Nutrition is a biological study of food and various modes of nutrition of living organisms. It is one of the ways the living organisms obtain energy required for all the vital processes of the body. On the basis of nutrition, all the organisms are divided into two main groups- autotrophs and heterotrophs. Their corresponding modes of nutrition are referred to as autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Let’s understand more about autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
What Is Autotrophic And Heterotrophic Mode Of Nutrition?
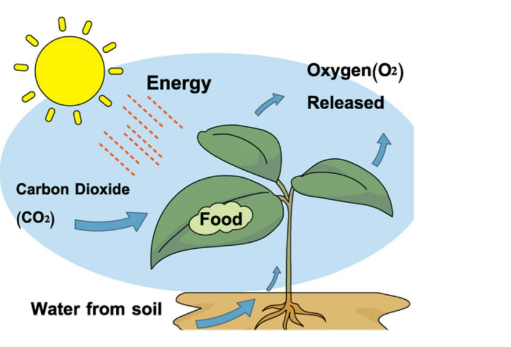
Autotrophic nutrition is the mode of nutrition whereby a living organism is able to create/produce its own food. Green plants and some types of bacteria are usually considered as a good example of autotrophs. They can synthesize inside their cells organic food such as starch, sugar, fats and proteins. They do this with the help of carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. Examples of autotrophs include:
- Plants
- Algae-Green algae and red algae
- Bacteria such as cyanobacteria
Heterotrophic mode of nutrition is the mode of nutrition whereby a living organism cannot create/produce their own food. They are dependent on green plants or animals for their food. All the non green plants and animals inclusive of human beings are usually categorized as heterotrophs.
The non-green plants such as fungi, yeast, mushroom and bread mold lack chlorophyll which is necessary to carry out the process of food synthesis referred to as photosynthesis. When compared to autotrophs which occupy the base of the food web, heterotrophs occupy the upper levels of the food web given that their existence is dependent on the producers (autotrophs). More examples of heterotrophs include:
- Ants
- Tiger
- Lion
- Dogs
- Cats
- Buffalo
- Mosquitoes
- Cows
- Snakes

What You Need To Know About Autotrophic Nutrition
- Autotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which an organism prepares its own food with the help of simple inorganic materials like water and carbon dioxide from the surrounding.
- For autotrophic nutrition, presence of chlorophyll (green pigment) and sunlight are necessary. In other words, autotrophic nutrition takes place during day time.
- All green plants synthesizing their own food through the biological process referred to as photosynthesis are examples of autotrophs.
- In the food chain, autotrophs are the primary producers
- Types of autotrophic mode of nutrition include: phototrophic and chemotrophic
- Autotrophs are independent of any organisms.
- Autotrophs are capable of storing sunlight and chemical energy.
- In autotrophs, the process of digestion is absent.
Also Read: Difference Between Gross And Net Primary Productivity
What You Need To Know About Of Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which an organism cannot prepare its own food and depend upon other organisms for its food.
- No green pigment and sunlight is required for heterotrophic nutrition.
- Animals including herbivores, omnivores and carnivores are examples of heterotrophs.
- Heterotrophs are consumers; they are place at secondary or tertiary level.
- Types of heterotrophic mode of nutrition include: holozoic, saprophytic, parasitic and symbiotic association.
- Heterotrophs rely on other organisms for their food whereas Heterotrophs are not capable of storing energy
- Heterotrophs can move from one place to another in search of food while autotrophs cannot move from one place to another.
- In heterotrophs, the process of digestion is required to convert complex molecules into simpler molecules.
Also Read: Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web
Autotrophic Nutrition Vs. Heterotrophic Nutrition In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION | AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITION |
| Description | Autotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which an organism prepares its own food with the help of simple inorganic materials like water and carbon dioxide from the surrounding. | Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which an organism cannot prepare its own food and depend upon other organisms for its food. |
| Requirement | For autotrophic nutrition, presence of chlorophyll (green pigment) and sunlight are necessary. Autotrophic nutrition takes place during day time. | No green pigment and sunlight is required for heterotrophic nutrition. |
| Examples | All green plants synthesizing their own food through the biological process are referred to as photosynthesis are examples of autotrophs. | Animals including herbivores, omnivores and carnivores are examples of heterotrophs. |
| In food Chain | In the food chain, autotrophs are the primary producers. | Heterotrophs are consumers; they are place at secondary or tertiary level. |
| Types | Types of autotrophic mode of nutrition include: phototrophic and chemotrophic. | Types of heterotrophic mode of nutrition include: holozoic, saprophytic, parasitic and symbiotic association. |
| Dependency | Autotrophs are independent of any organisms. | Heterotrophs rely on other organisms for their food. |
| Storage of Energy | Autotrophs are capable of storing sunlight and chemical energy. | Heterotrophs are not capable of storing energy. |
| Movement | Heterotrophs can move from one place to another in search of food. | Autotrophs cannot move from one place to another. |
| Digestion | In autotrophs, the process of digestion is absent. | Heterotrophs, the process of digestion is required to convert complex molecules into simpler molecules. |
Also Read:
- Difference Between Grazing Food Chain And Detritus Food Chain
- Difference Between Biotic And Abiotic Factors
Comments are closed.