What Is Divergent Evolution?
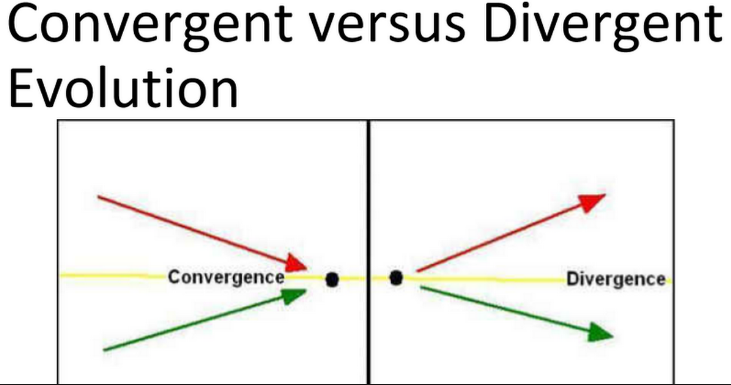
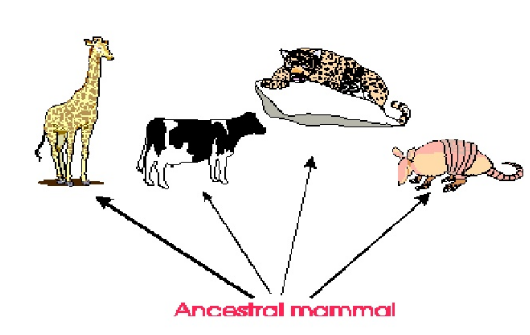
Divergent evolution is type of evolution whereby a single or same species with marginally different variations in genetic code evolve different traits and diverge into two or more different species. Divergent evolution may occur as a response to changes in abiotic factors such as change in environmental conditions or when a new nichie becomes available. Also, divergent evolution may happen in response to changes in biotic factors such as increased or decreased competition pressure.
Examples of divergent evolution include:
- Limbs of vertebrates
- The side fine of whale
- Wings of bat and paws of a cat
- Dinosaurs
- Darwin’s finches
- Forelimb structures of vertebrates
All these structures evolved from one primal stock of ancestors. Another good example of divergent evolution is a cat and a tiger, though they are different in size, however, they have almost similar features. This is an indication that the two shared a common ancestry but evolved to become separate species.
What You Need To Know About Divergent Evolution
- Divergent is a type of evolution in which a single species evolve different traits and diverge into two or more different species
- Divergent evolution evolves homologous structures (organs that have same structure but vary in their function)
- During divergent evolution a single species evolves into multiple species
- Divergent evolution occurs due to migration or may be due to environmental changes
- Organisms that have evolved through divergent evolution are usually different from both outside and inside appearance
- Organisms that have evolved through divergent evolution live differently and do not resemble their ancestors
What Is Convergent Evolution?
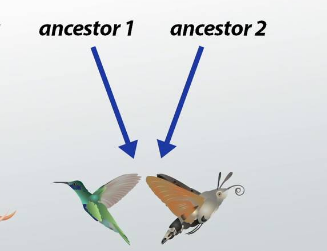
Convergent evolution on the other hand, is a type of evolution whereby organisms not closely related, independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. There are several circumstances that can result in convergent evolution when organisms are required to adapt to similar environmental conditions such as in the evolution of thick water-retaining leaves and spines on cacti and Euphorbia species, which are adapted to tolerate extreme drought but are natives to separate continents.
Other examples of convergent evolution include:
- Ostriches
- Rheas
- Emus
- Wings of birds, insects and bats
- Streamlined body of dolphins and shark
What You Need To Know About Convergent Evolution
- Convergent evolution is a type of evolution in which two or more different species develop similar traits and evolve to a single specie
- Convergent evolution evolves analogous structures (organs that have same function but different in their structure and origin)
- During convergent evolution, different species evolves into a single specie
- Convergent evolution occurs due to change in environmental conditions or due to adaptation to the place where they live
- Organisms that have evolved through convergent evolution resemble their ancestors internally, but the outer structure may be different
- Examples of convergent evolution include ostriches, rheas, emus, wings of birds, insects and bats, streamlined body of dolphins and shark.
- Organisms that have evolved through convergent evolution resemble their ancestors in their way of living
- Species that have evolved through convergent evolution live within the same environment
Differences Between Divergent and Convergent Evolution in a Tabular Form
| Basis of Comparison | Convergent | Divergent |
| Definition | Convergent evolution is a type of evolution in which two or more different species develop similar traits and evolve into a single species. | Divergent is a type of evolution in which a single specie evolve different traits and diverge into two or more different species. |
| Structures | Evolves analogous structures (organs that have same function but different in their structure and origin). | Evolves homologous structures (organs that have same structure but vary in their function). |
| Species | Different species evolve into a single species. | A single species evolves into multiple species. |
| Cause of Evolution | Occurs due to change in environmental conditions or due to adaptation to the place where they live. | Occurs due to migration or may be due to environmental changes. |
| Appearance | Organisms that have evolved through convergent evolution resemble their ancestors internally, but the outer structure may be different. | Organisms that have evolved through divergent evolution are usually different from both outside and inside appearance. |
| Examples | Examples of convergent evolution include ostriches, rheas, emus, wings of birds, insects and bats, streamlined body of dolphins and shark. | Examples of divergent evolution include dinosaurs, darwin’s finches and forelimb structures of vertebrates. |
| Way of Living | Organisms that have evolved through convergent evolution resemble their ancestors in their way of living. | Organisms that have evolved through divergent evolution live differently and do not resemble their ancestors. |
| Environment | Species that have evolved through convergent evolution live within the same environment. | Organisms that evolve through divergent evolution live in different environments. |
Similarities Between Convergent and Divergent Evolution
- Both generate variation, aiding species to perform their niche in the environment.
- Both have contributed to development of present organisms from the past organisms.