Learn the difference between born and cartilage. The basis of comparison includes: description, composition, types, function, bone marrow presence, growth pattern, Capillaries repair, bone cells, blood capillaries, lacunae, location, flexibility, calcium salts, protein, metabolic activity among others.
Key Differences
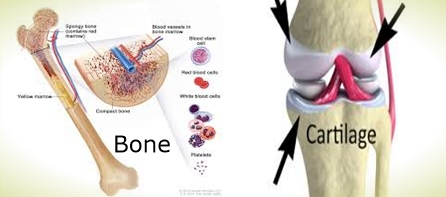
Characteristics of Bone
- Bone is a rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. It can also be described as hard, inelastic and tough organ that forms part of the vertebral skeleton.
- Bones are made up of proteins, calcium and phosphorous.
- Protect the body from mechanical damage, provide a framework and shape for the body. It also helps in movement of the body, store minerals and produce red blood cells and white blood cells.
- The bones are categorized into two types of bones which are compact bones and spongy bones.
- Bones usually have bone marrow at the center which actually helps to create blood cells.
- The growth pattern of bones is bidirectional.
- Bones posses high extensive repair capabilities.
- There is presence of blood vessels such as capillaries in the bones and therefore have a rich blood supply.
- Bones consist of cells known as osteocytes and osteoclasts, osteocytes are mature bone cells while osteoclast are large cells that breakdown bone tissue for growth and repair.
- The lacunae of bones consist of canaliculi between oesteocytes
- Bones make up the majority of the axial and appendicular skeleton.
- Bone is porous and cannot be bent.
- Bone possesses Haversian system and Volkman’s canals.
- Bone matrix has calcium salts specifically calcium phosphates.
- Bone matrix protein is referred to as ossein.
- The covering of the bone is referred to as periosteum.
- Metabolic activity of bone is high.
- Bone matrix is both organic and inorganic.
Characteristics of Cartilage
- Cartilage is a strong, flexible type of connective tissue found within a body. It is made of cells known as chondroblasts and chondrocytes.
- Cartilage matrix is made up of proteins and sugars.
- Cartilage supports the respiratory tract, acts as shock absorbers between weight-bearing bones, maintains the shape and flexibility of fleshy appendages and reduces friction at joints.
- Cartilages are categorized into three types, hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage.
- A tissue like bone marrow or similar structure is absent in cartilage.
- The growth pattern of the cartilage is unidirectional.
- Cartilages have very limited range of repair capabilities.
- Cartilages do not have blood vessels like capillaries, though there is presence of few capillaries in the perichondrium.
- Cartilages comprise chondroblasts, chondrocytes and a dense matrix of collagen and elastic fibers, in which the mature chondrocytes are embedded.
- The lacunae of cartilages do not contain canaliculi between chondrocytes.
- Cartilage is much softer, more pliable component that is mostly found in between the joints of the bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs.
- Cartilage is non-porous and can be bent
- Cartilage does not have Haversian system and Volkman’s canals.
- The cartilage matrix may or may not have calcium salts.
- Cartilage matrix has a protein referred to as chondrin.
- The covering of cartilage is called perichondrium.
- Metabolic activity of cartilage is low.
- The cartilage matrix is entirely organic.
Also Read: Difference Between Endoskeleton And Exoskeleton
Difference Between Bone And Cartilage In Tabular Form
| POINTS OF DIFFERENCE | BONE | CARTILAGE |
| Description | Bone is a rigid body tissue consisting of cells embedded in an abundant hard intercellular material. It can also be described as hard, inelastic and tough organ that forms part of the vertebral skeleton. | Cartilage is a strong, flexible type of connective tissue found within a body. It is made of cells known as chondroblasts and chondrocytes. |
| Composition | Bones are made up of proteins, calcium and phosphorous. | Cartilage matrix is made up of proteins and sugars. |
| Function | Protect the body from mechanical damage, provide a framework and shape for the body. It also helps in movement of the body, store minerals and produce red blood cells and white blood cells. | Cartilage supports the respiratory tract, acts as shock absorbers between weight-bearing bones, maintains the shape and flexibility of fleshy appendages and reduces friction at joints. |
| Types | The bones are categorized into two types of bones which are compact bones and spongy bones. | Cartilages are categorized into three types, hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage. |
| Bone Marrow | Bones usually have bone marrow at the center which actually helps to create blood cells. | A tissue like bone marrow or similar structure is absent in cartilage. |
| Growth Pattern | The growth pattern of bones is bidirectional. | The growth pattern of the cartilage is unidirectional. |
| Repair Capabilities | Bones posses high extensive repair capabilities. | Cartilages have very limited range of repair capabilities. |
| Blood Capillaries | There is presence of blood vessels such as capillaries in the bones and therefore have a rich blood supply. | Cartilages do not have blood vessels like capillaries, though there is presence of few capillaries in the perichondrium. |
| Bone Cells | Bones consist of cells known as osteocytes and osteoclasts, osteocytes are mature bone cells while osteoclast are large cells that breakdown bone tissue for growth and repair. | Cartilages comprise chondroblasts, chondrocytes and a dense matrix of collagen and elastic fibers, in which the mature chondrocytes are embedded. |
| Lacunae | The lacunae of bones consist of canaliculi between oesteocytes | The lacunae of cartilages do not contain canaliculi between chondrocytes. |
| Location | Bones make up the majority of the axial and appendicular skeleton. | Cartilage is much softer, more pliable component that is mostly found in between the joints of the bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs. |
| Flexibility | Bone is porous and cannot be bent. | Cartilage is non-porous and can be bent |
| Haversian and Volkman’s | Cartilage does not have Haversian system and Volkman’s canals. | Cartilage does not have Haversian system and Volkman’s canals. |
| Calcium Salts | Bone matrix has calcium salts specifically calcium phosphates. | The cartilage matrix may or may not have calcium salts. |
| Protein | Bone matrix protein is referred to as ossein. | Cartilage matrix has a protein referred to as chondrin. |
| Bone& Cartilage Covering | The covering of the bone is referred to as periosteum. | The covering of cartilage is called perichondrium. |
| Metabolic Activity | Metabolic activity of bone is high. | Metabolic activity of cartilage is low. |
| Nature of the Matrix | Bone matrix is both organic and inorganic. | The cartilage matrix is entirely organic. |
What are the Similarities Between Bone and Cartilage?
- Both bone and cartilage are connective tissues.
- Both bones and cartilages are involved in the formation of the skeletal system of vertebrates.
- Both bone and cartilage are involved in support of muscle attachment.
- Both cartilage and bones provide shape to body parts.
- Both cartilage and bones compose of specialized cells embedded in the matrix of fibrous proteins.
- Both also act as a protection to vital body organs.
Also Read: Difference Between Osteoblasts And Osteoclasts
Summary
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the vertebrate skeleton. Bones protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body and enable mobility. Cartilage on the other hand, is a connective tissue found in many areas of the body including joints between bones e.g the elbows, knees and ankle. It helps to reduce friction at joints and supports the respiratory tract.