Xylem and phloem are the major conducting tissues in vascular plants. The main function of xylem is conduction of water and minerals towards the apical shoot. Xylem tissues can be classified as primary and secondary xylem depending on where they originate. The primary xylem is the type of xylem that is produced from the primary growth whereas secondary xylem is the type of xylem that is produced from the secondary growth. Primary xylem can further be classified into Metaxylem and Protoxylem.
Both Metaxylem and Protoxylem are components of primary vascular bundle and are majorly involved in the conduction of water and minerals towards the apical shoot. More importantly, they are both produced by procambium and contain parenchyma, vessels and tracheids.
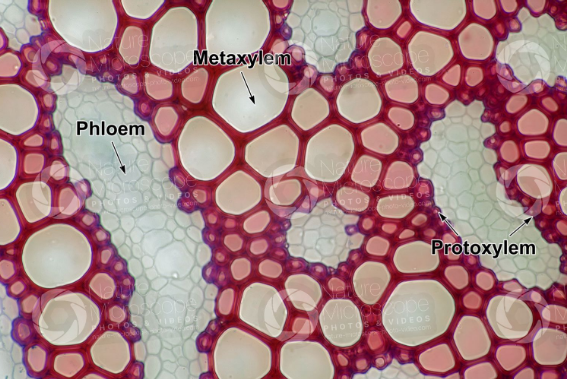
However, Metaxylem and Protoxylem differ extensively both in structure and function of their elements. Below is a detailed description of differences between Metaxylem and Protoxylem in a primary vascular bundle of a young stem. The Basis of comparison include: Formation, differentiation, tracheids, wall thickenings, Lignification, xylem fibres, water conduction efficiency, tylose formation and many more.
What You Need To Know About Protoxylem
- First formed part of xylem in the vascular bundles.
- In the root of vascular plants, Protoxylem occurs closest to the periphery of the root.
- The cells produced by the procambium differentiate into the Protoxylem.
- Protoxylem matures before the plant organs have completed their elongation.
- Lignification occurs in Protoxylem elements before the completion of elongation of the plants.
- The wall thickenings of conducting elements are of simple and primitive type (annular or spiral).
- The tracheids of protoxylems have a narrow lumen.
- Protoxylem is less efficient in conducting water than Metaxylem.
- Protoxylem is responsible for the formation of the lysigenous cavity in the monocot stem.
- Protoxylem contains a less amount of tracheids and a large amount of parenchyma.
- Formation of Tyloses does not happen in Protoxylem.
- Xylem fibers are absent in the Protoxylem.
- In the stem of vascular plants, Protoxylem is arranged towards the center.
- In majority of monocots, Protoxylem elements get crushed during growth and the area comes to have a cavity.
- Protoxylem elements are capable of being stretched.
What You Need To Know About Metaxylem
- Metaxylem is the xylem part formed after the Protoxylem.
- In the root of vascular plants, Metaxylem occurs closest to the center.
- The cells produced by the fascicular cambium differentiate into the Metaxylem.
- Matures after the completion of growth of the plant organ.
- Lignification occurs in the Metaxylem elements after the completion of elongation in the plant part.
- The wall thickenings are of complex and advanced type (reticulate, scalariform or pitted).
- The tracheids of Metaxylem have a wide lumen.
- Metaxylem is more efficient in conduction of water than Metaxylem.
- Metaxylem is never involved in the formation of the lysigenous cavity in monocots.
- Metaxylem contains a large number of tracheids and a less number of parenchyma.
- Tylose formation is very common in Metaxylem.
- Xylem fibers are very much present in the Metaxylem.
- In the stem of vascular plants, Metaxylem is arranged towards the exterior.
- In majority of monocots, Metaxylem elements do not get crushed during growth.
- Metaxylem cannot be stretched.
Protoxylem Vs Metaxylem In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PROTOXYLEM | METAXYLEM |
| Formation | First formed part of xylem in the vascular bundles. | It is the xylem part formed after the Protoxylem. |
| Occurrence | In the root of vascular plants, it occurs closest to the periphery of the root. | In the root of vascular plants, it occurs closest to the center. |
| Differentiation | The cells produced by the procambium differentiate into the Protoxylem. | The cells produced by the fascicular cambium differentiate into the Metaxylem. |
| Maturity | Matures before the plant organs have completed their elongation. | Matures after the completion of growth of the plant organ. |
| Lignification | Lignification occurs in Protoxylem elements before the completion of elongation of the plants. | Lignification occurs in the Metaxylem elements after the completion of elongation in the plant part. |
| Wall Thickenings | The wall thickenings of conducting elements are of simple and primitive type (annular or spiral). | The wall thickenings are of complex and advanced type (reticulate, scalariform or pitted). |
| Tracheids | The tracheids of protoxylems have a narrow lumen. | The tracheids of Metaxylem have a wide lumen. |
| Water Conduction Efficiency | It is less efficient in conducting water than Metaxylem. | It is more efficient in conduction of water than Metaxylem. |
| Formation Of Lysigenous Cavity | It is responsible for the formation of the lysigenous cavity in the monocot stem. | It is never involved in the formation of the lysigenous cavity in monocots. |
| Tracheid Vs Parenchyma Number | It contains a less amount of tracheids and a large amount of parenchyma. | It contains a large number of tracheids and a less number of parenchyma. |
| Tylose Formation | Formation of Tyloses does not happen in Protoxylem. | Tylose formation is very common in Metaxylem. |
| Xylem Fibers | Xylem fibers are absent in the Protoxylem. | Xylem fibers are very much present in the Metaxylem. |
| Arrangement In The Stem of Vascular Plants | In the stem of vascular plants, Protoxylem is arranged towards the center. | In the stem of vascular plants, Metaxylem is arranged towards the exterior. |
| Getting Crushed During Growth | In majority of monocots, Protoxylem elements get crushed during growth and the area comes to have a cavity. | In majority of monocots, Metaxylem elements do not get crushed during growth. |
| Flexibility | Protoxylem elements are capable of being stretched. | Metaxylem cannot be stretched. |
What Are Some Of The Similarities Between Protoxylem And Metaxylem
- Both contain tracheids, paremchyma and vessels.
- They both develop only in the primary vascular bundles.
- Both Protoxylem and Metaxylem contain dead and living.
- Both Metaxylem and Protoxylem develop from primary meristem and pro-cambium.
- They both can conduct minerals and water.
You May Also Read:
- Difference Between Primary Xylem And Secondary xylem
- Difference Between Metaphloem And Metaxylem
- Difference Between Vascular And Non-vascular Plants
Comments are closed.