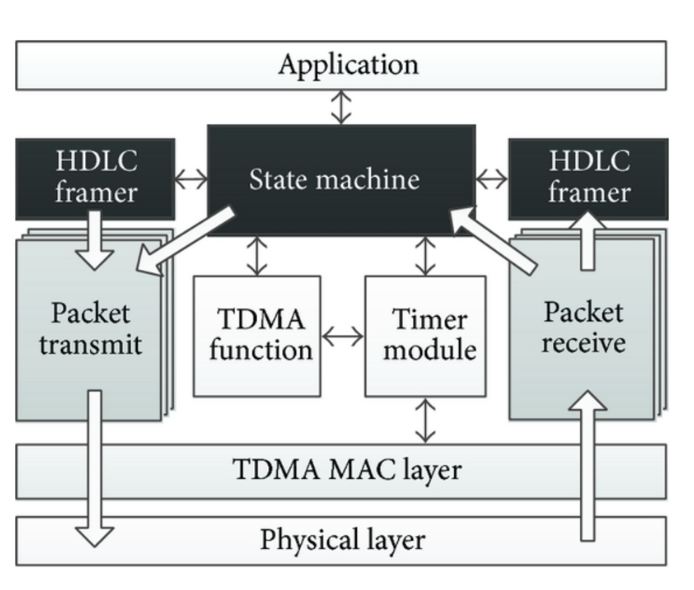
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
HDLC (High-level Data Link Control) is a group of protocols or rules for transmitting data between network points, sometimes referred to as nodes. In HDLC, data is organized into a unit called frame and sent across a network to a destination that verifies its successful arrival. The HDLC frames consist of a flag byte followed by address and control information, data bits and a CRC byte. A control field at the start of a frame is used for establishing and terminating data link connections.
High-level data link control (HDLC) was derived from synchronous data link control (SDLC) and was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for point-to-point communication. It was later adapted by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) for X.25 Link Access protocol. (An X.25 network is one in which packets of data are moved to their destination along routes determine by network conditions as perceived by routers and reassembled in the right order at the ultimate destination).
A HDLC link consists of a primary station and a secondary station with the primary station issuing the commands and the secondary station issuing the responses. Now, given that HDLC is mainly used in point-to-point communication, it does not require to have addressing implemented at the data-link layer because the local and remote stations are connected directly.
What You Need To Know About HDLC
- HDLC is a bit-oriented code-transparent synchronous data link layer protocol developed by ISO.
- It is used to perform encapsulation of data without using other encapsulation protocols.
- HDLC operates at layer-2 of Data link layer.
- HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol.
- There are two types of HDLC protocol, that is, ISO HDLC and Cisco HDLC.
- It supports both synchronous and asynchronous links.
- HDLC does not support authentication i.e it fails to provide authentication between two nodes.
- HDLC is not compatible with non-cisco devices.
- Dynamic addressing is not provided by HDLC
- HDLC is implemented by Point-to-point configuration and also multi-point configurations.
- HDLC fails to check for quality of a link established.
- HDLC does not have a method to detect the errors.
- HDLC provides a frame format which contains a propriety field. The other 6 fields are similar to PPP protocol frame fields. ISO HDLC do not have propriety field and hence has only 6 fields.
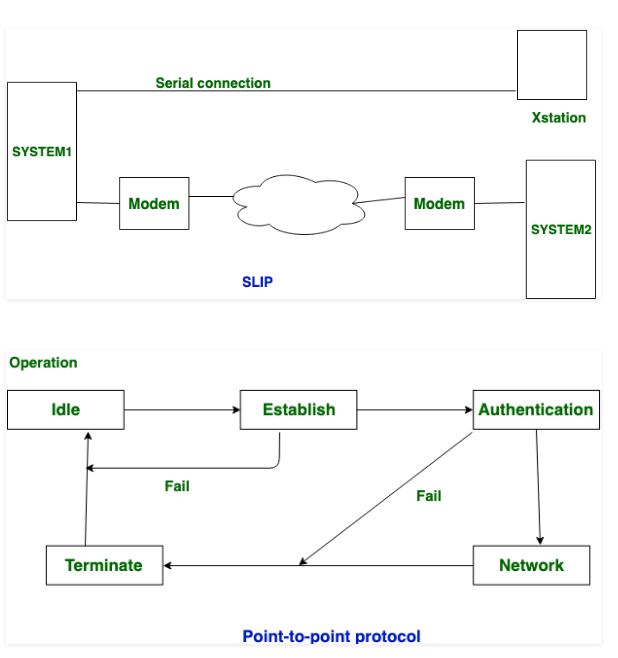
PPP (Point-to-Point)
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer (layer-2) communications protocol between two routers directly without any host or any other networking in between. It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption and compression.
PPP is configured to work at the data link open systems interconnection (OSI) layer and helps data transmission by utilizing a multiprotocol setup through the physical, data link and network layers of the OSI model. PPP is commonly used to encapsulate a connection on a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) based network through a modem and a telephone line, a router connected to another router and via other connection methods and media.
PPP is a byte-oriented protocol that is widely used in broadband communications having heavy loads and high speeds. Given that it is a data link layer protocol, data is transmitted in frames. It is also referred to as RFC 1661.
What You To Know About PPP
- PPP is a data link layer communication protocol used to establish a direct connection between two nodes.
- PPP cannot encapsulate data without the help of other encapsulation protocols such as HDLC, SDLC (synchronous data link control).
- PPP operates at layer-2 and layer-3 of Network layer.
- PPP is a byte-oriented protocol.
- PPP uses HDLC format as defined by ISO.
- It supports synchronous, asynchronous, HSSI (high speed serial interface) and ISDN links.
- PPP supports authentication using protocols such as PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Protocol).
- PPP can be used with non-cisco devices.
- Dynamic addressing is provided by PPP protocol.
- PPP is implemented by Point-to-Point configuration only.
- PPP uses link control protocol (LCP) to check for quality of the established link.
- PPP uses a frame check sequence (FCS) to detect the error while transmitting the data. FCS is an error-detecting code added to a frame in a communication protocol.
- PPP provides a frame format which contains a protocol field. The other 6 fields are similar to HDLC frame field.
Difference Between HDLC And PPP Protocol In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | HDLC | PPP |
| Description | HDLC is a bit-oriented code-transparent synchronous data link layer protocol developed by ISO. | PPP is a data link layer communication protocol used to establish a direct connection between two nodes. |
| Data Encapsulation | It is used to perform encapsulation of data without using other encapsulation protocols. | PPP cannot encapsulate data without the help of other encapsulation protocols such as HDLC, SDLC (synchronous data link control). |
| Operation | It operates at layer-2 of Data link layer. | It operates at layer-2 and layer-3 of Network layer. |
| Basis | It is a bit-oriented protocol. | It is a byte-oriented protocol. |
| Types | There are two types of HDLC protocol, that is, ISO HDLC and Cisco HDLC. | PPP uses HDLC format as defined by ISO. |
| Synchronous And Asynchronous Links | It supports both synchronous and asynchronous links. | It supports synchronous, asynchronous, HSSI (high speed serial interface) and ISDN links. |
| Authentication | It does not support authentication i.e it fails to provide authentication between two nodes. | It supports authentication using protocols such as PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Protocol). |
| Compatibility With Non-Cisco Devices | It is not compatible with non-cisco devices. | It can be used with non-cisco devices. |
| Dynamic Addressing | Dynamic addressing is not provided by HDLC | Dynamic addressing is provided by PPP protocol. |
| Implementation | It is implemented by Point-to-point configuration and also multi-point configurations. | It is implemented by Point-to-Point configuration only. |
| Link Quality Check | It fails to check for quality of a link established. | It uses link control protocol (LCP) to check for quality of the established link. |
| Error Detection | It does not have a method to detect the errors. | It uses a frame check sequence (FCS) to detect the error while transmitting the data. FCS is an error-detecting code added to a frame in a communication protocol. |
| Frame Format | It provides a frame format which contains a propriety field. The other 6 fields are similar to PPP protocol frame fields. ISO HDLC do not have propriety field and hence has only 6 fields. | It provides a frame format which contains a protocol field. The other 6 fields are similar to HDLC frame field. |