In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons are the simplest class of organic compounds and are composed solely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are generally divided into two classes, depending on the presence of a benzene ring, that is, aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds also referred to as non-aromatic hydrocarbons.
Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compound can be described as any of a large class of unsaturated chemical compounds characterized by one or more planar rings of atoms joined by covalent bonds of two different kinds. Aromatic compounds are produced from a variety of sources including petroleum and coal tar. They are generally nonpolar and immiscible with water. They are also less reactive than alkenes, making them useful industrial solvents for nonpolar compounds. Due to their high ratio of carbon to hydrogen, aromatic compounds are characterized by a sooty yellow flame.

Aromatic compounds are also interesting because of their presumed role in the origin of life as precursors to nucleotides and amino acids.
Examples of aromatic compounds include:
- Benzene
- Naphthalene
- Toluene
- Indene
- Biphenyl
- Anthracene
- Phenanthrene
Characteristics Of Aromatic Compounds
- In aromatic compounds, the carbon compounds are linked to each other in a ring structure manner with conjugated pi electrons.
- These compounds follow Huckel’s rule.
- These compounds burn with a sooty flame.
- Aromatic compounds require special conditions to react.
- In Aromatic compounds, the benzene ring is conjugated due to the presence of alternating double bonds.
- Aromatic compounds are always cyclic as they contain the benzene ring as part of its structure.
- Aromatic compounds are always unsaturated.
- Carbon to hydrogen ratio is less in aromatic compounds.
- Aromatic compounds produce a sweet pleasant odor.
Aliphatic Compounds
Aliphatic compounds are also referred to as aliphatic hydrocarbons or eliphatic compounds. Aliphatic compound can be described as any chemical compound belonging to the organic class in which the atoms are connected by single, double or triple bonds to form non-aromatic structures.
Aliphatic compound can also be described as an organic compound containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings.
Aliphatic compounds can be classified into one of the following groups: alkanes, alkenes and alkynes based on the presence of double or triple bonds in the chemical structure.
Examples of aliphatic compounds include:
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
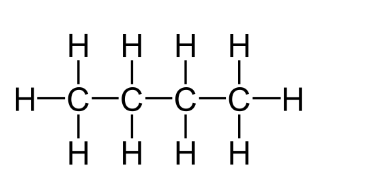
Characteristics Of Aliphatic Compounds
- In aliphatic compounds the carbon compounds are linked to each other in a straight chain manner.
- These compounds do not follow Huckel’s rule.
- These compounds burn with a non sooty flame.
- Aliphatic compounds react more freely and easily.
- The majority of aliphatic compounds are not conjugated.
- Aliphatic compounds can be linear as well as cyclic.
- Aliphatic compounds can be saturated as well as unsaturated.
- Carbon to hydrogen ratio is more in aliphatic compounds.
- Aliphatic compounds are usually odorless or sometimes there can a slight odor.
Also Read: Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Difference Between Aromatic And Aliphatic Compounds
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | AROMATIC COMPOUNDS | ALIPHATIC COMPOUNDS |
| Description | In aromatic compounds, the carbon compounds are linked to each other in a ring structure manner with conjugated pi electrons. | In aliphatic compounds the carbon compounds are linked to each other in a straight chain manner. |
| Huckel’s Rule | These compounds follow Huckel’s rule. | These compounds do not follow Huckel’s rule. |
| Burning Flame | These compounds burn with a sooty flame. | These compounds burn with a non sooty flame. |
| Reactivity Profile | Aromatic compounds require special conditions to react. | Aliphatic compounds react more freely and easily. |
| Conjugation | In Aromatic compounds, the benzene ring is conjugated due to the presence of alternating double bonds. | The majority of aliphatic compounds are not conjugated. |
| Cyclic | Aromatic compounds are always cyclic as they contain the benzene ring as part of its structure. | Aliphatic compounds can be linear as well as cyclic. |
| Saturation | Aromatic compounds are always unsaturated. | Aliphatic compounds can be saturated as well as unsaturated. |
| Carbon To Hydrogen Ratio | Carbon to hydrogen ratio is less in aromatic compounds. | Carbon to hydrogen ratio is more in aliphatic compounds. |
| Odor | Aromatic compounds produce a sweet pleasant odor. | Aliphatic compounds are usually odorless or sometimes there can a slight odor. |