Sometimes galvanic cells are just referred to as electrochemical cells while they are electrochemical cells; electrolytic cells are also electrochemical cells. Electrolytic and galvanic cells are however not the same.
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell which converts chemical potential energy to electrical potential energy through a spontaneous chemical reaction. A galvanic cell has two half-cells with each half cell containing an electrode in an electrolyte. Usually, separation is important in order to prevent direct chemical contact of the oxidation and reduction reactions, creating a potential difference. The electrons produced during oxidation reaction travel through an external circuit before being used by the reduction reaction.
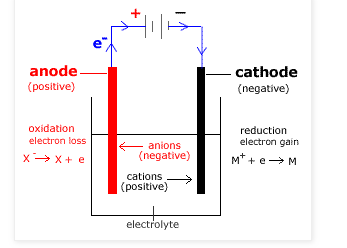
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical potential energy to chemical potential energy by using electricity to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. An electrolytic cell is usually activated by applying an electrical potential across the electrode to force an internal chemical reaction between the electrodes and ions that are in the electrolyte solution. This process is referred to as electrolysis.
The Key Difference
- An Electrolytic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy whereas a galvanic cell, converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- In electrolytic cell, the anode is positive and cathode is the negative electrode. The reaction at the anode is oxidation and at the cathode is reduction. On the contrary, in galvanic cell, the anode is negative and cathode is positive. The reaction at the anode is oxidation and at the cathode is reduction.
- In electrolytic cell, the redox reaction is not spontaneous and electrical energy has to be supplied to begin the reaction. On the other hand, in galvanic cell, the redox reaction is spontaneous and is responsible for the production of electrical energy.
- In electrolytic cell, the external battery supplies the electrons. The electrons enter through the cathode and come out through the anode whereas in galvanic cell, the electrons are supplied by species getting oxidized. They move from anode to the cathode in the external circuit.
- In an electrolytic cell, both electrodes are immersed in the same container in solution of molten electrolyte. The electrolyte may be melt or aqueous solution of some salt, acid or alkali. On the other hand, in galvanic cell, the two half-cells are arranged in different containers, being connected through the salt bridge or semi-permeable membrane.
- Electrolytic cells have different uses such as electroplating, extracting pure metals from alloys, production of oxygen and hydrogen for commercial and industrial use. On the other hand, galvanic cells are commonly referred to as accumulators or batteries and are usually used as a source of electric current.
Difference Between Electrolytic Cell And Galvanic Cell
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | ELECTROLYTIC CELL | GALVANIC CELL |
| Function | An Electrolytic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy. | A galvanic cell, converts chemical energy into electrical energy. |
| Anode & Cathode | The anode is positive and cathode is the negative electrode. The reaction at the anode is oxidation and at the cathode is reduction. | The anode is negative and cathode is positive. The reaction at the anode is oxidation and at the cathode is reduction. |
| Supply Of Electrons | The external battery supplies the electrons. The electrons enter through the cathode and come out through the anode. | The electrons are supplied by species getting oxidized. They move from anode to the cathode in the external circuit. |
| Design | Both electrodes are immersed in the same container in solution of molten electrolyte. The electrolyte may be melt or aqueous solution of some salt, acid or alkali. | The two half-cells are arranged in different containers, being connected through the salt bridge or semi-permeable membrane. |
| Uses | Have different uses such as electroplating, extracting pure metals from alloys, production of oxygen and hydrogen for commercial and industrial use. | Commonly referred to as accumulators or batteries and are usually used as a source of electric current. |