Key Differences
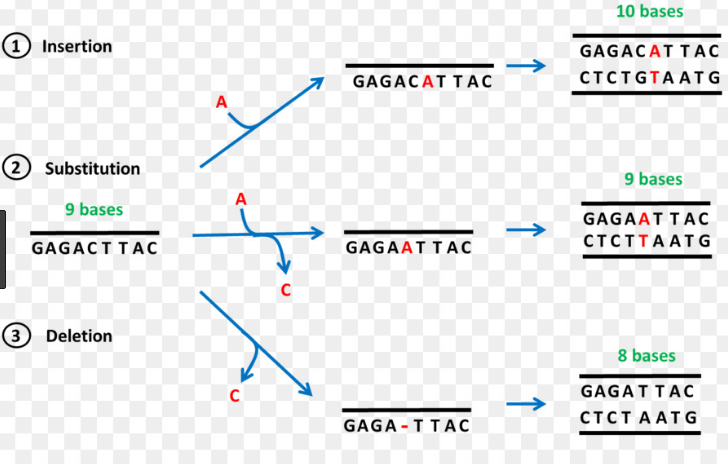
Point Mutations
A point mutation is a type of mutation in the cell’s genetic material, whereby one single nucleotide base is added, deleted or changed from a sequence of DNA or RNA. The deletion or insertion causes the DNA or RNA to be different from normal or wild type gene sequence. The nucleotide bases include cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine (in DNA) and Uracil (in RNA).
Point mutations are sometimes caused by mutations that spontaneously occur during DNA replication. the chances of mutations may be high when a cell is exposed to certain environmental factors such as ultraviolet light, X-rays, extreme heat or certain chemical carcinogens like aflatoxin B1 and benzene.
Point mutations can have three effects:
- The base substitution can be a silent mutation whereby the altered codon corresponds to the same amino acid.
- The base substitution can be a missense mutation whereby the altered codon corresponds to a different amino acid.
- The base substitution can be a nonsense mutation whereby the altered codon corresponds to a stop signal.
Point mutation can cause diseases such as:
- Tay–Sachs disease, a disease that causes nerve cells to deteriorate over time, which in turn results to decline of physical and mental functioning.
- Sickle-Cell-Anemia, a disease that results in thin sickle-shaped blood cells that sometimes cannot carry oxygen properly.
- Cyst Fibrosis- cyst fibrosis is associated with thick mucus in the lungs and trouble breathing, salty sweat, infertility in certain individuals and a shortened life expectancy.
Frameshift Mutation
Frameshift mutations are insertions or deletions in the genome that are not in multiples of three nucleotides. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame, resulting in a completely different translation from the original.
Now, what is important is number three or what is called multiples of three, because the cell reads a gene in groups of three bases. In frameshift mutation, the number of bases that are either added or subtracted can’t be in multiples of three or can’t be divisible by three. Given that frameshift mutation disrupts these ‘’multiple three’’ reading frame, the wrong amino acid will be put in place, and therefore the entire DNA sequence will be disrupted or read incorrectly.
Diseases caused by frameshift mutations in genes include Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), familial hypercholesterolaemia and some forms of cancer.
Difference Between Point Mutation And Frame Shift Mutation In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | POINT MUTATION | FRAMESHIFT MUTATION |
| Description | A point mutation is a type of mutation in the cell’s genetic material, whereby one single nucleotide base is added, deleted or changed from a sequence of DNA or RNA. | Frameshift mutations are insertions or deletions in the genome that are not in multiples of three nucleotides. |
| Occurrence | Occur due to alterations in the single nucleotide. | Occur due to alterations in numerous nucleotides. |
| Changes | It results to changes in the structure of a gene because of the substitutions with another base pair. | It results to changes in the number of nucleotides due to either insertions or deletions of the nucleotides. |
| Nucleotides Involved | Involves single nucleotide alterations. | Involve alterations in several nucleotides. |
| Diseases Associated With The Mutation | Sickle-Cell Anemia, Cyst Fibrosis and Tay-Sachs. | Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), familial hypercholesterolaemia and some forms of cancer. |
Similarities Between Point Mutation And Frameshift Mutation
- Both point mutation and frameshift mutation are involved in the production of non-functional proteins.
- In order to maintain a point mutation or a frameshift mutation, each alteration should be replicated.