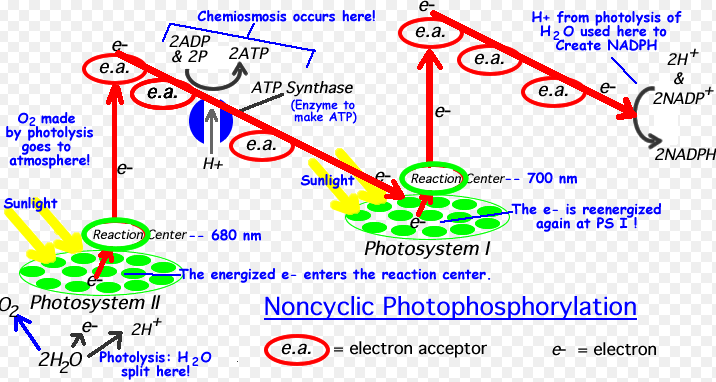
Photophosphorylation is the process of synthesizing energy-rich ATP molecules by transferring the phosphate group into ADP molecules in the presence of light. This process can either be a cyclic process or a noncyclic process.
The Photophosphorylation process that results in movement of electrons in a cyclic manner for synthesizing of ATP molecules is referred to as cyclic photophosphorylation. On the other hand, the photophosphorylation process which results in the movement of the electrons in a non-cyclic manner (unidirectional manner) for synthesizing ATP molecules using energy from excited electrons provided by photosystem II is referred to as non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
During cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons are transferred back to P700 instead of moving into NADP from the electron acceptor. This downward movement of electrons from an acceptor to P700 results in the formation of ATP molecules.
During non-cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons released by P700 are carried by primary acceptor and are finally passed on to NADP where electrons combine with protons -H+ which are produced by splitting up of water molecules and consequently reducing NADP tO NADPH2. In this process, the lost electrons by P680 of photosystem II are occupied by P700 of photosystem I and are not reverted back to P680.
The key Difference
- Cyclical Photophosphorylation can be defined as the synthesis of ATP during the light reaction stage of photosynthesis, resulting to a cyclic of electrons to and from P700. In contrast, Non-cyclic photophosphorylation can be defined as the synthesis of ATP during the light reaction stage of photosynthesis in which an electron donor is required and oxygen is produced as a by-product.
- Noncyclic photophosphorylation occurs mainly in aerobic conditions whereas the cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in anaerobic conditions.
- Both ATP and reduced coenzymes are produced in non-cyclic Photosphorylation whereas only ATP is produced in cyclic Photophosphorylation.
- Noncyclic photophosphorylation occurs when the concentration of carbon dioxide is sufficient in the atmosphere whereas cyclic photophosphorylation occurs when the concentration of carbon dioxide is less in the atmosphere.
- Noncyclic Phosphorylation occurs under higher light intensity whereas cyclic photophosphorylation occurs under low light intensity.
- In noncyclic photophosphorylation oxygen is produced while in cyclic photophosphorylation oxygen is not produced.
- Photolysis of water does occur in noncyclic photophosphorylation whereas it does not occur in cyclic photophosphorylation.
- In noncyclic photophosphorylation P700 is the electron donor and the final electron acceptor whereas in cyclic photophosphorylation P680 is the first electron donor and NADP+ is the final electron acceptor.
- In noncyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are not returned to the reaction center of P680 and they are accepted by NADP+. On the contrary, electrons return to the P700 after passing through electron transport system (ETS) in cyclic photophosphorylation.
- In noncyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are first-expelled from the reaction center of P II (680) whereas in cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are first-expelled from the reaction center of P I (P700).
- Both photosystem I and II are involved in noncyclic photophosphorylation whereas only photosystem I is involved in the cyclic photophosphorylation.
- In noncyclic photophosphorylation, electrons move in linear pattern whereas in cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons move in cyclic pattern.
- Noncyclic photophosphorylation occurs in plants, algae and cynobacteria. On the other hand, cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in isolated chloroplasts and photosynthetic bacteria.
- Noncyclic photophosphorylation occurs in oxygenic photosynthesis whereas cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in anoxygenic photosynthesis.
- Electron circle is closed in cyclic photophosphorylation whereas the electron circle is not closed in noncyclic photophosphorylation.
Difference Between Cyclic And Noncyclic Photophosphorylation In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION | NONCYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION |
| Description | Cyclical Photophosphorylation can be defined as the synthesis of ATP during the light reaction stage of photosynthesis, resulting to a cyclic of electrons to and from P700. | Non-cyclic photophosphorylation can be defined as the synthesis of ATP during the light reaction stage of photosynthesis in which an electron donor is required and oxygen is produced as a by-product. |
| Occurrence | Occurs in anaerobic conditions. | Occurs mainly in aerobic conditions. |
| Production of ATP And Enzymes | Only ATP is produced. | Both ATP and reduced coenzymes are produced. |
| Occurrence Condition | Occurs when the concentration of carbon dioxide is less in the atmosphere. | Occurs when the concentration of carbon dioxide is sufficient in the atmosphere. |
| Light Intensity | Occurs under low light intensity. | Occurs under higher light intensity. |
| Oxygen Production | Oxygen is not produced. | Oxygen is produced. |
| Photolysis of water | Photolysis of water does not occur. | Photolysis of water does occur. |
| Electron Donor And Acceptor | In cyclic photophosphorylation P680 is the first electron donor and NADP+ is the final electron acceptor. | In noncyclic photophosphorylation P700 is the electron donor and the final electron acceptor |
| Electron Return | Electrons return to the P700 after passing through electron transport system (ETS) in cyclic photophosphorylation. | Electrons are not returned to the reaction center of P680 and they are accepted by NADP+. |
| Electron Expulsion | Electrons are first-expelled from the reaction center of P I (P700). | Electrons are first-expelled from the reaction center of P II (680). |
| Photosytem I and II | Only photosystem I is involved in the cyclic photophosphorylation. | Both photosystem I and II are involved in noncyclic photophosphorylation. |
| Electron Movement Pattern | Electrons move in cyclic pattern. | Electrons move in linear pattern. |
| Occurrence | Occurs in isolated chloroplasts and photosynthetic bacteria. | Occurs in plants, algae and cynobacteria. |
| Occurrence | Occurs in anoxygenic photosynthesis. | Occurs in oxygenic photosynthesis. |
| Electron Cycle | The electron circle is not closed. | Electron circle is closed. |
What Are Some Of The Similarities Between Cyclic And Noncyclic Photophosphorylation?
- Both are dependent on light.
- Both are electron transport systems.
- Both generate ATP.
- Both occur in light reaction of photosynthesis.
- Both pathways produce assimilatory powers.