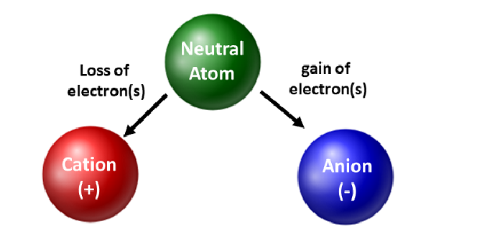
In Chemistry, anions and cations are both ions. Ions are atoms or molecules which have gained or lost one or more valence electrons, giving the ion a net positive or negative charge. Therefore, the main difference between a cation and an anion is the net electrical charge of the ion.
A negative charge is as a result of a chemical species having more electrons than protons whereas a positive charge is as a result of a chemical species having more protons than electrons. Usually, the number of neutrons determines the isotope of an element but does not in any way determine the electrical charge. Consequently, Cations can be described as ions with a net positive charge whereas Anions can be described as ions with a net negative charge.
Examples of Cations include:
- Silver (Ag+ )
- Hydronium (H3O+ )
- Ammonium (NH 4+)
- Calcium (Ca2+ )
- Magnesium (Mg2+ )
- Aluminium (Al 3+)
- Hydrogen (H+)
- Potassium (K + )
- Iron (II) (Fe2+)
- Iron (III) Fe3+
- Barium (Ba2+)
- Lead II (Pb2+)
- Beryllium (Be2+) etc.
Examples of anions include:
- Hydroxide anion (OHˉ)
- Oxide anion (O2- )
- Sulfate anion (SO42-)
- Fluoride (F-)
- Bromide (Br-)
- Iodide (I-)
- Nitride (N3-)
- Hydride (H-)
- Chloride (Cl-) etc.
What You Need To Know About Cations (Characteristics)
- A cation is a positively charged ion resulting from the release of one or more electrons from its shells in the attempt to increase stability.
- A cation has more protons than electrons, a factor that gives it a net positive charge.
- They are usually formed by metal atoms.
- They are formed when a metal loses its electrons. They lose one or more than one electron and do not lose any protons.
- A net positive charge (cation) is indicated with a superscript + (positive) after the chemical formula, such as Ca2+
- During the process of electrolysis, cation always moves towards the cathode which produces the negative charge.
- Cations form electrostatic interactions with anions to form ionic compounds.
- When using the periodic table, the position of an atom in the periodic table can be used to predict whether it will form cations. Alkali metals, most other metals (e.g iron, silver, nickel) and alkaline earth metals always form cations.
- When writing the formula of a compound, the cation is listed before the anion. For example MgCl, NaCl, CaSO4, FeCl etc.
What You Need To Know About Anion (Characteristics)
- An anion is a negatively charged ion resulting from acceptance of one or more electrons to its shells in the attempt to increase stability.
- An anion has more electrons than protons, a factor that gives it a net negative charge.
- They are usually formed by metal atoms.
- They are formed when non-metals gains the electrons. They gain one or more electrons and do not lose any protons.
- A negative charge (anion) is indicated with a superscript – (negative) after the chemical formula, such as OHˉ.
- During the process of electrolysis, anion always moves towards the anode which produces the positive charge.
- Anions form electrostatic interactions with cations to form ionic compounds.
- When using the periodic table, the position of an atom in the periodic table can be used to predict whether it will form anions. Halogens & most of the nonmetals (e.g oxygen, carbon and sulfur) always form anions.
- When writing the formula of a compound, the cation is listed before the anion. For example MgCl, NaCl, CaSO4, FeCl etc.
Difference Between Cation And Anion In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | CATION | ANION |
| Description | A cation is a positively charged ion resulting from the release of one or more electrons from its shells in the attempt to increase stability. | An anion is a negatively charged ion resulting from acceptance of one or more electrons to its shells in the attempt to increase stability. |
| Electrons Vs Protons | It has more protons than electrons, a factor that gives it a net positive charge. | It has more electrons than protons, a factor that gives it a net negative charge. |
| Formation | They are usually formed by metal atoms. | They are usually formed by metal atoms. |
| How It Is Formed | They are formed when a metal loses its electrons. | They are formed when non-metals gains the electrons. |
| Charge Indication | A net positive charge (cation) is indicated with a superscript + (positive) after the chemical formula, such as Ca2+ | A negative charge (anion) is indicated with a superscript – (negative) after the chemical formula, such as OHˉ. |
| During Electrolysis | During the process of electrolysis, cation always moves towards the cathode which produces the negative charge. | During the process of electrolysis, anion always moves towards the anode which produces the positive charge. |
| Electrostatic Interactions | Cations form electrostatic interactions with anions to form ionic compounds. | Anions form electrostatic interactions with cations to form ionic compounds. |
| Examples | Examples of cations include: Silver (Ag+ ) Hydronium (H3O+ ) Ammonium (NH 4+) Calcium (Ca2+ ) Magnesium (Mg2+ ) etc. | Examples of anions include: Hydroxide anion (OHˉ) Oxide anion (O2- ) Sulfate anion (SO42-) Fluoride (F-) Bromide (Br-) Iodide (I-) Nitride (N3-) Hydride (H-) etc. |
| Periodic Table Predication | When using the periodic table, the position of an atom in the periodic table can be used to predict whether it will form cations. Alkali metals, most other metals (e.g iron, silver, nickel) and alkaline earth metals always form cations. | When using the periodic table, the position of an atom in the periodic table can be used to predict whether it will form anions. Halogens & most of the nonmetals (e.g oxygen, carbon and sulfur) always form anions. |
| Writing Formula Of Compound | When writing the formula of a compound, the cation is listed before the anion. For example MgCl, NaCl, CaSO4, FeCl etc. | When writing the formula of a compound, the cation is listed before the anion. For example MgCl, NaCl, CaSO4, FeCl etc. |