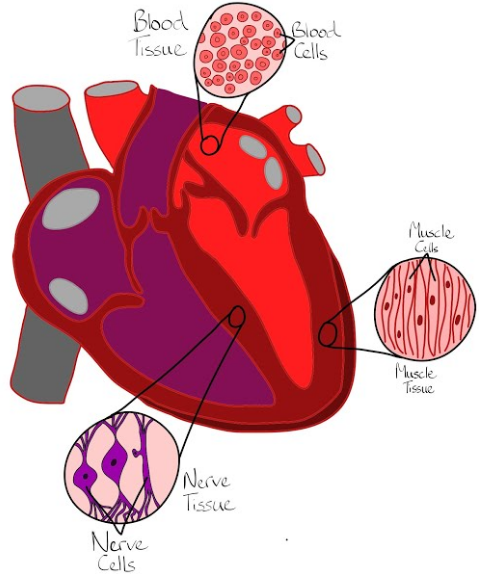
Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform similar function. In plants, tissues are categorized into three types: vascular, ground and epidermal. In animals, there are four different types of tissues: connective, muscle, nervous and epithelial. Organs on the other hand, are structures made up of two or more tissues organized to carry out a particular function. For example, the heart contains muscle tissue that contracts to pump blood, fibrous tissue that make up the heart valves and special cells that maintain the rate and rhythm of heartbeats.
The differences
Here are more insights on the differences between a Tissue and Organ:
Definition
A tissue is a collection of similar cells with similar functions and structures plus the extracellular materials found in-between cells. In contrast, an organ comprises of two or more tissues with one or more functions.
Structure
Tissues are evenly distributed structures while organs are hollow structures.
Examples
Examples of tissues include epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, nerve tissue and ground tissue. On the other hand, examples of organs include stomach, skin, Brain, penis, heart, intestine, lungs and kidneys
Function
Given that tissues form organs, they may have a unique function in the body. An organ on the other hand has vital physiological function in the body.
Formations
Tissues form organs in the body whereas organs form organ systems in the body.
Repair process
Damaged tissues in the body usually repair through regeneration and fibriosis while damaged organs are repaired by repairing the tissues.
Importance
Tissue is the major structural component of the organ while organs are the structural components of the organ system.
Components
A tissue is composed of similar types of cells whereas an organ is composed of several types of tissues.
Complexity
Tissue is involved in performing a single function in the body or organ while an organ has the ability to perform several functions in the body.
Size
An organ is composed of collections of similar tissues and therefore an organ is larger than tissues.
Energy Requirements
Given that an organ is apparently larger than a tissue, an organ requires comparatively more energy or ATP to perform their functions unlike a tissue that require comparatively less energy.
Recognition
Organs are relatively much more recognizable over tissues.
Differences Between Tissue And Organ In Tabular Form
| Basis of comparison | Tissue | Organ |
| Function | A tissue is a collection of similar cells with similar functions and structures plus the extracellular materials found in-between cells. | An organ comprises of two or more tissues with one or more functions. |
| Structure | Evenly distributed structures | Are hollow structures. |
| Examples | Examples of tissues include epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, nerve tissue and ground tissue. | Examples of organs include stomach, skin, Brain, penis, heart, intestine, lungs and kidneys |
| Function | Given that tissues form organs, they may have a unique function in the body. | An organ has vital physiological function in the body. |
| Formations | Tissues form organs in the body. | Organs form organ systems in the body. |
| Repair Process | Damaged tissues in the body usually repair through regeneration and fibriosis. | Damaged organs are repaired by repairing the tissues. |
| Importance | Tissue is the major structural component of the organ. | Organs are the structural components of the organ system. |
| Components | Is composed of similar types of cells. | An organ is composed of several types of tissues. |
| Complexity | Tissue is involved in performing a single function in the body or organ. | An organ has the ability to perform several functions in the body. |
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Energy Requirements | Requires comparatively less energy. | Requires comparatively more energy to perform functions. |
Similarities between Tissue and Organ
- Both tissue and organs perform a unique function in the body.
- Both tissue and organs are made up of cells.
- Both tissue and organs represent two higher organizational levels in the body of multi-cellular organisms.
Summary
A tissue is a collection of similar cells with similar functions and structures plus the extracellular materials found in-between cells. In contrast, an organ comprises of two or more tissues with one or more functions.
very very useful and effective for students
Smoooooking…. indeed..