What Is A Database System?
A database system is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. A database system represents some aspects of the real world and is designed to be build and be populated with data for certain tasks. A database system contains information organized in columns, rows and tables that is periodically indexed to make accessing relevant information more flexible.
What Is A Data Warehouse?
Data warehouse also referred to as enterprise data warehouse is an aggregate of corporate information and data derived from both operational systems and external sources. A data warehouse is designed to support business decisions by allowing data aggregation, analysis and reporting at different stages.
In data warehouse from different sources is extracted into a single area, transformed according to the decision support system needs and store into a warehouse so as to contribute to future decision making.
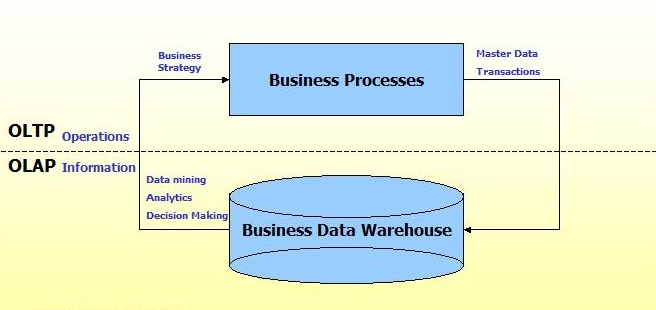
Also Read: Difference Between Operational And Information System
Difference Between Database System And Data Warehouse In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | DATABASE SYSTEM | DATA WAREHOUSE |
| Description | A database system contains information organized in columns, rows and tables that is periodically indexed to make accessing relevant information more flexible. | A data warehouse is a system that pulls together data from many different sources within an organization for reporting and analysis. |
| Purpose | A database is built to store current transactions and enable fast access to specific transactions for ongoing business processes, known as Online Transaction Processing (OLTP). | A data warehouse is built to store large quantities of historical data and enable fast, complex queries across all data, typically using (Online Analytical Processing (OLAP). |
| Data | Data within operational database systems are generally updated regularly. | Data within a data warehouse is non-volatile, meaning when data is added old data is not erased so rarely updates. |
| Concurrent Users | A data base system is able to handle thousands of users simultaneously without affecting the system performance. | Data warehouse supports a limited number of concurrent users. |
| Applications | With databases, there is one-to-one relationship with a single application as its source. | With data warehouses, there is one-to-many relationships between a data warehouse and the application that serve as the data source. |
| Represents | Database system reads current (day to day) transactions within an organization. | Data warehouse system reads historical data for analytical purposes and business reporting. |
| Usage | ER modeling techniques are used for designing. | Data modeling techniques are used for designing. |
| Data Storage Approach | Flat relational approach method is used for data storage. | Data warehouse uses dimensional and normalized approach for data structure. Example snowflake schema and star. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Due to number of table joins, performing analytical queries is difficult and requires an experienced database administrator familiar with the application to write queries that result in meaningful analysis. | In data warehouse, tables are de-normalized to yield and integrated to produce summarized data, multidimensional views and faster query response times. |
| Data Structure | Databases use normalized data structure, whereby data is re-organized so that it does not contain redundant data and all related data items are stored together into multiple tables. | Data warehouse uses a de-normalized data structure whereby few tables are used to group information for analytical purposes. |
| Skilled Personality | A skilled personality or analyst familiar with the application is required to write analytical queries that will eventually result in logical analysis. | Structure of data in data warehouse make analytical queries much simpler and flexible hence no skills or firsthand knowledge of the data base is required. |
| SLA’s | The database is directly linked to the front end applications and therefore real-data is always available. SLA’s therefore states that the database must meet 99.9% uptime. | In data warehouse are separated from frontend application and therefore SLA’s for data warehouses have downtime built in to accommodate periodic uploads of new data. |
Similarities Between Data Warehouse and Database
- Data warehouse and databases are both relational data systems.
- They are both data storage systems.
- Both can be used by multiple users
- Both can be complex with many tables and large amounts of data.
- Both can be queried to get answers or pull out data sets based on commonality or exclusion.
- Databases and data warehouses can be on premise or on cloud-based.