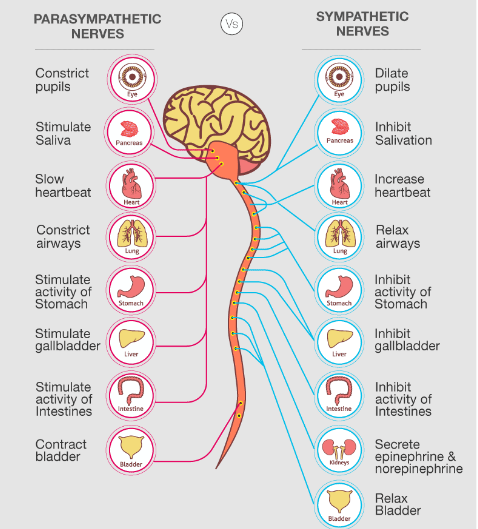
The reflex or involuntary functions in the body are regulated by a part of peripheral nervous system referred to as Autonomous Nervous system (ANS). The ANS controls the activities of organs and various involuntary muscles such as heart muscles, intestine, stomach and smooth muscles. The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) can be categorized into two:
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS or PSNS)
The Sympathetic Nervous System originates from the spinal cord of the thoracic and lumbar region. The SNS is involved in the stimulation of activities that prepare the body for action such as increasing the release of sugar from the liver into the blood, increasing the heart rate and other general responses considered to be ’’fight or flight’’ (responses that prepares one to fight off or retreat from danger).
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) on the other hand, originates from the spinal cord and medulla. The PNS stimulates the salivation, digestion, digestion, defecation, urination and lacrimation.
Facts About Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Parasympathetic nervous system originates from the cranial and sacral regions of the central nervous system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system originates from the cranial and sacral regions of the central nervous system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) relaxes the body and inhibits high energy functions.
- The action of parasympathetic nervous system is slow response.
- Ganglions of the parasympathetic nervous system are found away from the central nervous system but close to the effector.
- Parasympathetic nervous system increases the urinary output and relaxes the rectum.
- Parasympathetic nervous system ha s no action on the adrenaline gland.
- Parasympathetic nervous system generates an inhibitory homeostatic effect.
- The size of the post-ganglionic fibers is short in the parasympathetic nervous system.
- A small number of post-ganglionic fibers are found in the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system covers a small area in the body.
- The pre-ganglionic fibers are long in the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system generates a localized effect at the target area.
- Parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart beat, blood level and metabolic rate.
- Parasympathetic nervous decreases the activity of the digestive system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system has no effect on the glycogen breakdown.
- Parasympathetic nervous system constricts the bronchial tubules.
- Parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the secretion of saliva.
- Parasympathetic nervous system restores the sensory awareness to the normal level.
- At the effector, the Acetylcholine is released by the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the pupil of the eyes.
Facts About Sympathetic Nervous System
- Sympathetic Nervous system originates from cranial, thoracic and lumbar regions of the central nervous system.
- Sympathetic Nervous system originates from cranial, thoracic and lumbar regions of the central nervous system.
- Sympathetic nervous System (SNS) prepares the body for intense physical activity.
- The action of sympathetic nervous is a quick response.
- Ganglions of the sympathetic nervous system are found close to the central nervous system.
- Sympathetic nervous system decreases the urinary output and contracts the rectum.
- The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the production of adrenaline from adrenaline glands.
- Sympathetic nervous system generates an excitatory homeostatic effect.
- The size of the post-ganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system is long.
- A large number of the post-ganglionic fibers are found in the sympathetic nervous system.
- The sympathetic nervous system covers a large area in the body.
- The pre-ganglionic fibers are short in the sympathetic nervous system.
- The sympathetic nervous system generates a diffuse effect at its target area.
- Sympathetic nervous system increases heart beat, blood level and metabolic rate.
- Sympathetic nervous system increases the activity of the digestive system.
- Sympathetic nervous system increases the rate of breakdown of glycogen.
- The sympathetic nervous system dilates the bronchial tubules.
- The sympathetic nervous system inhibits saliva secretion.
- The sympathetic nervous system raises the sensory awareness.
- The sympathetic nervous system releases Noradrenaline at the effector.
- The sympathetic nervous system dilates the pupil of the eye.
Difference Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM | SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM |
| Point Of Origin | Originates from the cranial and sacral regions of the central nervous system. | Originates from cranial, thoracic and lumbar regions of the central nervous system. |
| Role | Relaxes the body and inhibits high energy functions. | Prepares the body for intense physical activity. |
| The Action | The action is slow response. | The action is a quick response. |
| Ganglions Location | Ganglions of the parasympathetic nervous system are found away from the central nervous system but close to the effector. | Ganglions of the sympathetic nervous system are found close to the central nervous system. |
| Effect on the Urinary Output And Rectum | Increases the urinary output and relaxes the rectum. | Decreases the urinary output and contracts the rectum. |
| Effect on Adrenaline Gland | Ha s no action on the adrenaline gland. | Stimulates the production of adrenaline from adrenaline glands. |
| Kind Of Homeostatic Effect | Generates an inhibitory homeostatic effect. | Generates an excitatory homeostatic effect. |
| Size Of Post-ganglionic Fibers | The size of the post-ganglionic fibers is short in the parasympathetic nervous system. | The size of the post-ganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system is long. |
| Effect On Target Area | Parasympathetic nervous system generates a localized effect at the target area. | The sympathetic nervous system generates a diffuse effect at its target area. |
| Number Of Post-ganglionic | A small number of post-ganglionic fibers are found in the parasympathetic nervous system. | A large number of the post-ganglionic fibers are found in the sympathetic nervous system. |
| Body Coverage | Covers a small area of the body. | Covers a large area of the body. |
| The Size Of Pre-ganglionic Fibers | The pre-ganglionic fibers are long in the parasympathetic nervous system. | The pre-ganglionic fibers are short in the sympathetic nervous system. |
| Effect On Metabolic Rate, Heat Beat And Blood Level | Decreases heart beat, blood level and metabolic rate. | Increases heart beat, blood level and metabolic rate. |
| Effect On The Digestive System | Decreases the activity of the digestive system. | Increases the activity of the digestive system. |
| Effect On Glycogen Breakdown | Has no effect on the glycogen breakdown. | Increases the rate of breakdown of glycogen. |
| Effect On Bronchial Tubules | Constricts the bronchial tubules. | Dilates the bronchial tubules. |
| Effect On Secretion Of Saliva | Stimulates the secretion of saliva. | Inhibits saliva secretion. |
| Sensory Awareness | Restores the sensory awareness to the normal level. | Raises the sensory awareness. |
| What Is Released At The Effector | At the effector, the Acetylcholine is released by the parasympathetic nervous system. | The sympathetic nervous system releases Noradrenaline at the effector. |
| Effect On The Pupil Of The Eye | Stimulates the pupil of the eyes. | Dilates the pupil of the eye. |
Similarities Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are part of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS).
- Both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system play a role in maintain balance of body systems (homeostasis).
- Both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are made of pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic neurons.
- Both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems originate from the spinal cord.
- Both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems regulate physiological processes of the body such as urination, reproduction, respiration, circulation and digestion.