According to Bohr’s atomic model, an orbit is a fixed circular path along which electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom. Thus, all atoms particularly revolve in an orbit. According to Bohr model, the first shell holds 2 electrons. However, Bohr’s atomic model has been rejected. The generally accepted model is the one that group electrons into regions referred to as orbitals.
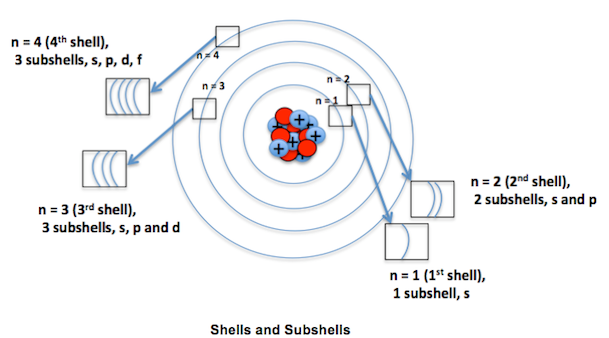
An orbital is often depicted a three-dimensional region within which there is a 95 percent probability of finding an electron. Orbitals can be categorized into several types, the most common being the S, P, D and F orbitals. Each of these orbitals can hold 2 electrons.
Atomic orbitals are often designated by a combination of numerals and letters that represents specific properties of the electrons associated with the orbitals for example 1 s, 2 p, 3d, 4 f etc.
The Difference
- An orbit is a fixed circular path along which electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom. On the contrary, an orbital (an electron orbital) is the three-dimensional space around the nucleus in which the probability of finding electrons is maximum (90-95%).
- An orbit indicates an exact position of an electron in an atom whereas an orbital does not specify the exact position of an electron in an atom.
- An orbital represents the planar motion of an electron while an orbital represents the three dimensional motion of an electron around the nucleus.
- Orbits give a definite path of an electron and this concept is not in accordance with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. An orbital on the other hand, does not specify definite path and according to this concept, electron may be anywhere in this region. This concept is in accordance Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
- All orbits are circular in shape whereas orbitals have different shapes, for example, s-orbital is spherical, p-orbital is dump bell shaped.
- An orbit can be designated as K, L, M, N etc whereas orbitals can be designated as s, p, d, f etc
- Orbits do not have directional characteristics whereas all orbitals, except s=orbitals, have directional characteristics.
- An orbit can accommodate electrons equal to 2n^2 where n represents the principle quantum number. On the other hand, an orbital cannot accommodate more than two electrons.
ALSO READ: Difference Between Valence Bond Theory (VBT) and Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)
Difference Between Orbit And Orbitals In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | ORBIT | ORBITALS |
| Description | An orbit is a fixed circular path along which electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom. | An orbital (an electron orbital) is the three-dimensional space around the nucleus in which the probability of finding electrons is maximum (90-95%). |
| Position Of An Electron In An Atom | An orbit indicates an exact position of an electron in an atom. | An orbital does not specify the exact position of an electron in an atom. |
| What It Represents | An orbital represents the planar motion of an electron. | An orbital represents the three dimensional motion of an electron around the nucleus. |
| Uncertainty Principle | Orbits give a definite path of an electron and this concept is not in accordance with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. | An orbital does not specify definite path and according to this concept, electron may be anywhere in this region. This concept is in accordance Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. |
| Shape | All orbits are circular in shape. | Orbitals have different shapes, for example, s-orbital is spherical, p-orbital is dump bell shaped. |
| Designation | An orbit can be designated as K, L, M, N etc. | Orbitals can be designated as s, p, d, f etc. |
| Directional Characteristics | Orbits do not have directional characteristics. | All orbitals, except s=orbitals, have directional characteristics. |
| Electron Accommodation | An orbit can accommodate electrons equal to 2n^2 where n represents the principle quantum number. | An orbital cannot accommodate more than two electrons. |