A turbine is a rotatory mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator. There are two types of turbine Impulse and reaction turbine.
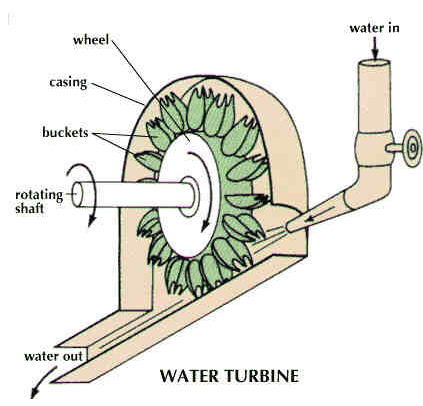
A reaction turbine is a turbine with rotating blades curved and arranged so as to develop torque from gradual decrease of steam pressure from inlet to exhaust. Usually, a pressure casement is needed to contain the working fluid as it acts on the turbine stages or the turbine must be fully immersed in the fluid flow as is the case with wind turbines. The work of the casing is to contain and direct the working fluid; and to maintain the suction imparted by the draft tube. Reaction turbines are most efficient to higher flow velocities or where upstream pressure (fluid head) is low.
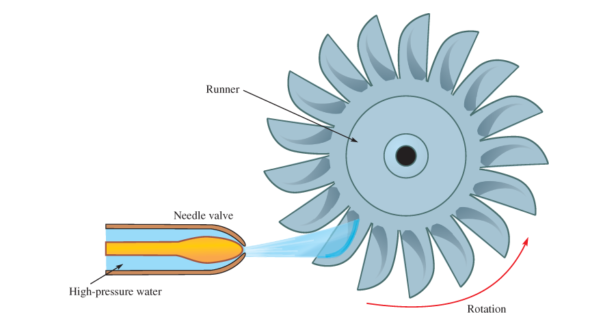
An Impulse turbine is a turbine that is driven by high velocity jets of water or steam from a nozzle directed on to the blades or buckets attached to a wheal. The resulting impulse spins the turbine and leaves the fluid flow with diminished kinetic energy. There is usually no pressure change of the fluid or gas in the turbine blades as is the case of a steam or gas turbine, all pressure drop takes place in the stationary blades (the nozzle). Impulse turbines are most efficient for use in cases where the flow is low and the inlet pressure is high.
The Difference
- In reaction turbine steam first flows through the guide mechanism and then flows through the moving blades whereas in impulse turbine, the steam flows through the nozzle and strikes on the moving blades.
- In Reaction turbine, the wheels must always run full; what this means is that fluid (gas, steam or water) must be injected in such a way that no gap is left in between wheel and the vanes. On the other hand, in impulse turbine, fluid (gas, water or steam) may or may not be injected full on the rotator wheels; there can be some gap between the wheel and vanes.
- In reaction turbine, relative velocity of fluid (Gas, Steam or water) increases gradually across the blades. On the contrary, in impulse turbine, relative velocity of fluid (Gas, Steam or water) remains fairly same across the blades.
- In reaction turbine, casing is very necessary because the pressure at the inlet of the turbine is much higher than the pressure at the outlet. It is sealed from atmospheric pressure. In impulsive turbine, casing has no hydraulic function to perform because the jet is at atmospheric pressure. This casing serves only to prevent splashing of water.
- Examples of reaction turbine are: Francis Turbine, Kaplan and Propeller turbine, Deriaz turbine, Tubuler Turbine, Fourneyron etc. On the other hand, impulse turbine is Pelton wheel, Banki turbine.
- Regulation of flow in reaction turbine is carried out by means of a guide-valve, scroll casing, stay ring runner and the draft tub. In contrast, regulation in impulse turbine is done by means a needle valve fitted into the nozzle.
- In reaction turbine, water flow in radial and axial direction to turbine wheel whereas in impulse turbine, water flow is in tangential direction to the turbine wheel.
- In reaction turbine, it is not possible to regulate the flow without loss whereas in impulse turbine, it is possible to regulate the flow without loss.
- In reaction turbine, during the flow of steam through moving blades its pressure reduces whereas in impulse turbine, during the flow of steam through moving blades, its pressure remains constant.
- Reaction turbine is suitable for medium and higher power generation whereas impulse turbine is suitable for small power generation.
- Reaction turbine has high maintenance work whereas impulse turbine has less maintenance work.
- Reaction turbine is usually connected to the tail race through a draft tube which is a gradually expanding passage. It may be installed below or above the tail race. On the other hand, the impulse turbine is always installed above the tail race and there is no draft tube used.
- Reaction turbine has low operating speed whereas impulse turbine has high operating speed.
- Reaction turbine is mainly used for electricity generation whereas impulse turbine is used for steam propulsion of ship and submarines, electricity generation and for cargo operation on ship and refineries.
- For the same power development, the number of stages required in an impulse turbine is way less when compared to the number of stages required in reaction turbine.
Impulse Vs. Reaction Turbine In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | REACTION TURBINE | IMPULSE TURBINE |
| Flow Of Steam | In reaction turbine steam first flows through the guide mechanism and then flows through the moving blades. | In impulse turbine, the steam flows through the nozzle and strikes on the moving blades. |
| Some Gap Between The Wheel And Vanes | The wheels must always run full; what this means is that fluid (gas, steam or water) must be injected in such a way that no gap is left in between wheel and the vanes. | Fluid (gas, water or steam) may or may not be injected full on the rotator wheels; there can be some gap between the wheel and vanes. |
| Relative Velocity | Relative velocity of fluid (Gas, Steam or water) increases gradually across the blades. | Relative velocity of fluid (Gas, Steam or water) remains fairly same across the blades. |
| Casing | Casing is very necessary because the pressure at the inlet of the turbine is much higher than the pressure at the outlet. | Casing has no hydraulic function to perform because the jet is at atmospheric pressure. This casing serves only to prevent splashing of water. |
| Examples | Francis Turbine Kaplan Propeller turbine Deriaz turbine Tubuler Turbine Fourneyron etc. | Pelton wheel, Banki turbine |
| Flow Regulation | Regulation of flow in reaction turbine is carried out by means of a guide-valve, scroll casing, stay ring runner and the draft tub. | Regulation in impulse turbine is done by means a needle valve fitted into the nozzle. |
| Water Flow | Water flow in radial and axial direction to turbine wheel. | Water flow is in tangential direction to the turbine wheel. |
| Regulation Of Flow With/without Loss | It is not possible to regulate the flow without loss. | It is possible to regulate the flow without loss. |
| Pressure Of Steam | During the flow of steam through moving blades its pressure reduces. | During the flow of steam through moving blades, its pressure remains constant. |
| Suitability | It is suitable for medium and higher power generation. | It is suitable for small power generation. |
| Maintenance Work | Reaction turbine has high maintenance work. | Impulse turbine has less maintenance work. |
| Connection | Reaction turbine is usually connected to the tail race through a draft tube which is a gradually expanding passage. It may be installed below or above the tail race. | The impulse turbine is always installed above the tail race and there is no draft tube used. |
| Operation Speed | Has a low operating speed. | Has a high operating speed. |
| Use | Mainly used for electricity generation. | Used for steam propulsion of ship and submarines, electricity generation and for cargo operation on ship and refineries. |
| For the same power development, the number of stages required in reaction turbine is way more when compared to the number of stages required in an impulse turbine. | For the same power development, the number of stages required in an impulse turbine is way less when compared to the number of stages required in reaction turbine. |