What Is Phototropism?
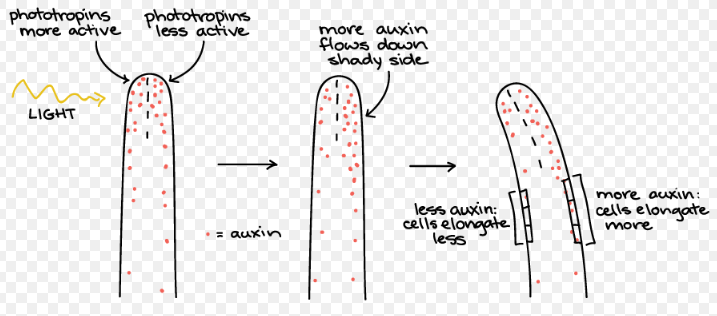
Phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Growth towards a light source is referred to as positive phototropism whereas growth away from the light source is referred to as negative phototropism. Positive phototropism is common among the shoots of higher plants while roots usually exhibit negative phototropism. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi.
There are several molecules that act as signals that help the plant to determine the exact side from which light source is coming from, this helps the plant activate several genes that correspondingly changes the hormone gradient (Auxins) allowing the plant to grow towards the source of light. Coleoptile (tip of the plant) in plant is very necessary in light sensing whereas the middle portion of coleoptile is where the shoot curvature occurs.
Facts About Phototropism
- Phototropism is the orientation of a plant to light or other organisms in response to light, either towards the source of light or away from it. Phototropism in most often observed in plants but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi.
- Phototropism is regulated by Auxin hormones.
- The stimuli of phototropism are perceived by apical meristem.
- In phototropism, yellow colored pigment referred to as Carotenoids acts as the photoreceptors.
- Phototropism occurs due to differential growth of an organ in the zone of elongation.
- Phototropism induces curvature in plants parts.
- Phototropism occurs when the light rays fall on the plant from one direction.
What is Photoperiodism?
Photropism ‘’Photo’’ means light whereas ‘’period’’ means length of time, therefore by definition, Photoperiodism is the developmental responses of plants to the relative lengths of light and dark periods. It occurs in both plants and animals. Phototropism can also be defined as a physiological reaction of organisms to the length of day and night.

Most plants have the ability to detect changes within their environment i.e the length of day and night and flower at the right time. In this regard, they make use of photoreceptor (light-sensitive) proteins referred to as phytochrome or crytochrome. Each plant has a different photoperiod that it requires to flower and propagate. Plants generally fall into three photoperiod categories:
- Long-day plants
- Short-day plants
- Day-neural plants
It is important to note that, the effect of phototropism in plants is not limited to when they will flower. Phototropism can also have an effect on the growth of roots and stems; it also has an effect on the loss of leaves in some plants during different seasons.
Plants can further be divided into obligate photoperiodic plants and facultative photoperiodic plants. Obligate photoperiodic plants absolutely require a long or short enough night before flowering whereas facultative photoperiodic plants are more likely to flower under one condition.
Facts About Photoperiodism
- Phototropism is the functional or behavioral response of an organism to changes of duration in daily, seasonal or yearly cycles of light or darkness.
- In phototropism, flowering is induced by cytokinins and Gibberrellins.
- The stimuli of photoperiodism are perceived by the leaves.
- In photoperiodism, the blue colored pigments referred to as Phytochromes act as the photoreceptors.
- Photoperiodism occurs due to conversion of vegetative bud into floral bud.
- Photoperiodism induces flowering in plants.
- Photoperiodism occurs irrespective of the direction of the light.
READ FURTHER: Difference Between Photoperiodism and Vernalization
Phototropism Vs. Photoperiodism In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | PHOTOTROPISM | PHOTOPERIODISM |
| Description | Phototropism is the orientation of a plant to light or other organisms in response to light, either towards the source of light or away from it. Phototropism in most often observed in plants but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. | Phototropism is the functional or behavioral response of an organism to changes of duration in daily, seasonal or yearly cycles of light or darkness. |
| Hormones | Phototropism is regulated by Auxin hormones. | In phototropism, flowering is induced by cytokinins and Gibberrellins. |
| The Stimuli | The stimuli of phototropism are perceived by apical meristem. | The stimuli of photoperiodism are perceived by the leaves. |
| Photoreceptors | In phototropism, yellow colored pigment referred to as Carotenoids acts as the photoreceptors. | In photoperiodism, the blue colored pigments referred to as Phytochromes act as the photoreceptors. |
| Occurrence | Phototropism occurs due to differential growth of an organ in the zone of elongation. | Photoperiodism occurs due to conversion of vegetative bud into floral bud. |
| Inducement | Phototropism induces curvature in plants parts. | Photoperiodism induces flowering in plants. |
| Direction Of Light | Phototropism occurs when the light rays fall on the plant from one direction. | Photoperiodism occurs irrespective of the direction of the light. |
Also Read: Difference Between Nastic And Tropic Movements
What Are Some Of The Similarities Between Phototropism And Photoperiodism
- Both processes are stimulated by hormones.
- Both photoperiodism and phototropism requires photoreceptors to trap the light energy (Stimuli).
- Phototropism and photoperiodism occur in both animals and plants.
- Light is the major stimuli in both processes.