What Is Land Breeze?
A land breeze is a local nighttime and early morning wind that occurs along coasts and blows offshore (from the land out to the sea). It arises at sunset when the sea surface is warmer than the adjacent land due to the land having a lower heat capacity and cooling off faster. It then continues into early morning hours until the heating of the day begins.
How Does A Land Breeze Occur?
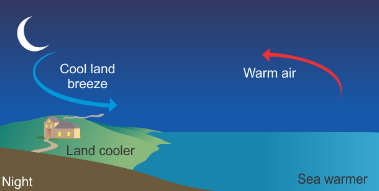
During the day, the sun heats land surface, but only to a depth of a few inches. When night comes around, the temperature of the land drops quickly because the surface no longer receives heating from the sun and heat is rapidly radiated back to the surrounding air.
Given that water retains more of its heat than land surfaces because of its higher heat capacity. The water along the shore becomes warmer than the coastal land, creating a net movement of air from the land surfaces toward the ocean.
What You Need To Know About Land Breeze
- Typically, when winds blow from high to low pressure areas, the cooler breeze that comes from the shore is what is referred to as land breeze.
- Land breeze is formed at nighttime.
- Land breeze comes from land.
- Land breezes are most common in autumn and winter due to the cooler nights.
- Land breezes’ pace span from 5 to 8 knots.
- Land breezes usually blow dry winds.
- The temperature might remain the same when the land breeze occurs.
- Land breezes influences weather, particularly when a strong change of wind direction occurs at night.
- Cooling of the air over land typically occurs within a shallower layer at night, the land breeze is shallower when compared to sea breeze.
- Due to temperature difference, land breezes are weaker when compared to sea breeze.
What Is A Sea Breeze?

A sea breeze or onshore breeze can be described as a coastal local wind that blows from sea to the land. It develops due to differences in air pressure created by the differing heat capacities of water and dry land. A sea breeze is common during spring and summer month because of the greater temperature difference between the ocean and nearby land, particularly in the afternoon when the land is at maximum heating from the sun.
How is A Sea Breeze Formed?
During the day, the sun heats up both the ocean surface and land. Water is a good absorber of the energy from the sun. The land absorbs much of the sun’s energy as well. However, water heats up much more slowly than land and therefore, the air above the land will be warmer compared to the air over the ocean. The warm air over the land will rise throughout the day, causing pressure at the surface.
Over the water, high surface pressure will form because of the colder air. To compensate, the air will sink over the ocean. The wind will blow from the higher pressure over the water to lower pressure over the land causing the Sea Breeze. The magnitude of the sea breeze will vary depending on the temperature difference between the land and ocean.
What You Need To Know About Sea Breeze
- Typically, when the denser air above the water moves to the space above the land.
- Sea breeze is formed at daytime.
- Sea breeze comes from water.
- Sea breezes are more often experienced during spring and summer because of the significant temperature differences between land and water.
- Sea breezes’ pace span from 10 to 20 knots.
- The sea breeze contains more amount of moisture due to the particles absorbed from the water bodies.
- Sea breeze tends to decrease the air temperature.
- Sea breezes are not often observed during winter.
- Sea breeze is deeper when compared to land breeze.
- Sea breezes are stronger than land breezes due to the bigger temperature difference.
Effects of sea breeze
- Sea breeze brings relief from oppressive hot weather
- It can trigger thunderstorms especially when the air carries moisture and it unstable.
- It brings changes to local air quality
- It allows moisture in the air
Also Read: Difference Between Transpiration And Evaporation
Difference Between Land Breeze And Sea Breeze In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | LAND BREEZE | SEA BREEZE |
| Description | Typically, when winds blow from high to low pressure areas, the cooler breeze that comes from the shore is what is referred to as land breeze. | Typically, when the denser air above the water moves to the space above the land. |
| Formation | Land breeze is formed at nighttime. | Sea breeze is formed at daytime. |
| Season Of Occurrence | Land breezes are most common in autumn and winter due to the cooler nights. | Sea breezes are more often experienced during spring and summer because of the significant temperature differences between land and water. |
| Origin | Land breeze comes from land. | Sea breeze comes from water. |
| Magnitude | Land breezes’ pace span from 5 to 8 knots. | Sea breezes’ pace span from 10 to 20 knots. |
| Winds | Land breezes usually blow dry winds. | The sea breeze contains more amount of moisture due to the particles absorbed from the water bodies. |
| Air Temperature | The temperature might remain the same when the land breeze occurs. | Sea breeze tends to decrease the air temperature. |
| Influence On Weather | Land breezes influences weather, particularly when a strong change of wind direction occurs at night. | Sea breezes are not often observed during winter. |
| Depth | Cooling of the air over land typically occurs within a shallower layer at night, the land breeze is shallower when compared to sea breeze. | Sea breeze is deeper when compared to land breeze. |
| Strength | Due to temperature difference, land breezes are weaker when compared to sea breeze. | Sea breezes are stronger than land breezes due to the bigger temperature difference. |