What Is Real Image?
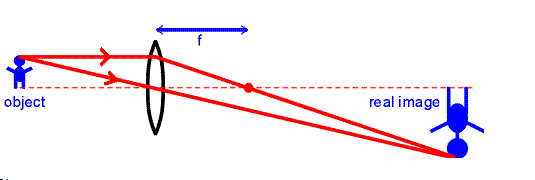
A real image can be described as the image produced by the reflection or refraction when the light rays arising from the object converge at a point before a mirror or lens. A real image can be projected onto the screen.
Examples of real images include the image seen on a cinema screen (the source being the projector), the image produced on a detector in the rear of a camera and the image produced on an eyeball retina. Real images can be produced by concave mirrors and converging lenses only if the object is placed further away from the mirror/lens than the focal point and this real image is inverted. As the object approaches the focal point the image approaches infinity and when the object passes the focal point the image becomes virtual and is not inverted.
What You Need To Know About Real Image
- A real image can be described as the image produced by the reflection or refraction when the light rays arising from the object converge at a point before a mirror or lens.
- Real images are formed due to the actual intersection of light rays.
- Real images are inverted.
- The real image is produced by actual intersection of the rays of light. Hence they can be captured on the screen.
- The concave mirror is used in producing a real image.
- The converging lens is used to form a real image.
- A real image is formed on the same side of the object.
- Image developed on the photographic film of a camera is an example of a real image.
- The light rays diverge from the same side of the mirror after converging and forming the real image.
What Is Virtual Image?
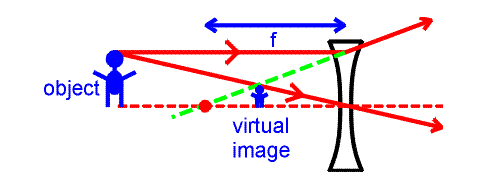
A virtual image can be described as an image produced when the light rays originating from an object appear to strike at a certain point. In a virtual image, the rays never really converge at a real point. They only appear to have converged based on their diverging path. A virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen because the apparent point of convergence (focus) isn’t real. A virtual image can be viewed through a lens or in a mirror, but it cannot be projected on a screen or recorded without additional optical elements.
A plane mirror forms a virtual image if the object between its principal focus and the pole of the mirror. A convex lens also produces a virtual image when the object is kept between the principal focus and its optic center. Since the virtual images are due to imaginary rays, they are drawn using broken lines. Examples of virtual images include: Image formed in a plane mirror, image formed on the front and back surfaces of a spoon.
What You Need To Know About Virtual Image
- A virtual image can be described as an image produced when the light rays originating from an object appear to strike at a certain point.
- Virtual images are formed due to the imaginary intersection of light rays.
- Virtual images are erect or upright.
- Virtual image is produced by an imaginary intersection of the rays of light and hence cannot be cast on screen.
- Virtual images are produced by a plane mirror, convex mirror and sometimes concave mirror.
- A virtual image is produced with the help of a diverging lens.
- A virtual image is formed on the backside of the mirror.
- Image developed by a plane mirror is an example of a virtual image.
- The light rays assumed to diverge from a point somewhere behind the mirror.
Also Read: Difference Between Convex And Concave Mirror
Difference Between Real And Virtual Image In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | REAL IMAGE | VIRTUAL IMAGE |
| Description | A real image can be described as the image produced by the reflection or refraction when the light rays arising from the object converge at a point before a mirror or lens. | A virtual image can be described as an image produced when the light rays originating from an object appear to strike at a certain point. |
| Image Formation | Real images are formed due to the actual intersection of light rays. | Virtual images are formed due to the imaginary intersection of light rays. |
| Nature Of Image | Real images are inverted. | Virtual images are erect or upright. |
| Image Production | The real image is produced by actual intersection of the rays of light. Hence they can be captured on the screen. | Virtual image is produced by an imaginary intersection of the rays of light and hence cannot be cast on screen. |
| Mirror | The concave mirror is used in producing a real image. | Virtual images are produced by a plane mirror, convex mirror and sometimes concave mirror. |
| Lens | The converging lens is used to form a real image. | A virtual image is produced with the help of a diverging lens. |
| Image Formation | A real image is formed on the same side of the object. | A virtual image is formed on the backside of the mirror. |
| Examples | Image developed on the photographic film of a camera is an example of a real image. | Image developed by a plane mirror is an example of a virtual image. |
| Light Rays | The light rays diverge from the same side of the mirror after converging and forming the real image. | The light rays assumed to diverge from a point somewhere behind the mirror. |