We’ve all heard the terms (heart attack and cardiac arrest); and each one signifies a health crisis involving the heart. But heart attack and cardiac arrest aren’t the same thing. They’re two different medical emergencies with radically different causes and treatments and therefore, understanding the difference between them is incredibly important.
A heart attack is when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked. The heart muscle is robbed of its vital blood supply and, if left untreated, will begin to die because it is not getting enough oxygen. A cardiac arrest is an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes it to stop beating entirely.
What is a heart attack?
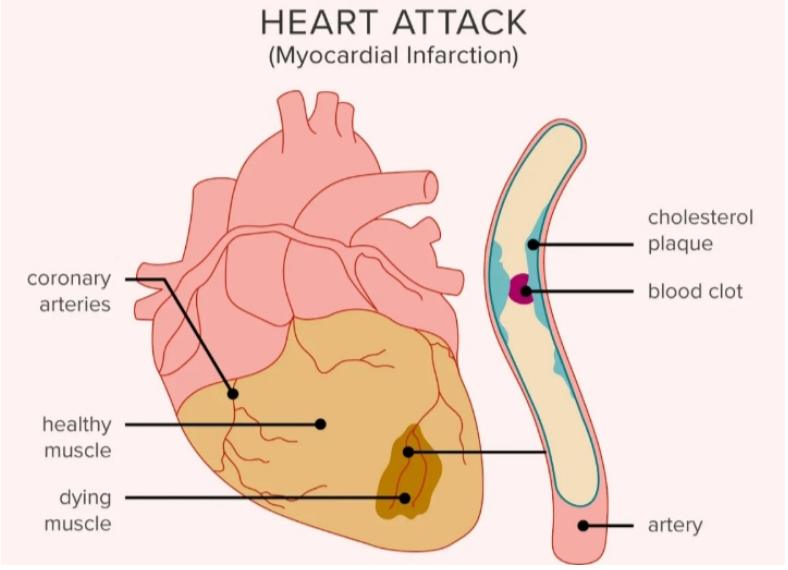
A heart attack occurs when a blocked artery prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching a section of the heart. If the blocked artery is not reopened quickly, the part of the heart normally nourished by that artery begins to die. The longer a person goes without treatment, the greater the damage.
A heart attack is a life threatening medical emergency. The sooner you can get medical treatment that restores normal blood flow to your heart, the better your chance of a successful outcome.
Symptoms include tightness or pain in the chest, neck, back or arms, as well as fatigue, lightheadedness, abnormal heartbeat and anxiety. Women are more likely to have atypical symptoms than men. Some heart attacks are sudden and intense. But most start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort.
What is cardiac arrest?
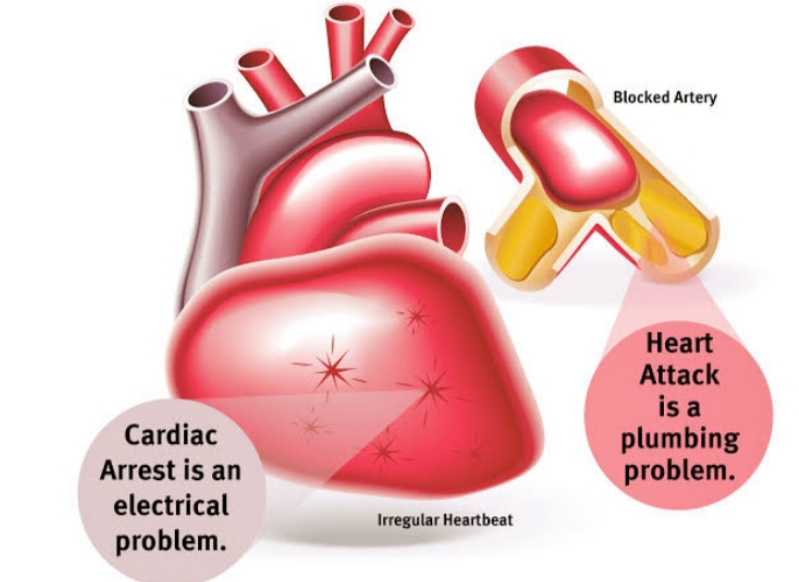
A cardiac arrest is an electrical problem. The electrical circuit to your heart goes out–it’s like a black out. It starts when the electrical signals that control the timing and the organisation of the heartbeat become chaotic and then the heart suddenly stops pumping. Without blood pumping to the brain, loss of consciousness and death occurs.
A cardiac arrest happens suddenly, usually without warning, when the heart stops pumping blood around the body. A person can fall unconscious and die within minutes if they do not receive immediate treatment.
Many cardiac arrests occur because a person has had a heart attack, which causes an abnormal heart rhythm, known as arrhythmia.
A common cause of cardiac arrest is an arrhythmia called ventricular fibrillation (VFib). VFib happens when the heart’s electrical circuitry becomes chaotic. Instead of beating, the heart fibrillates, meaning that it quivers.
In most cases, the first symptom of a cardiac arrest is loss of consciousness. Sometimes, a person experiences warning signs of a cardiac arrest within the hour before the cardiac arrest. Also sometimes cardiac arrest can be triggered by another traumatic event, like drowning, electrocution, drug abuse, and even a heart attack.
Heart Attack vs Cardiac Arrest: Key Differences
| Heart Attack | Cardiac Arrest |
| Heart attacks usually occur due to the blockage of a coronary artery in the heart. | Cardiac Arrests usually occur when the heart stops beating due to certain reasons. |
| The primary cause for getting heart attacks is due to the blood clots that occur in the arteries. | Cardiac arrests cause the stopping of the heart, leading to heart failure primarily due to Ventricular fibrillation. |
| Heart attacks may be caused due to a variety of different factors including drowning, shock, hypothermia etc. | Cardiac arrests, on the other hand, can also occur due to heart attacks. |
| Symptoms of a heart attack are chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing and coughing. | Symptoms of a cardiac arrest are unconsciousness, shortness of breath and no pulse |
| Heart attack victims are usually smokers and people with unhealthy diets. | Cardiac arrest victims may also be overweight people and those without regular exercise. |
Key Takeaways
- A heart attack is when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked. The heart muscle is robbed of its vital blood supply and, if left untreated, will begin to die because it is not getting enough oxygen.
- A cardiac arrest is when a person’s heart stops pumping blood around their body and they stop breathing normally.
- Heart attacks can increase the risk for cardiac arrest because heart attacks can alter electrical signals in the heart. When cardiac arrest occurs suddenly with no other existing heart conditions, it’s more likely to be caused by a heart attack.