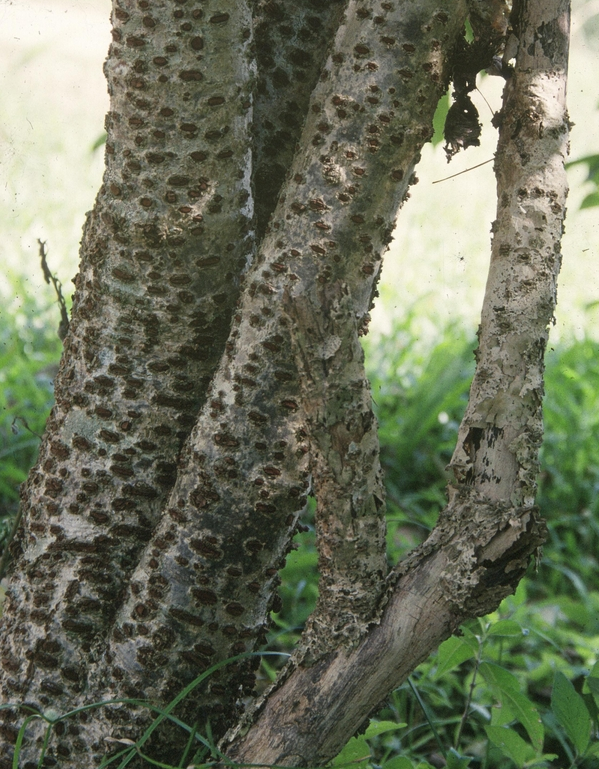
During secondary growth, the periderm replaces the epidermis in the protective function. The deadcork cells with suberised walls are partly impervious to gases. Therefore, gaseous exchange between the internal living cells and outer atmosphere becomes difficult. Some pores which look like lens-shaped raised spots on the surface of the stem now develop and take up the function of gaseous exchange. These pores are referred to as Lenticels and therefore when vapor get out through these minute pores, the process is then referred to as Lenticular Transpiration or Lenticellate .
Therefore, Lenticular transpiration can be described as loss of water in form of vapor through the lenticels. This type of transpiration is found in woody branches of trees and accounts for about 3% of the total transpiration. It occurs throughout the day and night.

Stomatal Transpiration
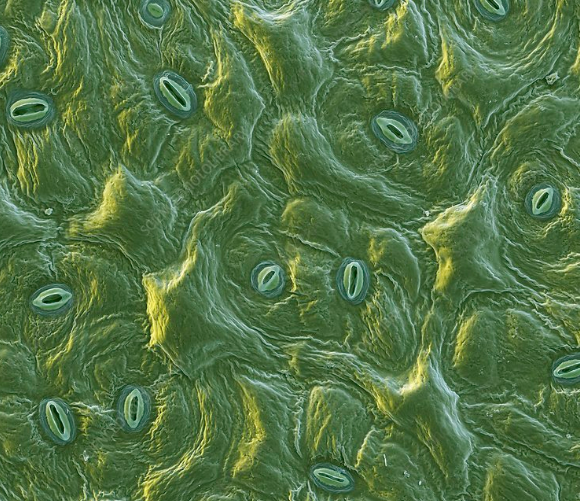
Stomatal transpiration is the loss of water in the form of vapor through specialized pores in the leaves referred to as stomata. Stomatal transpiration is the main type of transpiration in higher plants, it accounts for around 80-90% of the total water loss from plants. The stomata are found mostly on the upper or lower epidermis of leaves. A few of them occur on the young stems, flowers and fruits. Almost all land plants have stomata.
Stomata have two main functions. First is gaseous exchange i.e intake of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen. Second is facilitating the process of transpiration. The stomata pore is formed by a pair of cells referred to as guard cells. These guard cells regulate loss of water through opening and closing of the stomata.
Cuticular Transpiration

Cuticular transpiration is the loss of water in form of vapor in plants through the cuticle. Water vapor directly diffuses through the cuticle on leaves and escape to the atmosphere. The cuticle is an impermeable, waxy or resinous layer of cutin, a fatty substance, covering the outside (epidermis) of leaves and stems of plants. The thickness of the cuticle varies from one plant species to another.
Cuticular transpiration accounts for only about 5-10% of the total water loss from leaves. In herbaceous shade loving plants where the cuticle is very thin, the cuticular transpiration may be upto 50% of the total. Cuticular transpiration rate can be higher than stomatal transpiration during extreme dry conditions due to stomatal closure. On the contrary, in plants having leaves with thin cutin cover, loss of water can be significantly higher under conditions that favor high rate of transpiration. Just like lenticular transpiration, cuticular transpiration continues throughout day and night.
Also Read: Difference Between Stomata And Lenticels
Difference Between Lenticular, Stomatal And Cuticular Transpiration In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | LENTICULAR TRANSPIRATION | STOMATAL TRANSPIRATION | CUTICULAR TRANSPIRATION |
| Description | It is the loss of water in form of vapor through the lenticels. | It is the loss of water in the form of vapor through the stomata. | It is the loss of water in form of water vapor through the cuticle. |
| Occurrence | It occurs throughout the day and night. | It occurs only during day time. | Cuticular transpiration continues throughout day and night. |
| Percentage | It accounts for about 3% of the total transpiration. | Stomatal transpiration is the main type of transpiration in higher plants, it accounts for around 80-90% of the total water loss from plants. | Cuticular transpiration accounts for only about 5-10% of the total water loss from leaves. |
| Presence of The main Structure | Lenticels are present in woody stems, twigs and fruits. | Stomata are found in the epidermis of leaves and young stems. | Cuticles are found in leaves and outmost layer of stems. |
Also Read: Difference Between Stomata And Hydathodes
Comments are closed.