What Is A Travelling Wave Tube?
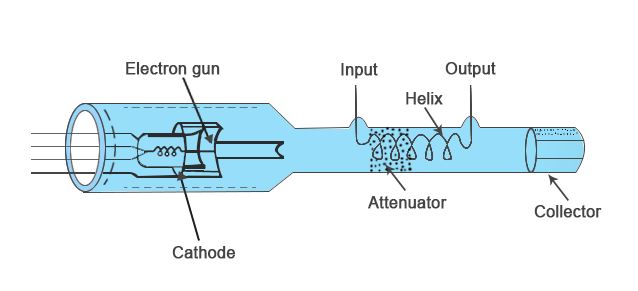
A travelling wave tube (TWT) is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. The TWT belongs to a category of ‘’linear beam’’ tubes, such as the Klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube.
There are several types of Travelling wave tube (TWT), the two major categories include:
- Helix TWT– In which the radio waves interact with the electron beam while travelling down a wire helix which surrounds the beam. These have wide bandwidth, but output power is limited to a few hundred watts.
- Coupled Cavity– In which the radio wave interact with the beam in a series of cavity resonators through which the beam passes. These function as narrowband power amplifiers.
What You need To know About A Travelling Wave Tube
- The interaction of an electron beam and EM field in the TWT is continuous over the entire length of circuit.
- In travelling wave tube, the microwave circuit is non-resonant.
- The wave in the TWT is the propagating wave.
- Travelling wave tube uses non-resonant wave circuits for input and output and is a wide band device.
- In coupled cavity TWT, coupling effect takes place between cavities.
- Travelling wave tube does not have resonant cavity. It uses helix structure.
- Travelling wave tube has wider bandwidth of operation.
- TWT operates on lower efficiency.
- Travelling wave has high power output.
- There two types of TWT, that is, helix and coupled cavity.
- Frequency of operation is from 300MHz to 50 GHz.
- Has a long life when compared to klystron.
- Handles CW power upto 200Watt.
What Is Klystron?
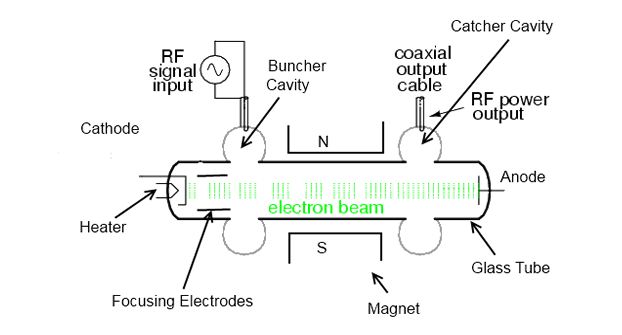
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. It was invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian from university of Stanford. Klystrons are velocity-modulated tubes and used in radars as amplifiers or oscillators. They are also used in satellite systems and television broadcast as well as particle accelerators and medicine. The UHF region range of klystron amplifiers ranges from 300 MHz-3 GHz to 400 GHz.
Klystron can be categorized into two types depending on the cavities. The types include:
- Two-cavity klstron amplifier
- Reflex klystron amplifier
What You need To know About Klystron
- Interaction of the electron in the klystron occurs only at the gaps of a few resonant cavities.
- Klystron circuit is a resonant type.
- The wave in klystron is not propagating wave.
- Klystron uses cavities for input and output circuits and is a narrow band device.
- In klystron, each cavity operates independently and there is no mutual coupling.
- Klystron has resonant cavities.
- Klystron has smaller bandwidth of operation.
- Klystron has comparatively high efficiency.
- Klystron tube has low power output.
- There are two types of klystron, that is, Two or multi-cavity and reflex klystron.
- Frequency of operation is from 4 GHz to 200GHz.
- Has a short life when compared to TWT.
- Handles power of 1mW to 2.5W.
Difference Between Travelling Wave Tube And Klystron In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | TRAVELLING WAVE TUBE (TWT) | KLYSTRON |
| Interaction Of Electron | The interaction of an electron beam and EM field in the TWT is continuous over the entire length of circuit. | Interaction of the electron in the klystron occurs only at the gaps of a few resonant cavities. |
| Type of Microwave Circuit | The microwave circuit is non-resonant. | Its microwave circuit is a resonant type. |
| Type Of Wave | The wave in the TWT is the propagating wave. | The wave in klystron is not propagating wave. |
| Input And Output | Travelling wave tube uses non-resonant wave circuits for input and output and is a wide band device. | Klystron uses cavities for input and output circuits and is a narrow band device. |
| Cavities | In coupled cavity TWT, coupling effect takes place between cavities. | In klystron, each cavity operates independently and there is no mutual coupling. |
| Bandwidth | It has wider bandwidth of operation. | It has smaller bandwidth of operation. |
| Efficiency | TWT operates on lower efficiency. | It has comparatively high efficiency. |
| Power Output | Travelling wave has high power output. | Travelling wave has high power output. |
| Types | There two types of TWT, that is, helix and coupled cavity. | There are two types of klystron, that is, Two or multi-cavity and reflex klystron. |
| Frequency | Frequency of operation is from 300MHz to 50 GHz. | Frequency of operation is from 4 GHz to 200GHz. |
| Life Span | Has a long life when compared to klystron. | Has a short life when compared to TWT. |
| Power | Handles CW power upto 200Watt. | Handles power of 1mW to 2.5W. |