A map is a visual representation of an area, illustrating its physical features, political boundaries, or other specific information. Maps help people understand spatial relationships, locations, and geographic patterns. They are tools for navigation, planning, research, and education, allowing us to interpret complex landscapes in a simplified, accessible form.
Maps can represent physical features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts, or human-made features, like cities, roads, and borders. Physical maps help us understand the natural environment, while political maps show the divisions created by humans. Some maps, like topographic maps, combine both aspects to give a detailed understanding of an area’s terrain and settlements.
One of the key aspects of maps is their ability to show data visually, making complex information easier to interpret. Thematic maps focus on a particular topic, such as population, climate, or resources, and help researchers, planners, and decision-makers identify patterns and trends. This makes maps essential tools in geography, sociology, economics, and environmental science.
Maps also vary by scale and detail. Some maps provide a broad overview of continents or countries, while others focus on small areas, like a city or neighborhood. The scale determines how much detail can be shown and how distances are represented, which is crucial for navigation, construction, or planning purposes.
Advancements in technology have transformed traditional maps into digital and interactive maps. GPS-based maps, satellite imagery, and online mapping platforms allow real-time tracking, route planning, and exploration of remote areas. These innovations have made maps more accurate, accessible, and user-friendly than ever before.
Types of Maps
Physical Map
A physical map shows the natural features of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and deserts. These maps use colors and shading to indicate elevation and terrain types, making it easier to visualize the landscape.
Physical maps are commonly used in education, geography studies, and outdoor activities like hiking or travel planning. They help people understand the physical characteristics of a region, including its topography and natural landmarks.
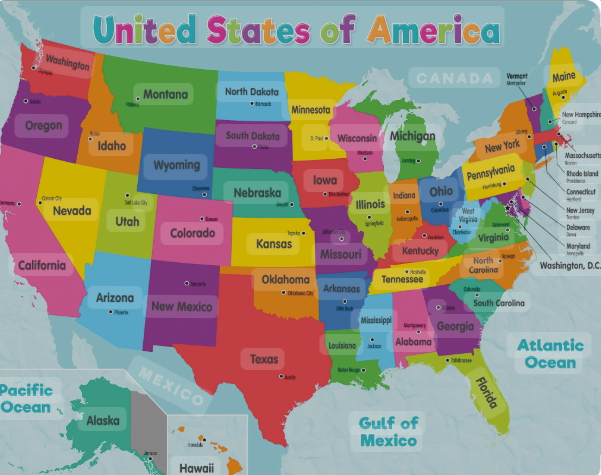
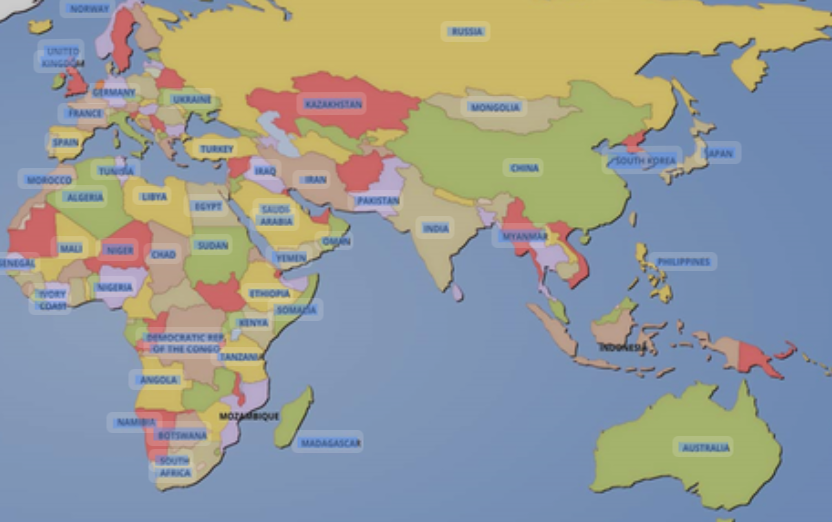
Political Map
Political maps focus on boundaries and divisions between countries, states, cities, or territories. They highlight borders, capitals, and major cities, often using different colors to distinguish each area.
These maps are widely used in government, education, and travel. They provide information about administrative divisions, helping people understand geopolitical relationships and locations of important political centers.
Topographic Map
Topographic maps represent the shape and elevation of the terrain using contour lines. Each line connects points of equal elevation, allowing users to see hills, valleys, slopes, and other landforms in detail.
These maps are essential for engineers, surveyors, hikers, and environmental researchers. They are used for planning construction projects, exploring natural landscapes, and understanding the physical geography of an area.
Thematic Map
Thematic maps emphasize specific themes or data rather than geographical features. They can display information like population density, climate zones, rainfall distribution, or economic activity.
These maps are widely used by researchers, urban planners, and educators. By focusing on a particular subject, thematic maps help people analyze patterns, trends, and relationships across a region.
Climate Map
A climate map shows information about the weather patterns and climate of a particular region. It uses colors, symbols, and lines to indicate temperature ranges, rainfall, humidity, and seasonal variations.
Climate maps are useful for meteorologists, farmers, and travelers. They help people understand the environmental conditions of a region, make agricultural decisions, and prepare for weather-related events.
Economic or Resource Map
Economic or resource maps show the distribution of resources, industries, and economic activities across a region. They can indicate locations of mines, factories, farms, and other economic centers using symbols and colors.
These maps are useful for economists, planners, and students studying geography. By visualizing resource availability and economic activity, they help in decision-making for development, trade, and resource management.
Road Map
Road maps focus on transportation networks, showing highways, streets, railways, and major routes connecting cities and towns. They often include distances, landmarks, and points of interest to help travelers navigate efficiently.
These maps are essential for drivers, tourists, and delivery services. Road maps provide practical guidance for planning journeys, estimating travel times, and finding alternative routes.
Geological Map
Geological maps illustrate the structure, composition, and age of rocks beneath the Earth’s surface. They use colors and symbols to indicate rock types, faults, folds, and mineral deposits.
Geologists, engineers, and environmental researchers use these maps for mining, construction, and studying Earth’s history. They are essential in assessing natural hazards, locating resources, and planning sustainable land use.
Navigation Map (Nautical and Aeronautical)
Navigation maps are designed for safe travel by sea or air. Nautical charts show coastlines, water depths, hazards, and navigational aids, while aeronautical charts display air routes, airports, and airspace information.
These maps are crucial for pilots, sailors, and air traffic controllers. They ensure safe and efficient travel by providing critical information about routes, obstacles, and regulations in the respective environment.
Political-Physical Hybrid Map
A political-physical hybrid map combines elements of both political and physical maps. It shows boundaries, cities, and capitals along with terrain features such as mountains, rivers, and plains.
These maps are widely used in education, research, and planning. They provide a comprehensive view of a region by showing both human and natural aspects, helping people understand geography more fully.
Population Map
Population maps illustrate the distribution of people across a particular area. They often use colors, shading, or symbols to indicate population density, growth rates, or demographic patterns.
These maps are useful for urban planners, governments, and researchers. By visualizing population trends, they help in planning infrastructure, public services, and resource allocation.
Tourist Map
Tourist maps highlight landmarks, attractions, hotels, restaurants, and points of interest in a region. They are designed to help visitors navigate and explore an area efficiently.
Tourist maps are widely used by travelers, tour operators, and local businesses. They often include colorful illustrations, symbols, and suggested routes to enhance the travel experience and ensure convenience.
Weather Map
Weather maps display current or forecasted weather conditions over a region. They use symbols, colors, and lines to show temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and pressure systems.
These maps are essential for meteorologists, pilots, farmers, and the general public. They help people prepare for weather events, plan agricultural activities, and ensure safety during travel.
Topological Map
Topological maps emphasize the spatial relationships and connectivity of features rather than scale or exact distances. They often simplify the layout of roads, railways, or networks to show connections clearly.
These maps are useful in urban planning, public transportation, and network analysis. They allow users to understand how places are linked without getting distracted by geographic precision.
Contour Map
Contour maps, also called topographic contour maps, use lines to represent elevation and terrain shape. Each contour line connects points of equal height above sea level.
These maps are valuable for engineers, hikers, and geographers. They help in planning construction projects, studying landforms, and navigating natural landscapes safely by understanding slopes and elevations.