What Is Endosmosis?
When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water move inside the cell causing it to swell or bulge. This movement of water inside a cell is known as endosmosis. This happens because the solute concentration of the surrounding solution is less than that inside the cytoplasm of the cell. Examples of endosmosis in plants include absorption of capillary water from the soil by roots and the entrance of water into the xylem vessels.
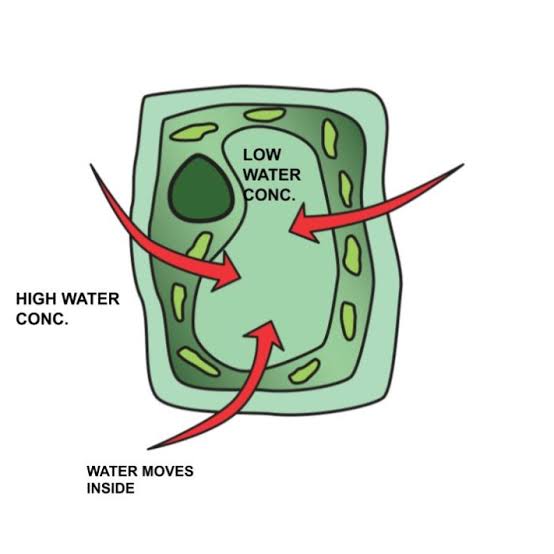
What You Need Know About Endosmosis
- Endosmosis is the process by which water molecules enter into inside of a cell.
- Endosmosis occurs when the solute concentration of the surrounding is less than the solute concentration inside the cell.
- Water or solvent moves inside the cell during endosmosis.
- Endosmosis occurs when cells are placed in hypotonic solutions.
- In endosmosis, the higher solvent concentration is found inside the cell.
- The cells may swell and become turgid as a result of endosmosis.
- Occurs when there is lower osmotic pressure.
- The water potential in endosmosis is higher outside the cell than inside.
- In humans, too much endosmosis results in intoxication.
- Examples of endosmosis in plants include absorption of capillary water from the soil by roots and the entrance of water into the xylem vessels.
What Is Exosmosis?
When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks or becomes flaccid. This movement of water out of the cell is known as exosmosis. This happens because the solute concentration of the surrounding solution is higher than that inside the cytoplasm of the cell. Example of Exosmosis in plants includes the movement of water from the root hair cells to the cortical cells of the root.
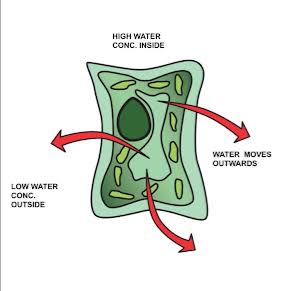
What You Need To Know About Exosmosis
- Exosmosis is the process by which water molecules move out of the cell.
- Exosmosis occurs when solute concentration of the surrounds is higher than the solute concentration inside the cell.
- Water or solvent flows out of the cells.
- Exosmosis occurs when cells are placed in hypertonic solutions.
- In Exosmosis, the highly concentrated solvent is found outside the cell.
- Shrinkage of cells may occur as a result of Exosmosis.
- Occurs when the osmotic pressure is higher.
- The water potential in Exosmosis is higher inside the cell than outside the cell.
- In humans, too much Exosmosis results to dehydration.
- Example of Exosmosis in plants includes the movement of water from the root hair cells to the cortical cells of the root.
Also Read: Difference Between Diffusion And Osmosis
Difference Between Endosmosis And Exosmosis In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | ENDOSMOSIS | EXOSMOSIS |
| Description | Endosmosis is the process by which water molecules enter into inside of a cell. | Exosmosis is the process by which water molecules move out of the cell. |
| Occurrence | Endosmosis occurs when the solute concentration of the surrounding is less than the solute concentration inside the cell. | Exosmosis occurs when solute concentration of the surrounds is higher than the solute concentration inside the cell. |
| Solvent Flow | Water or solvent moves inside the cell during endosmosis. | Water or solvent flows out of the cells. |
| Solvent Concentration | Endosmosis occurs when cells are placed in hypotonic solutions. | Exosmosis occurs when cells are placed in hypertonic solutions. |
| Higher Solvent Concentration | In endosmosis, the higher solvent concentration is found inside the cell. | In Exosmosis, the highly concentrated solvent is found outside the cell. |
| Cells Behavior | The cells may swell and become turgid as a result of endosmosis. | Shrinkage of cells may occur as a result of Exosmosis. |
| Osmotic Pressure | Occurs when there is lower osmotic pressure. | Occurs when the osmotic pressure is higher. |
| Water Potential | The water potential in endosmosis is higher outside the cell than inside. | The water potential in Exosmosis is higher inside the cell than outside the cell. |
| Importance | In humans, too much endosmosis results in intoxication. | In humans, too much Exosmosis results to dehydration. |
| Examples | Examples of endosmosis in plants include absorption of capillary water from the soil by roots and the entrance of water into the xylem vessels. | Example of Exosmosis in plants includes the movement of water from the root hair cells to the cortical cells of the root. |