What Is A Covalent Bond?
A covalent bond also referred to as a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is referred to as covalent bonding.
Covalent bonds mostly occur between nonmetals or between two of the same (or similar) elements. Two atoms with similar electronegativity will not exchange an electron from their outermost shell; the atoms instead share electrons so that their valence electron shell is filled.
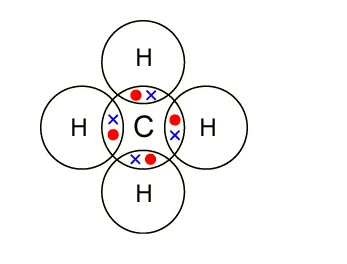
In organic chemistry, covalent bonds are much more common than ionic bonds. A covalent bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration.
A good example of where covalent bond is found is between the oxygen and each hydrogen in a water molecule (H2O). Each of the covalent bonds contains two electrons, one from a hydrogen atom and one from the oxygen atom. Both atoms share the electrons.
Examples of compounds that contain covalent bonds include:
- Methane (CH4)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Iodine monobromide (IBr)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Hydrogen (H2)
- Nitrogen (N2)
Due to the sharing of electrons, covalent compounds exhibit characteristic physical properties that include lower melting points and electrical conductivity compared to the ionic compounds.
What You Need To Know About Covalent Bonds
- Electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms.
- Covalent bonds form between two nonmetals.
- Molecules formed by covalent bonds have a low melting point.
- Molecules formed by covalent bonds have a low boiling point.
- At room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure, covalently bonded molecules are either liquids or gases.
- Covalent bonds are easier to break.
- The reaction components of covalent bonds are electrically neutral.
- Covalent bond compounds are insoluble in water and other polar solvents.
- Covalent bond compounds are poor conductors.
- Molecular reactions of covalently bonded atoms are comparatively slow.
- Electron orbitals in covalent bond overlaps.
What Are Ionic Bonds?
Ionic bonding occurs when there is a large difference in electronegativity between two atoms. This large difference leads to the loss of an electron from the less electronegative atom and the gain of that electron by the more electronegative atom, resulting in two ions. These oppositely charged ions feel an attraction to each other and this electrostatic attraction constitutes an ionic bond.
In simpler words, an ionic bond results from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal in order to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms i.e formation of sodium chloride. When sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) are combined, the sodium atoms lose an electron, forming cations (Na+) and the chlorine atoms each gain an electron to form anions (Cl–). These ions are then attracted to each other in the same proportion (1:1 ratio) to form sodium chloride (NaCl).

In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively charged cation whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion. This transfer of electrons is referred to as electrovalence.
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when in aqueous or molten state and not when solid. Depending on the charge they posses, ionic compounds have a high melting point. The higher the charge the stronger the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point. More importantly, they tend to be soluble in water, the stronger the cohesive forces, the lower the solubility.
Example of Ionic Bonds and compounds
- Sodium Bromide (NaBr)
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
- Sodium Fluoride (NaF)
- Calcium Chloride (CaCl2)
- Potassium Iodide (KI)
- Potassium Bromide (KBr)
- Potassium Chloride (KCl)
- Potassium Oxide (K2O)
What You Need To Know About Ionic Bonds
- An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond.
- Ionic bonds form between a metal and a nonmetal.
- Molecules formed by ionic bonds have high melting point.
- Molecules formed by ionic bonds have high boiling point.
- At room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure, ionic compounds are solids.
- Ionic bonds are difficult to break.
- The reaction components of ionic bonds are electrically charged.
- Ionic bond compounds are soluble in water and other polar solvents.
- Ionic bond compound are only poor conductors in solid state, but they are good conductors in molten state or in solution form.
- The reaction of ionic bonded atoms is comparatively faster.
- Electron orbitals in ionic bonds are separate.
Also Read: Difference Between Covalent And Hydrogen Bonds
Difference Between Ionic And Covalent Bonds In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | COVALENT BOND | IONIC BOND |
| Electrons | Electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms. | An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond. |
| Occurrence | Covalent bonds form between two nonmetals. | Ionic bonds form between a metal and a nonmetal. |
| Melting Point | Molecules formed by covalent bonds have a low melting point. | Molecules formed by ionic bonds have high melting point. |
| Boiling Point | Molecules formed by covalent bonds have a low boiling point. | Molecules formed by ionic bonds have high boiling point. |
| State At STP | At room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure, covalently bonded molecules are either liquids or gases. | At room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure, ionic compounds are solids. |
| Breakage | Covalent bonds are easier to break. | Ionic bonds are difficult to break. |
| Electrical Charge | The reaction components of covalent bonds are electrically neutral. | The reaction components of ionic bonds are electrically charged. |
| Solubility | Covalent bond compounds are insoluble in water and other polar solvents. | Ionic bond compounds are soluble in water and other polar solvents. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Covalent bond compounds are poor conductors. | Ionic bond compound are only poor conductors in solid state, but they are good conductors in molten state or in solution form. |
| Reactivity | Molecular reactions of covalently bonded atoms are comparatively slow. | The reaction of ionic bonded atoms is comparatively faster. |
| Electron Orbital | Electron orbitals in covalent bond overlaps. | Electron orbitals in ionic bonds are separate. |
Similarities Between Covalent And Ionic Bonds
- They are both primary bonds.
- Valence electrons are involved in both bonding processes.
- Both types of bonds lead to the formation of stable chemical compounds
- Formation of covalent and ionic bonds is exothermic
- Compounds with both covalent and ionic compounds are not malleable.
- Both bonds result in the formation of complex structures
- They are both strong bonds.