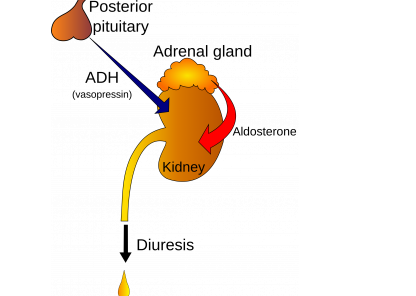
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is also referred to as vasopressin or arginine vasopressin (AVP). It is a neuro-secretary peptide hormone, produced naturally in an area of the brain referred to as the hypothalamus. It is then released by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain.
ADH being a hormone is a protein in nature and it contains nine amino acids such as tyrosine, phenylalanine, glutamine, asparagines, proline, arginine, glycine, cysteine etc. Anti-diuretic hormone acts to maintain blood pressure, blood volume and tissue water content and hence the concentration of urine excreted by the kidney.
Low levels of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) will cause the kidneys to excrete too much water. Urine volume will increase leading to dehydration and a fall in blood pressure. On the other hand, high levels of anti-diuretic hormone cause the kidneys to retain water in body. Excess levels of anti-diuretic hormone might be caused by drug side-effect, lung condition or diseases of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
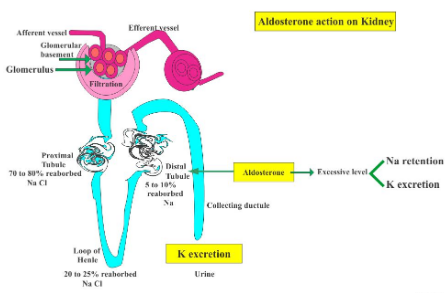
Aldosterone on the other hand, is a hormone in the cortex (outer section) of the adrenal glands of the kidney. Its main function is regulation of blood pressure by stimulating organs such as kidney and the colon to increase the amount of sodium (salt) reabsorption into the bloodstream and increase the amount of potassium excreted in the urine. Aldosterone also causes water to be reabsorbed along with sodium; this increases blood volume and consequently blood pressure.
Key Difference: ADH Vs Aldosterone
- ADH is a peptide hormone while aldosterone is a steroid hormone.
- ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) is a neuro-secretary peptide hormone and it prevents the production of dilute urine. On the other hand, Aldosterone is a corticosteroid hormone that stimulates the absorption of sodium by the nephron to regulate water and salt balance.
- ADH stimulates the kidney to reabsorb more water whereas aldosterone increases the NaCl (sodium chloride) and water absorption capacity of the kidney by making an osmotic pressure.
- ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland whereas aldosterone is synthesized and secreted by the adrenal cortex.
- ADH is made up of nine amino acids, namely: tyrosine, phenylalanine, glutamine, asparagines, proline, arginine, glycine & cysteine. Aldosterone on the other hand, is a mineralocorticoid, which is a corticosteroid made of cholesterol. Mineralocorticoid is similar in chemical structure to sex hormones like estrogen.
- ADH is made in the hypothalamus, the part of the brain responsible for a wide variety of the body’s metabolic processes. In contrast, Aldosterone is made in the adrenal cortex of the kidney.
- ADH conserves water directly through its re-absorption whereas aldosterone conserves water indirectly through re-absorption of sodium.
- ADH makes the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting tubules (CT) more permeable to water. On the contrary, Aldosterone makes the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) more permeable to sodium ions.
- ADH is discharged in response to hypertonicity of the blood and in response to cholecystokinin. On the other hand, aldosterone is discharged in response to the increased plasma angiotensin III, ACTH, serum potassium concentrations, simulation of the stretch receptors in the atria etc.
- ADH is inhibited by diuretics such as alcohol whereas aldosterone is inhibited by Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), dopamine, and atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH).
- ADH increases the blood pressure through vasoconstriction whereas aldosterone has no effect on the blood vessels.
- ADH is secreted when the body is dehydrated whereas aldosterone is secreted when blood pressure is low.
Also Read: Difference Between Progesterone And Estrogen
Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH)Vs Aldosterone In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | ADH | ALDOSTERONE |
| Type Of Hormone | ADH is a peptide hormone. | Aldosterone is a steroid hormone. |
| Description | ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) is a neuro-secretary peptide hormone and it prevents the production of dilute urine. | Aldosterone is a corticosteroid hormone that stimulates the absorption of sodium by the nephron to regulate water and salt balance. |
| Role | It stimulates the kidney to reabsorb more water. | It increases the NaCl (sodium chloride) and water absorption capacity of the kidney by making an osmotic pressure. |
| Secretion | It is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. | It is synthesized and secreted by the adrenal cortex. |
| Structure | It is made up of nine amino acids, namely: tyrosine, phenylalanine, glutamine, asparagines, proline, arginine, glycine & cysteine. | It is a mineralocorticoid, which is a corticosteroid made of cholesterol. |
| Synthesis | It is made in the hypothalamus, the part of the brain responsible for a wide variety of the body’s metabolic processes. | It is made in the adrenal cortex of the kidney. |
| Water Conservation | It conserves water directly through its re-absorption. | It conserves water indirectly through re-absorption of sodium. |
| Role On DCT & CT | It makes the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting tubules (CT) more permeable to water. | It makes the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) more permeable to sodium ions. |
| Discharge | It is discharged in response to hypertonicity of the blood and in response to cholecystokinin. | It is discharged in response to the increased plasma angiotensin III, ACTH, serum potassium concentrations, simulation of the stretch receptors in the atria etc |
| Inhibition | It is inhibited by diuretics such as alcohol. | It is inhibited by Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), dopamine, and atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH). |
| Effect On Blood | It increases the blood pressure through vasoconstriction. | It has no effect on the blood vessels. |
| Secretion Time | It is secreted when the body is dehydrated. | It is secreted when blood pressure is low. |
Also Read: Difference Between Enzymes And Hormones
What Are The Similarities Between ADH And Aldosterone?
- Both ADH and aldosterone hormones increase the water re-absorption from the nephron.
- They are both secreted under low blood pressure.
- They both increase blood pressure while producing concentrated urine.
- They both have an effect on collecting tubules (CT) and the distal convoluted tubules (DCT) of the nephron.
- Both ADH and aldosterone levels are regulated by negative feedback loops.
Comments are closed.